| Date | November 2011 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 11N.3.hl.TZ0.F5 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | Justify and State | Question number | F5 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Stereochemistry is the study of the spatial arrangement of atoms in molecules. A molecule containing a chiral carbon atom exists as two enantiomers. Three different conventions can be used for naming purposes.
Use the CORN rule to determine whether the structure of 2-aminopropanoic acid (alanine) represents the D or L form. Justify your answer.
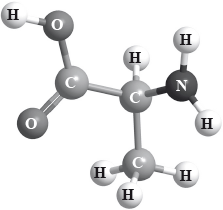
State the (d) or the (l) convention.
Markscheme
L isomer;
molecule is viewed with C–H bond pointing away from observer/viewer and COOH, \({\text{R/C}}{{\text{H}}_3}\) and \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2}\) (groups) are arranged anti-clockwise (around the asymmetric carbon atom);
Accept converse description.
Award M2 if there is reference to groups being arranged anti-clockwise without identifying the groups.
d rotates plane of polarized light clockwise/dextrorotatory/+ / l rotates plane of polarized light anti-clockwise/laevorotatory/–;
Examiners report
The vast majority chose the correct “L” isomer for the structure given, but only about half of them could give a convincing explanation or justify their answer.
About half were correctly able to state the (d) or the (l) convention.

