| Date | May 2013 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 13M.1.sl.TZ2.25 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 1 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Deduce | Question number | 25 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
The overall reaction in the voltaic cell below is:
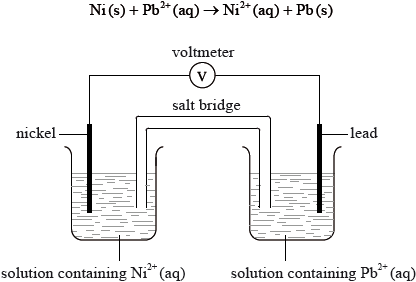
Which statement is correct for the nickel half-cell?
A. Nickel is the positive electrode (cathode) and is reduced.
B. Nickel is the negative electrode (anode) and is reduced.
C. Nickel is the positive electrode (cathode) and is oxidized.
D. Nickel is the negative electrode (anode) and is oxidized.
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
[N/A]
Syllabus sections
Show 122 related questions
- 17N.2.hl.TZ0.7e: State and explain the products of electrolysis of a concentrated aqueous solution of sodium...
- 17N.2.hl.TZ0.7c: Calculate the cell potential, in V, when the standard iodine and manganese half-cells are...
- 17N.2.hl.TZ0.7b: Predict, giving a reason, the direction of movement of electrons when the standard nickel and...
- 17N.1.hl.TZ0.31: What are the products when an aqueous solution of copper(II) sulfate is electrolysed using...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ2.2c: Zinc is used to galvanize iron pipes, forming a protective coating. Outline how this process...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ2.2b.ii: Calculate the Gibbs free energy, ΔG θ, in kJ, which is released by the corrosion of 1 mole of...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ2.2b.i: Corrosion of iron is similar to the processes that occur in a voltaic cell. The initial steps...
- 17M.1.hl.TZ2.31: What are the relative volumes of gas given off at E and F during electrolysis of the two...
- 17M.1.hl.TZ2.30: What is the standard half-cell potential of copper if the “zero potential reference...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ1.3c.ii: Comment on the spontaneity of this reaction by calculating a value for \(\Delta {G^\theta...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ1.3b.ii: Identify, from the table, a non-vanadium species that could convert...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ1.3b.i: Identify, from the table, a non-vanadium species that can reduce VO2+(aq) to V3+(aq) but no...
- 17M.1.hl.TZ1.31: In the electrolysis of aqueous potassium nitrate, KNO3(aq), using inert electrodes, 0.1 mol...
- 17M.1.hl.TZ1.30: Which statement is correct for the overall reaction in a voltaic cell? 2AgNO3(aq) + Ni(s) →...
- 16N.3.hl.TZ0.21b: A concentration cell is an example of an electrochemical cell. (i) State the difference...
- 16N.2.hl.TZ0.4k: A magnesium half-cell, Mg(s)/Mg2+(aq), can be connected to a copper half-cell,...
- 16N.2.hl.TZ0.4j: Standard electrode potentials are measured relative to the standard hydrogen electrode....
- 16N.2.hl.TZ0.4i: Magnesium chloride can be electrolysed. (i) Deduce the half-equations for the reactions at...
- 16N.1.hl.TZ0.33: An iron rod is electroplated with silver. Which is a correct condition for this process? A....
- 16N.1.hl.TZ0.32: Which signs for both Eθcell and ΔGθ result in a spontaneous redox reaction occurring under...
- 16M.2.hl.TZ0.4b: Tin can also exist in the +4 oxidation state. Vanadium can be reduced from an oxidation...
- 16M.1.hl.TZ0.33: z...
- 16M.1.hl.TZ0.32: Which...
- 15M.1.hl.TZ1.31: Two half-cells are connected via a salt bridge to make a voltaic cell. Which statement about...
- 15M.1.hl.TZ1.32: Which signs are correct for a spontaneous redox reaction?
- 15M.1.hl.TZ1.33: Consider the standard electrode...
- 15M.1.hl.TZ2.32: The standard electrode potentials for three reactions involving copper and copper ions...
- 15M.1.hl.TZ2.33: The same quantity of electricity is passed through separate dilute aqueous solutions of...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ1.6f.i: Define the term standard electrode potential, \({E^\Theta }\).
- 15M.2.hl.TZ1.6d.ii: Predict the products formed at the electrodes during the electrolysis of concentrated aqueous...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ1.6f.ii: Draw a labelled diagram for the voltaic cell in which the following reaction...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.8e.i: Define the term standard electrode potential.
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.8e.iii: Predict the balanced equation for the spontaneous reaction which will produce a current in...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.8e.iv: Identify the negative and the positive electrodes in this cell.
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.8e.v: Predict the direction of movement of electrons in the external circuit.
