Industrialisation & Increased Carbon Dioxide
- Atmospheric carbon dioxide levels have fluctuated throughout Earth's history due to events such as volcanic eruptions and the weathering of limestone rocks
- Scientists know this from having analysed the gas composition of bubbles formed in ancient ice cores

Atmospheric carbon dioxide levels have fluctuated throughout earth’s history, but recent increases have been faster and higher than ever before (ppmv = parts per million by volume)
- Since the industrial revolution, however, atmospheric carbon dioxide levels have risen to their highest in Earth's history
- Prior to the industrial revolution, the highest atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration was around 300 parts per million (ppm), and it is currently above 400 ppm
- The industrial revolution began in the late 1700s, when the combustion of fossil fuels to power factories, transport, and homes became commonplace
- Fossil fuel combustion releases carbon dioxide
- A clear correlation can be seen between increasing levels of carbon dioxide since the industrial revolution and increasing global temperatures
- Early data on global temperatures can be found using climate indicators such as tree growth and soil cores
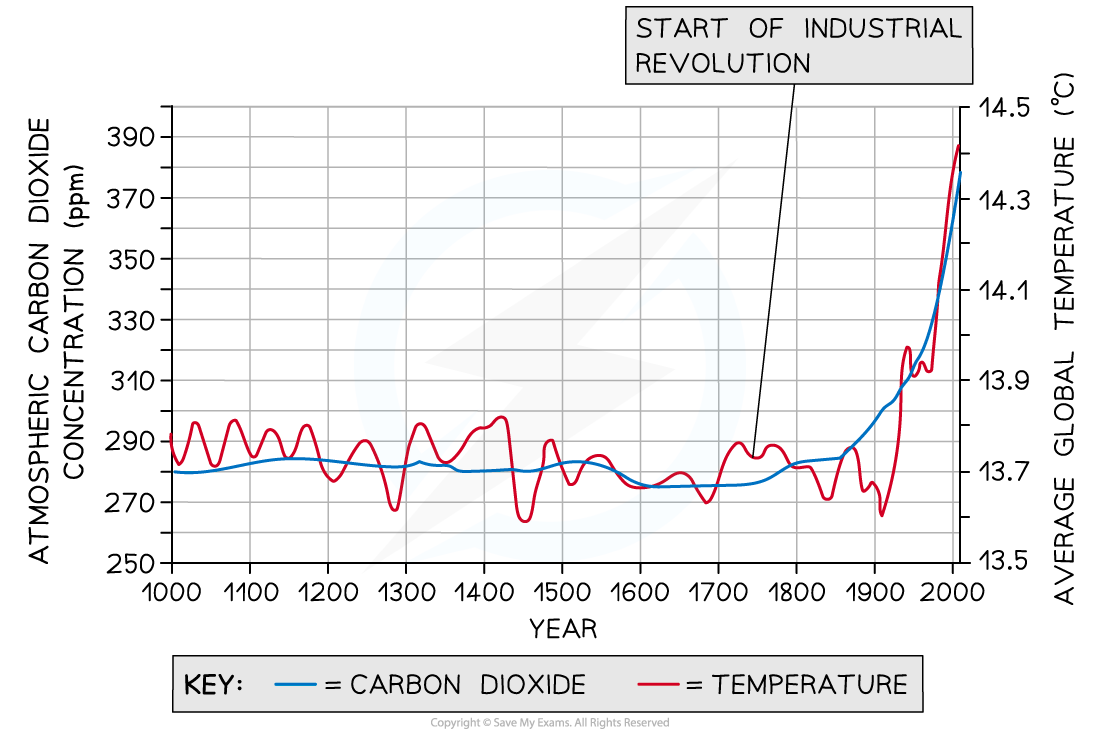
There is a correlation between increasing carbon dioxide levels since the start of the industrial revolution and increasing global temperatures
Combustion of Fossil Fuels
- The industrial revolution, beginning in the late 1700s, was the shift from hand production to machine production, often in factories powered by steam
- Factory production led to the need to transport goods over long distances, and so the railways were built, also powered by steam
- Steam would have been produced by the combustion (burning) of fossil fuels; initially coal, and later also oil and gas
- The combustion of fossil fuels releases carbon that has been stored for millions of years into the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide
- The improved standard of living for many that resulted from the industrial revolution lead to huge population growth, further increasing the need for production and movement of goods, and therefore the need for fossil fuels
- Although we often associate the industrial revolution with the Victorian era, the fastest increase in fossil fuel combustion has taken place since the 1950s
- The increase in fossil fuel use since the 1950s is correlated with the fastest increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide, providing evidence that it is human activity changing the composition of the atmosphere
Temperatures & Increased Carbon Dioxide
- We know that greenhouse gases absorb infrared radiation and warm the earth's atmosphere, and we know that carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas, so climate scientists have long hypothesised that increasing carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere will lead to warming global temperatures
- Evidence to support this hypothesis can be found by looking back at the connection between atmospheric carbon dioxide levels and temperatures over time
- Information about the ancient atmosphere and climate can be found by analysing ice cores, obtained by drilling into antarctic ice
- Ice is deposited as water freezes over time, so the deeper into the ice you go, the older it is
- Analysing the gas content of bubbles in ice can tell scientists about atmospheric gas concentrations over time
- Data about climate can be inferred by studying ancient pollen grains preserved in ice (certain plants would have survived in certain climates), as well as studying the chemistry of the water molecules
- Data show a correlation between changing atmospheric carbon dioxide levels and temperature over thousands of years
- Note that carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is not thought to be the only factor affecting climate; it is known that events such as solar winds and sun spots can affect the climate on Earth, but scientists think that the effects of such events are small in comparison to that of atmospheric carbon dioxide
