| Date | May 2012 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 12M.3.hl.TZ2.C3 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Distinguish | Question number | C3 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Distinguish between thermotropic liquid crystals and lyotropic liquid crystals.
Thermotropic:
Lyotropic:
Two substances that can be used in liquid crystals are commonly called PAA (4-azoxydianisole) and 5CB (4-pentyl-\({\text{4'}}\)-cyanobiphenyl).
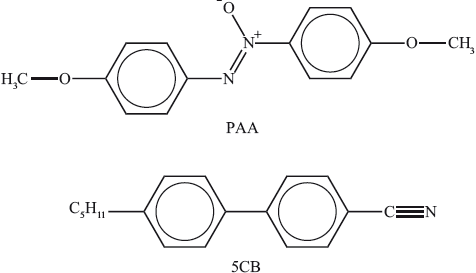
Discuss on the molecular level three different factors that explain their liquid-crystal properties.
Explain the workings of liquid crystals made up of compounds such as 5CB in liquid-crystal displays.
Markscheme
Thermotropic:
show liquid-crystal behaviour over a range of temperatures/at certain temperatures;
Lyotropic:
show liquid-crystal behaviour over a range of concentrations/at certain concentrations;
polar groups/N–O/C≡N help molecules to line up in a common direction / OWTTE;
biphenyl groups/benzene rings help to make the molecule rigid/rod-shaped/linear / OWTTE;
alkyl/hydrocarbon chains help prevent too close packing/help maintain liquid-crystal state / OWTTE;
each pixel contains a liquid-crystal film sandwiched between two glass plates;
glass plates have fine scratches and can polarize light;
liquid-crystal molecules line up to form a twisted arrangement / twisted nematic geometry;
liquid-crystal interacts with (plane-) polarized light which is rotated 90° as it passes through the film;
when two polarizers are aligned (with the scratches) light will pass through and pixel will appear bright;
when a potential difference is applied across the film molecules align with the film losing their twisted structure;
they no longer interact with polarized light and pixel appears dark;
Apply OWTTE throughout.
Examiners report
In (a), most understood the differences between thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals and scored both marks.
Answers to (b) rarely scored full marks. Some clearly knew very little about the relevant molecular features, and many of those who did, failed to link the features with the properties.
Part (c) was sometimes left blank, and few answers scored more than one or two marks. This part tested AS C.11.2, but most answers were vague and rambling and did not come close to matching the markscheme, which was very similar to the teacher’s notes for this assessment statement.