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.8e.vi: State the directions in which the negative ions (anions) and the positive ions (cations) flow...
- 14M.1.hl.TZ1.33: The overall equation of a voltaic cell...
- 14M.1.hl.TZ2.34: What is the cell potential, in V, of the reaction...
- 14M.1.hl.TZ2.33: Which components are used to make the standard hydrogen electrode? A. ...
- 14M.2.hl.TZ1.6b: (i) Deduce the order of reactivity of these four metals, from the least to the most...
- 14M.2.hl.TZ1.6c: (i) State the half-equation for the reaction that occurs at each electrode. Positive...
- 14M.2.hl.TZ1.6d: (i) Determine the mass of copper produced at one of the electrodes in cell 2 if the tin...
- 14M.2.hl.TZ2.8g: (i) Draw a labelled diagram of a suitable apparatus for the electrolysis. (ii) ...
- 14N.1.hl.TZ0.32: Consider the following standard electrode potentials. ...
- 14N.1.hl.TZ0.33: A number of molten metal chlorides are electrolysed, using the same current for the same...
- 14N.2.hl.TZ0.10f: (i) An aqueous solution of sodium chloride is electrolysed using inert electrodes....
- 14N.2.hl.TZ0.10g: Describe how electrolysis can be used to electroplate a bracelet with a layer of silver...
- 13N.1.hl.TZ0.33: Consider the following two standard electrode potentials at 298 K. ...
- 13N.1.hl.TZ0.34: What happens during the electrolysis of concentrated aqueous potassium chloride? I. ...
- 13N.2.hl.TZ0.6a: Define the term standard electrode potential, \({E^\Theta }\).
- 13N.2.hl.TZ0.6c: In the two experiments below, predict whether a reaction would occur and deduce an equation...
- 13N.2.hl.TZ0.6d.i: Using Table 14 of the Data Booklet, state the balanced half-equation for the reaction that...
- 13N.2.hl.TZ0.6d.ii: Calculate the cell potential in V.
- 13N.2.hl.TZ0.6d.iii: On the diagram above label with an arrow • the direction of electron flow in the wire • the...
- 13M.1.hl.TZ1.33: The standard electrode potentials of some half-reactions are given below. ...
- 13M.1.hl.TZ1.31: An aqueous solution of a metal salt is electrolysed. Which factor will have no effect on the...
- 13M.2.hl.TZ1.7c.iv: Identify another product that is formed if the solution of iron(II) bromide is concentrated.
- 13M.2.hl.TZ1.4f: Predict the sign of \(\Delta {G^\Theta }\) for this reaction.
- 13M.2.hl.TZ1.7c.iii: Predict and explain the products of electrolysis of a dilute iron(II) bromide solution.
- 13M.2.hl.TZ1.4e.ii: Explain the sign of the calculated standard electrode potential.
- 13M.2.hl.TZ1.7c.v: Explain why this other product is formed.
- 13M.1.hl.TZ2.32: Which statement is correct for electroplating an object with gold? A. The object must be...
- 13M.2.hl.TZ2.7d.ii: Using Table 14 of the Data Booklet, calculate the cell potential,...
- 13M.2.hl.TZ2.7e.iii: State why copper electrodes cannot be used in the electrolysis of water. Suggest instead...
- 13M.2.hl.TZ2.7c.i: Describe the standard hydrogen electrode including a fully labelled diagram.
- 13M.2.hl.TZ2.7e.iv: Deduce the half-equations for the reactions occurring at the positive electrode (anode) and...
- 13M.2.hl.TZ2.7c.ii: Define the term standard electrode potential, \({E^\Theta }\).
- 13M.2.hl.TZ2.7e.i: Deduce the sign of the standard free energy change, \(\Delta {G^\Theta }\), for any...
- 13M.2.hl.TZ2.7e.ii: State why dilute sulfuric acid needs to be added in order for the current to flow in the...
- 13M.2.hl.TZ2.7e.v: Deduce the overall cell reaction, including state symbols.
- 13M.2.hl.TZ2.7e.vii: Comment on what is observed at both electrodes.
- 13M.2.hl.TZ2.7f: Two electrolytic cells are connected in series (the same current passes through each cell)....
- 12N.2.hl.TZ0.4b: (i) Draw an annotated diagram of the electrolytic cell in process 1 and identify the...
- 10N.1.hl.TZ0.32: A voltaic cell is made by connecting two half-cells represented by the half-equations...
- 10N.1.hl.TZ0.33: For the electrolysis of aqueous copper(II) sulfate, which of the following statements is...
- 10N.2.hl.TZ0.4b: (i) Explain how molten magnesium chloride conducts an electric current. (ii) ...
