| Date | May 2012 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 12M.3.sl.TZ1.B2 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Outline | Question number | B2 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
The straight chain form of glucose is represented below.
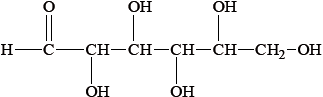
Fructose is an isomer of glucose, but they differ with regard to one functional group and hence in their redox properties.
Glucose is mainly present in one of two cyclic forms: \(\alpha \)-glucose and \(\beta \)-glucose. Distinguish between the two cyclic forms by completing the diagrams below.
(i) Identify the functional group present in glucose, but not fructose.
(ii) Identify the functional group present in fructose, but not glucose.
(iii) Identify the sugar that acts as a reducing agent.
Outline how the structure of cellulose is related to that of glucose.
Markscheme
\(\alpha \): C-1 OH below plane
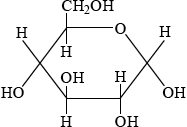 ;
;
\(\beta \): C-1 OH above plane
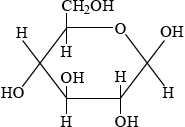 ;
;
(i) aldehyde/alkanal/CHO;
(ii) ketone/alkanone/CO;
(iii) glucose;
cellulose is (condensation) polymer of \(\beta \)-glucose;
(rings in cellulose) joined by \(\beta \)-1,4 linkages;
Examiners report
Part (a) was generally well answered with full marks awarded to more than half of the candidates. Those who did not score full marks usually reversed OH on carbon 4. Glucose has an aldehyde functional group which can undergo oxidation and this was covered in Topic 10. The fact that cellulose is a polymer of glucose and has beta-1,4 linkages seemed to have been overlooked by many candidates.
Glucose has an aldehyde functional group which can undergo oxidation and this was covered in Topic 10.
The fact that cellulose is a polymer of glucose and has beta-1,4 linkages seemed to have been overlooked by many candidates.

