| Date | May 2009 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 09M.3.sl.TZ2.C4 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Compare and State | Question number | C4 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
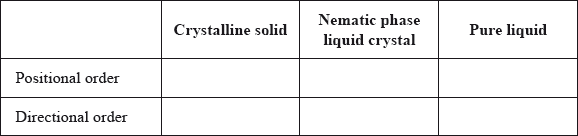
Compare the positional and directional order in a crystalline solid, nematic phase liquid crystal and a pure liquid. Show your answer by stating yes or no in the table below.
Markscheme
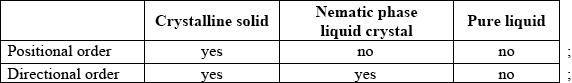
Need all three across table for each mark.
Examiners report
The positional and directional order were generally compared correctly.
Syllabus sections
Show 50 related questions
- 17N.3.sl.TZ0.7a: Outline two properties a substance should have to be used as liquid-crystal in a...
- 17M.3.sl.TZ2.6a: Two important properties of a liquid crystal molecule are being a polar molecule and having a...
- 16N.3.sl.TZ0.7b: Explain the effect of increasing the temperature of a nematic liquid crystal on its...
- 16N.3.sl.TZ0.7a: Outline how a lyotropic liquid crystal differs from a thermotropic liquid crystal.
- 16M.3.sl.TZ0.6b: Explain why the nitrile group enables these molecules to be used in liquid-crystal displays...
- 16M.3.sl.TZ0.6a: Suggest how changing the size or shape of the hydrocarbon chain would affect the molecule’s...
- 15M.3.hl.TZ1.10c: Describe and explain, in molecular terms, the workings of a twisted nematic liquid crystal.
- 15M.3.hl.TZ2.15a: Explain how the structure of biphenyl nitriles makes them suitable for use in liquid-crystal...
- 15M.3.sl.TZ1.8b.ii: Suggest how the C5H11 chain contributes to the liquid-crystal properties of the compound.
- 15M.3.sl.TZ1.8a: The diagram below shows eight molecules in the liquid state. Suggest, with a diagram, a...
- 15M.3.sl.TZ1.8b.i: Suggest, with reference to the structure, why the molecule is able to change orientation in...
- 15M.3.sl.TZ1.8b.iii: Explain why a liquid-crystal device may be unreliable at low temperatures.
- 15M.3.sl.TZ2.12b: Suggest the essential feature a liquid-crystal molecule must have so that the display can be...
- 15M.3.sl.TZ2.12a: Identify the structural feature of cholesteryl benzoate which makes it suitable for use as a...
- 14M.3.hl.TZ2.13b: List two properties needed for a substance to be used in a liquid-crystal display.
- 14M.3.hl.TZ2.13a: Describe the meaning of the term liquid crystal.
- 14M.3.sl.TZ1.10a: (i) Describe the meaning of the term liquid crystals and state which of the...
- 14M.3.sl.TZ1.10b: (i) State one difference between thermotropic and lyotropic liquid...
- 14N.3.hl.TZ0.12b: When a liquid-crystal display is warmed with a hairdryer, the display loses its clarity and...
- 14N.3.hl.TZ0.12a: Describe the meaning of the term liquid crystals.
- 14N.3.sl.TZ0.11a: Describe the meaning of the term liquid crystals.
- 14N.3.sl.TZ0.11b: When a liquid-crystal display is warmed with a hairdryer, the display loses its clarity and...
- 13N.3.hl.TZ0.12c: The molecule below has liquid-crystal display properties. Suggest two reasons why the...
- 13N.3.hl.TZ0.12a: State what the observer would see if the liquid crystal was not present and there was no...
- 13N.3.hl.TZ0.12b.i: Explain how the addition of a liquid crystal to the cell changes what the observer sees.
- 13N.3.hl.TZ0.12b.ii: Explain how the application of an electric field between the electrodes,...
- 13N.3.sl.TZ0.10: Liquid-crystal displays are used in many electronic appliances. The molecule below has...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ1.8b.ii: Suggest what would happen to the pH of the solution as the reaction proceeds.
- 13M.3.sl.TZ1.C3a: State the property of the liquid-crystal molecules that allows them to align when a voltage...
- 13M.3.sl.TZ1.C3b: List two substances that can behave as liquid crystals.
- 13M.3.sl.TZ1.C3c: Distinguish between thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals. Thermotropic liquid...
- 09N.3.hl.TZ0.C5b: Describe and explain in molecular terms the workings of a twisted nematic liquid crystal.
- 09N.3.hl.TZ0.C5a: Explain how the three different parts of the molecule contribute to the properties of the...
- 10M.3.hl.TZ1.C2e: Kevlar is an example of a lyotropic liquid crystal. Outline what is meant by lyotropic liquid...
- 10M.3.hl.TZ2.C3: (a) State one other example of a lyotropic liquid crystal and describe the difference...
- 10M.3.sl.TZ2.C4: Detergents are one example of lyotropic liquid crystals. State one other example of a...
- 09M.3.sl.TZ1.C2a: Describe the meaning of the term liquid crystals. State and explain which diagram, I or II,...
- 09M.3.sl.TZ1.C2b: Distinguish between thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals and state one example of each...
- 09M.3.sl.TZ1.C2c: Discuss the properties needed for a substance to be used in liquid crystal displays.
- 11M.3.sl.TZ2.C3a: Describe the liquid-crystal state, in terms of molecular arrangement, and explain what...
- 11M.3.sl.TZ2.C3b: Discuss three properties a substance should have if it is to be used in liquid-crystal displays.
- 12M.3.hl.TZ1.C4b: Discuss the additional properties that a substance must have to make it suitable for...
- 12M.3.hl.TZ1.C4c: Explain what is meant by the term lyotropic.
- 12M.3.hl.TZ1.C4a: State the properties that a molecule, such as Kevlar, must have in order to enable it to...
- 12M.3.sl.TZ1.C3d: One product that is made from crude oil is the chemical feedstock that can be used to...
- 12M.3.hl.TZ2.C3a: Distinguish between thermotropic liquid crystals and lyotropic liquid...
- 12M.3.hl.TZ2.C3b: Two substances that can be used in liquid crystals are commonly called PAA (4-azoxydianisole)...
- 12M.3.hl.TZ2.C3c: Explain the workings of liquid crystals made up of compounds such as 5CB in liquid-crystal...
- 11N.3.sl.TZ0.C4b: Explain the effect of increasing the temperature on the nematic liquid crystal.
- 11N.3.sl.TZ0.C4a: Describe the nematic liquid-crystal phase in terms of the arrangement of the molecules.