- 09N.1.hl.TZ0.31: Which are necessary conditions for the standard hydrogen electrode to have an \({E^\Theta }\)...
- 09N.2.hl.TZ0.4b.i: Deduce a balanced equation for the overall reaction which will occur spontaneously when these...
- 09N.2.hl.TZ0.4b.ii: Determine the cell potential when the two half-cells are connected.
- 10M.2.hl.TZ1.6d.iii: Two electrolytic cells are connected in series as shown in the diagram below. In one there is...
- 10M.2.hl.TZ1.6a.iii: Using Table 14 of the Data Booklet, calculate the cell potential for this cell.
- 10M.2.hl.TZ1.6b: The standard electrode potentials for three other electrode systems are given below. (i) ...
- 10M.2.hl.TZ1.6c: These values were obtained using a standard hydrogen electrode. Describe the materials and...
- 10M.3.hl.TZ1.C3: Discuss the production of chlorine and sodium hydroxide from brine using a membrane cell....
- 10M.2.hl.TZ2.8b: (i) Molten sodium chloride is electrolysed in a cell using inert electrodes. State the...
- 10M.2.hl.TZ2.8c: Electroplating is an important application of electrolytic cells with commercial...
- 09M.1.hl.TZ1.32: Consider these standard electrode...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.7a.i: Define the term standard electrode potential and state the meaning of the minus sign in the...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.7a.ii: Calculate the value for the standard electrode potential for the cobalt half-cell.
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.7c.i: Draw a labelled diagram of the cell. Use an arrow to show the direction of the electron flow...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.7c.ii: Give the formulas of all the ions present in the solution.
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.7c.iv: Deduce the molar ratios of the products obtained at the two electrodes.
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.7d.i: concentrated sodium chloride
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.7a.v: Explain the function of the salt bridge in an electrochemical cell.
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.7a.iv: Deduce the equation for the spontaneous reaction taking place when the iron half-cell is...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.7c.iii: Predict the products obtained at each electrode and state the half-equation for the formation...
- 09M.1.hl.TZ2.32: What is the cell potential, in V, for the reaction that occurs when the following two...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ2.6c.v: Electroplating is an important application of electrolysis. State the composition of the...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ1.9a.ii: Deduce the equations for the formation of the major product at the positive electrode (anode)...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ1.9b.i: Use Table 14 of the Data Booklet to deduce the equation for the spontaneous reaction...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ1.9b.ii: Calculate the standard potential for this cell.
- 11M.2.hl.TZ1.9b.iii: State the conditions necessary for the potential of the cell to equal that calculated in part...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ1.9c: Using the data below and data from Table 14 of the Data Booklet, predict and explain which...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ1.9d.i: Electrolysis is used in the electroplating of metals. The same amount of current is passed...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ1.9d.ii: For the \({\text{Sn(S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\) cell, suggest two...
- 11M.1.hl.TZ2.32: The standard electrode potentials for two metals are given...
- 11M.1.hl.TZ2.33: The same quantity of electricity was passed through separate molten samples of sodium...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ2.7a.i: Define standard electrode potential.
- 11M.2.hl.TZ2.7b.ii: Deduce which species can reduce \({\text{S}}{{\text{n}}^{4 + }}{\text{(aq)}}\) to...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ2.7b.iii: Deduce which species can reduce \({\text{S}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }}{\text{(aq)}}\) to Sn(s) under...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ2.7c.i: Draw a labelled diagram of a voltaic cell made from an Fe (s) /...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ2.7c.ii: Deduce the equation for the chemical reaction occurring when the cell in part (c) (i) is...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ2.7a.ii: Explain the significance of the minus sign in \( - {\text{0.45 V}}\).
- 11M.2.hl.TZ2.7b.i: State the species which is the strongest oxidizing agent.
- 11M.2.hl.TZ2.7e.ii: Explain why an aqueous solution of sodium chloride cannot be used to obtain sodium metal by...
- 12M.1.hl.TZ2.31: Two electrolytic cells are connected in series and the same current passes through each cell....
- 12M.1.hl.TZ2.30: Consider the following standard electrode...
- 11N.1.hl.TZ0.31: Four electrolytic cells are constructed. Which cell would produce the greatest mass of metal...
- 11N.2.hl.TZ0.7d.i: Draw a diagram of the voltaic cell, labelling the positive and negative electrodes (cathode...
- 11N.2.hl.TZ0.7d.ii: Define the term standard electrode potential.
- 11N.2.hl.TZ0.7d.iii: Calculate the cell potential, in V, under standard conditions, using information from Table...
- 11N.2.hl.TZ0.7f: Chromium is often used in electroplating. State what is used as the positive electrode...

