| Date | May 2019 | Marks available | 5 | Reference code | 19M.1.SL.TZ1.S_8 |
| Level | Standard Level | Paper | Paper 1 | Time zone | Time zone 1 |
| Command term | Find and Hence | Question number | S_8 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Let , .
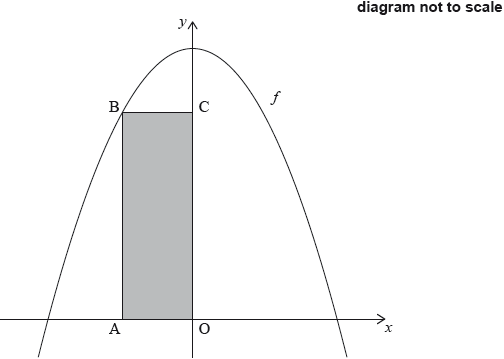
The following diagram shows part of the graph of .
Rectangle PQRS is drawn with P and Q on the -axis and R and S on the graph of .
Let OP = .
Consider another function , .
Find the -intercepts of the graph of .
Show that the area of PQRS is .
Hence find the value of such that the area of PQRS is a maximum.
Show that when the graphs of and intersect, .
Given that the graphs of and intersect only once, find the value of .
Markscheme
* This question is from an exam for a previous syllabus, and may contain minor differences in marking or structure.
valid approach (M1)
eg , , one correct solution
, 3 (accept (3, 0), (−3, 0)) A1 N2
[2 marks]
valid approach (M1)
eg height = , base = 2(OP) or , ,
correct working that clearly leads to given answer A1
eg
Note: Do not accept sloppy notation eg .
area = AG N0
[2 marks]
setting derivative = 0 (seen anywhere) (M1)
eg ,
correct derivative (must be in terms of only) (seen anywhere) A2
eg ,
correct working (A1)
eg ,
A1 N3
[5 marks]
valid approach (M1)
eg ,
correct working (A1)
eg ,
AG N0
[2 marks]
METHOD 1 (discriminant)
recognizing to use discriminant (seen anywhere) (M1)
eg Δ,
discriminant = 0 (seen anywhere) M1
correct substitution into discriminant (do not accept only in quadratic formula) (A1)
eg ,
correct working (A1)
eg ,
A1 N2
METHOD 2 (completing the square)
valid approach to complete the square (M1)
eg ,
correct working (A1)
eg ,
recognizing condition for one solution M1
eg ,
correct working (A1)
eg ,
A1 N2
METHOD 3 (using vertex)
valid approach to find vertex (seen anywhere) M1
eg ,
correct working (A1)
eg ,
(A1)
correct substitution (A1)
eg
A1 N2
[5 marks]