| Date | May 2014 | Marks available | 4 | Reference code | 14M.3.sl.TZ1.18 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Discuss | Question number | 18 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
The formula of linoleic acid is given in Table 22 of the Data Booklet.
Identify the structural formula of the triglyceride formed when three molecules of linoleic acid react with one molecule of glycerol (propane-1,2,3-triol), \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OHCHOHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}\).
State the other product formed during this reaction.
Explain why the triglyceride formed from linoleic acid and glycerol is a liquid and not a solid at room temperature.
Describe how the triglyceride formed from linoleic acid and glycerol could be converted into a saturated fat and give any necessary conditions.
Other than the fact that it is a solid at room temperature, discuss two advantages and two disadvantages of a saturated fat compared to an unsaturated fat or oil.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Markscheme
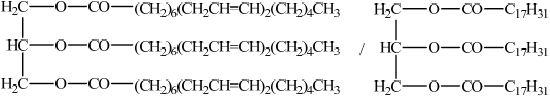 ;
;
Do not accept R for C17H31.
Penalize for incorrect bond connectivity.
water/\({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\);
double bonds cause a “kink” in the hydrocarbon chain / unsaturated hydrocarbon chains cannot pack so closely together (as saturated);
attractive forces/London/dispersion/van der Waals/vdW/LDF/ /instantaneous/temporary induced dipole-induced dipole forces between the molecules are weaker / less energy required to overcome the attraction between the molecules;
(d) addition of hydrogen/\({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\) / hydrogenation;
heat and catalyst/Zn/Cu/Ni/Pd/Pt;
Accept any temperature in range 140–225 °C.
Advantages:
decreases rate of oxidation / makes it more stable / slows rancidification / has longer shelf life;
greater energy released per gram / OWTTE;
controls hardness/plasticity/stiffness;
Disadvantages:
increase risk of heart disease / increase low-density/LDL cholesterol;
does not contain essential/omega-3/omega-6 fatty acids;
hydrogenated fats might contain trans-fatty acids;
Examiners report
Generally candidates struggled with the details of the triglyceride structure; very few were able to gain the mark for part (a). Almost all the candidates were able to state water as the other product and gain the mark in part (b). Candidates often missed the specific details for the answer to part (c); they were able to identify the presence of double bonds or unsaturation but had difficulty expanding and linking the idea to how this changed packing and intermolecular forces. For part (d) many candidates stated hydrogenation as the answer and scored one point but many were not able to state the two reaction conditions correctly. Most responses on advantages and disadvantages of saturated fats, part (e), were too general for example, affects your health. A common statement was ‘better storage/ transport’ as an advantage for saturated fats. Most candidates only scored one or two points for this question.
Generally candidates struggled with the details of the triglyceride structure; very few were able to gain the mark for part (a). Almost all the candidates were able to state water as the other product and gain the mark in part (b). Candidates often missed the specific details for the answer to part (c); they were able to identify the presence of double bonds or unsaturation but had difficulty expanding and linking the idea to how this changed packing and intermolecular forces. For part (d) many candidates stated hydrogenation as the answer and scored one point but many were not able to state the two reaction conditions correctly. Most responses on advantages and disadvantages of saturated fats, part (e), were too general for example, affects your health. A common statement was ‘better storage/ transport’ as an advantage for saturated fats. Most candidates only scored one or two points for this question.
Generally candidates struggled with the details of the triglyceride structure; very few were able to gain the mark for part (a). Almost all the candidates were able to state water as the other product and gain the mark in part (b). Candidates often missed the specific details for the answer to part (c); they were able to identify the presence of double bonds or unsaturation but had difficulty expanding and linking the idea to how this changed packing and intermolecular forces. For part (d) many candidates stated hydrogenation as the answer and scored one point but many were not able to state the two reaction conditions correctly. Most responses on advantages and disadvantages of saturated fats, part (e), were too general for example, affects your health. A common statement was ‘better storage/ transport’ as an advantage for saturated fats. Most candidates only scored one or two points for this question.
Generally candidates struggled with the details of the triglyceride structure; very few were able to gain the mark for part (a). Almost all the candidates were able to state water as the other product and gain the mark in part (b). Candidates often missed the specific details for the answer to part (c); they were able to identify the presence of double bonds or unsaturation but had difficulty expanding and linking the idea to how this changed packing and intermolecular forces. For part (d) many candidates stated hydrogenation as the answer and scored one point but many were not able to state the two reaction conditions correctly. Most responses on advantages and disadvantages of saturated fats, part (e), were too general for example, affects your health. A common statement was ‘better storage/ transport’ as an advantage for saturated fats. Most candidates only scored one or two points for this question.
Generally candidates struggled with the details of the triglyceride structure; very few were able to gain the mark for part (a). Almost all the candidates were able to state water as the other product and gain the mark in part (b). Candidates often missed the specific details for the answer to part (c); they were able to identify the presence of double bonds or unsaturation but had difficulty expanding and linking the idea to how this changed packing and intermolecular forces. For part (d) many candidates stated hydrogenation as the answer and scored one point but many were not able to state the two reaction conditions correctly. Most responses on advantages and disadvantages of saturated fats, part (e), were too general for example, affects your health. A common statement was ‘better storage/ transport’ as an advantage for saturated fats. Most candidates only scored one or two points for this question.

