| Date | May 2019 | Marks available | 3 | Reference code | 19M.3.hl.TZ2.2 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Determine | Question number | 2 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Bromine and methanoic acid react in aqueous solution.
Br2 (aq) + HCOOH (aq) → 2Br− (aq) + 2H+ (aq) + CO2 (g)
The reaction was monitored by measuring the volume of carbon dioxide produced as time
progressed.
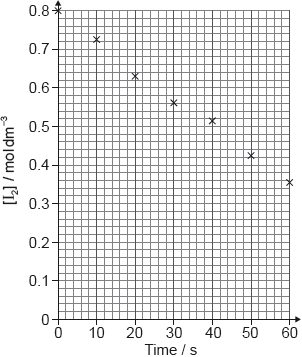
Determine from the graph the rate of reaction at 20 s, in cm3 s−1, showing your working.
Outline, with a reason, another property that could be monitored to measure the rate of this reaction.
Describe one systematic error associated with the use of the gas syringe, and how the error affects the calculated rate.
Identify one error associated with the use of an accurate stopwatch.
Markscheme
tangent drawn to curve at t = 20 s [✔]
slope/gradient calculation [✔]
0.35 «cm3 s–1» [✔]
Note: Accept values in the range 0.32–0.42 «cm3 s–1»
ALTERNATIVE 1
colour [✔]
Br2 /reactant is coloured «Br– (aq) is not» [✔]
ALTERNATIVE 2
conductivity [✔]
greater/increased concentration of ions in products [✔]
Note: Do not accept “changes in temperature” or “number of bubbles”.
ALTERNATIVE 3
mass/pressure [✔]
gas is evolved/produced [✔]
Note: Do not accept “mass of products is less than mass of reactants”.
ALTERNATIVE 4
pH [✔]
methanoic acid is weak AND HBr is strong
OR
increase in [H+] [✔]
ALTERNATIVE 1
gas may leak/be lost/escape
OR
plunger may stick/friction «so pressure is greater than atmospheric pressure»
OR
syringe may be tilted «up» so plunger moves less «with gravity acting on plunger»
OR
CO2 dissolved in water [✔]
calculated rate lower [✔]
ALTERNATIVE 2
syringe may be tilted «down» so plunger moves more «with gravity acting on plunger»
OR
syringe is held in hand so gets warmer and gas expands [✔]
calculated rate higher [✔]
Note: Calculated rate is lower or higher must be stated for M2.
Do not accept “scale on syringe is inaccurate”, “errors in reading syringe”, or “bubbles in syringe”.
human reaction time/delay «starting/stopping the stopwatch» [✔]
Examiners report
This part proved to be challenging for some candidates whereas other candidates were able to draw a tangent at 20 sec and then calculate the rate. A significant number of candidates calculated the average rate and achieved one mark.
Majority of the candidates stated another property, which could be monitored correctly. The most common error was changes in temperature, which was stated by some candidates.
This part was about the systematic error and was answered correctly, but many candidates failed to state how the error affected the calculated rate. Many candidates confused this with the concept of a random error and identified the uncertainty of reading the syringe, which is incorrect.
This part was well answered by most candidates although some candidates did not read the question clearly and commented on the stopwatch not working properly or not being accurate.