| Date | November 2013 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 13N.3.hl.TZ0.24 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | Describe and State | Question number | 24 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Stearic acid, oleic acid and linolenic acid are all fatty acids that contain 18 carbon atoms. Their structures are given in Table 22 of the Data Booklet.
Partial hydrogenation of linolenic acid may lead to a product known as a trans fatty acid.
Explain which acid has the highest melting point.
State the equation for the complete hydrogenation of linolenic acid. Describe the conditions used for this reaction.
Explain the meaning of the term trans.
Draw the structure of a possible trans fatty acid product.
Markscheme
stearic acid;
saturated molecule / more closely packed / greater surface area (of contact) / not “kinked”;
more/stronger van der Waals’ forces;
Accept intermolecular/London/dispersion forces instead of van der Waals’ forces.
\({{\text{C}}_{17}}{{\text{H}}_{29}}{\text{COOH(l)}} + {\text{3}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{(g)}} \to {{\text{C}}_{17}}{{\text{H}}_{35}}{\text{COOH(l)}}\);
Ignore state symbols.
Accept either condensed structural formulas or molecular formulas.
Any two correct conditions for second mark:
high temperature/heat;
Accept any temperature value/range greater than 100 °C.
(high) pressure;
(finely divided catalyst) Zn / Cu / Ni / Pt / Pd;
Accept room temperature only if Pt or Pd is given as catalyst.
trans fats have functional/bulky groups/hydrogen atoms on opposite sides of the carbon-carbon double bond;
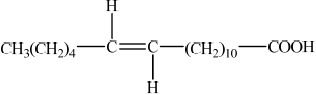 ;
;
Award mark for structures showing one or two double bonds with trans arrangement correctly shown.
Accept R as long as the trans arrangement is clear.
Ignore errors in hydrocarbon chain/position of double bonds so long as trans arrangement is clear.
Examiners report
Option F was one of the less popular options. Identification of the two functional groups in the three antioxidants and why they contain tert- in the prefix to their name was generally done well. Strong candidates were able to provide the correct formula of BHT but many weaker candidates were not and this is a source of concern as it involves skills that should be basic in chemistry. Explanation of how natural and synthetic antioxidants act chemically in the process of auto-oxidation was generally done well. However, the mode of action of \({\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\) as an antioxidant was not as successful as expected. The question on beta-carotene was done well.
Identification of the fatty acid with the highest melting point and the reason why was correctly answered by many but then many also failed to make use of intermolecular forces and therefore did not fully score. Another disappointing result was the equation for the complete hydrogenation of linolenic acid and once again related to difficulties in writing and balancing chemical equations. Many candidates were able to score the second mark by providing two correct conditions. The meaning of the term trans and the associated structure was answered very well.
Many correct answers were given for the meaning of a dispersed system but also many did not make use of subject specific vocabulary or repeated the word dispersed in the answer. The idea of an emulsion and foam was well understood as was the part on the structural features of an emulsifier.
Many candidates identified the chiral carbon atom correctly in the structure given and two different ways in which enantiomers might affect the properties of foods. However, the reason for the difference in optical activity when carvone is synthesized using limonene from natural or chemical source was poorly answered with many not scoring at all.
Option F was one of the less popular options. Identification of the two functional groups in the three antioxidants and why they contain tert- in the prefix to their name was generally done well. Strong candidates were able to provide the correct formula of BHT but many weaker candidates were not and this is a source of concern as it involves skills that should be basic in chemistry. Explanation of how natural and synthetic antioxidants act chemically in the process of auto-oxidation was generally done well. However, the mode of action of \({\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\) as an antioxidant was not as successful as expected. The question on beta-carotene was done well.
Identification of the fatty acid with the highest melting point and the reason why was correctly answered by many but then many also failed to make use of intermolecular forces and therefore did not fully score. Another disappointing result was the equation for the complete hydrogenation of linolenic acid and once again related to difficulties in writing and balancing chemical equations. Many candidates were able to score the second mark by providing two correct conditions. The meaning of the term trans and the associated structure was answered very well.
Many correct answers were given for the meaning of a dispersed system but also many did not make use of subject specific vocabulary or repeated the word dispersed in the answer. The idea of an emulsion and foam was well understood as was the part on the structural features of an emulsifier.
Many candidates identified the chiral carbon atom correctly in the structure given and two different ways in which enantiomers might affect the properties of foods. However, the reason for the difference in optical activity when carvone is synthesized using limonene from natural or chemical source was poorly answered with many not scoring at all.
Option F was one of the less popular options. Identification of the two functional groups in the three antioxidants and why they contain tert- in the prefix to their name was generally done well. Strong candidates were able to provide the correct formula of BHT but many weaker candidates were not and this is a source of concern as it involves skills that should be basic in chemistry. Explanation of how natural and synthetic antioxidants act chemically in the process of auto-oxidation was generally done well. However, the mode of action of \({\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\) as an antioxidant was not as successful as expected. The question on beta-carotene was done well.
Identification of the fatty acid with the highest melting point and the reason why was correctly answered by many but then many also failed to make use of intermolecular forces and therefore did not fully score. Another disappointing result was the equation for the complete hydrogenation of linolenic acid and once again related to difficulties in writing and balancing chemical equations. Many candidates were able to score the second mark by providing two correct conditions. The meaning of the term trans and the associated structure was answered very well.
Many correct answers were given for the meaning of a dispersed system but also many did not make use of subject specific vocabulary or repeated the word dispersed in the answer. The idea of an emulsion and foam was well understood as was the part on the structural features of an emulsifier.
Many candidates identified the chiral carbon atom correctly in the structure given and two different ways in which enantiomers might affect the properties of foods. However, the reason for the difference in optical activity when carvone is synthesized using limonene from natural or chemical source was poorly answered with many not scoring at all.
Option F was one of the less popular options. Identification of the two functional groups in the three antioxidants and why they contain tert- in the prefix to their name was generally done well. Strong candidates were able to provide the correct formula of BHT but many weaker candidates were not and this is a source of concern as it involves skills that should be basic in chemistry. Explanation of how natural and synthetic antioxidants act chemically in the process of auto-oxidation was generally done well. However, the mode of action of \({\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\) as an antioxidant was not as successful as expected. The question on beta-carotene was done well.
Identification of the fatty acid with the highest melting point and the reason why was correctly answered by many but then many also failed to make use of intermolecular forces and therefore did not fully score. Another disappointing result was the equation for the complete hydrogenation of linolenic acid and once again related to difficulties in writing and balancing chemical equations. Many candidates were able to score the second mark by providing two correct conditions. The meaning of the term trans and the associated structure was answered very well.
Many correct answers were given for the meaning of a dispersed system but also many did not make use of subject specific vocabulary or repeated the word dispersed in the answer. The idea of an emulsion and foam was well understood as was the part on the structural features of an emulsifier.
Many candidates identified the chiral carbon atom correctly in the structure given and two different ways in which enantiomers might affect the properties of foods. However, the reason for the difference in optical activity when carvone is synthesized using limonene from natural or chemical source was poorly answered with many not scoring at all.