- Correlation does not equal causation, but together with what scientists know about carbon dioxide as a greenhouse gas, this is strong evidence that carbon dioxide released since the industrial revolution is causing increasing global temperatures
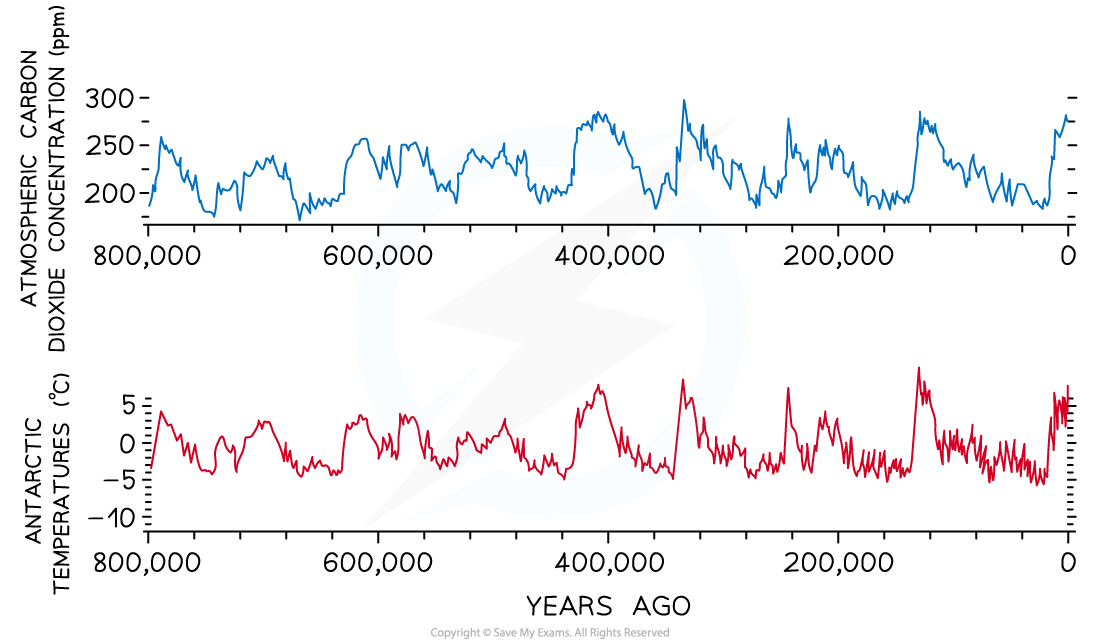
Data from antarctic sea ice show a correlation between atmospheric carbon dioxide and antarctic temperatures over the last 800 000 years
Investigating the Causes of Climate Change
Evaluating claims that human activities are not causing climate change
- Since scientists first began to associate burning fossil fuels with increasing global temperatures, there have been many who have claimed that human activity is not the cause of climate change
Evaluating Claims that Human Activities are Not Causing Climate Change Table

- It is important to evaluate any statement that is made about the causes of climate change in the light of scientific evidence
- Consider whether a statement addresses all of the evidence, or only part of it
- E.g. there may be some years when global temperatures go down, but there is strong evidence for an overall upward trend
- Find out whether the statement comes from a trustworthy, unbiased source
- E.g. Does the source have a financial or political interest in continuing to burn fossil fuels
- Several countries wrote to the United Nations in 2021 to ask that urgent recommendations against burning fossil fuels were toned down; all of these countries had economies that depended on the use of fossil fuels
- E.g. Does the source have a financial or political interest in continuing to burn fossil fuels
- Consider whether a statement addresses all of the evidence, or only part of it
NOS: Assessing claims; assessment of the claims that human activities are producing climate change
- Whenever you come across any scientific claim, it is important to assess its reliability
- Scientists know that before they present a new idea, they must carry out research and provide evidence to support their claim
- Any published research must be clear about the level of certainty that any data provide; this is the purpose of statistical tests such as the chi-squared test
- Research papers must include details of the method used so that other scientists can evaluate it and potentially repeat it to see if they achieve the same results
- When it is claimed that human activities are causing climate change, it is important to evaluate these claims while bearing the following factors in mind
- There is a great deal of scientific evidence that has been tested and checked by other scientists that supports the hypothesis that humans burning fossil fuels causes climate change; this increases the likelihood that further claims of this nature are correct
- Climate is highly complex, so scientists need to be careful not to state that one factor alone has led to a specific event
- Climate can be affected by any number of factors in any given year; it is important to look at all of the data
- You may have heard climate and weather experts in the media being asked about whether one particular extreme weather event is due to climate change; they always say that it is wrong to draw conclusions from one event, while also pointing to that event's place in a trend of increasingly extreme weather
- Climate change is not expected to be linear in effect; scientists expect that there may be a tipping point beyond which changes happen faster
- This makes it very difficult to make predictions about exact future climate conditions
- Climate can be affected by any number of factors in any given year; it is important to look at all of the data
- People always have a personal interest; some are especially passionate about the environment, while others depend financially on fossil fuels
- It is important that we are aware of the personal biases of those making claims about the causes of climate change
- If predictions about global warming are correct, then the potential impacts on the future of Earth are huge; as scientists, it is our responsibility to be aware of the important factors surrounding this debate so that we can help other to assess evidence thoroughly
