| Date | November 2016 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 16N.2.sl.TZ0.3 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | Determine | Question number | 3 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Sodium thiosulfate solution reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to form a precipitate of sulfur at room temperature.
Na2S2O3 (aq) + 2HCl (aq) → S (s) + SO2 (g) + 2NaCl (aq) + X
Identify the formula and state symbol of X.
Suggest why the experiment should be carried out in a fume hood or in a well-ventilated laboratory.
The precipitate of sulfur makes the mixture cloudy, so a mark underneath the reaction mixture becomes invisible with time.
10.0 cm3 of 2.00 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid was added to a 50.0 cm3 solution of sodium thiosulfate at temperature, T1. Students measured the time taken for the mark to be no longer visible to the naked eye. The experiment was repeated at different concentrations of sodium thiosulfate.
Show that the hydrochloric acid added to the flask in experiment 1 is in excess.
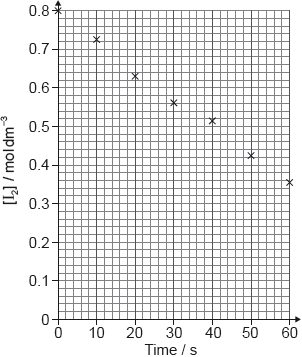
Draw the best fit line of against concentration of sodium thiosulfate on the axes provided.
A student decided to carry out another experiment using 0.075 mol dm-3 solution of sodium thiosulfate under the same conditions. Determine the time taken for the mark to be no longer visible.
An additional experiment was carried out at a higher temperature, T2.
(i) On the same axes, sketch Maxwell–Boltzmann energy distribution curves at the two temperatures T1 and T2, where T2 > T1.
(ii) Explain why a higher temperature causes the rate of reaction to increase.
Suggest one reason why the values of rates of reactions obtained at higher temperatures may be less accurate.
Markscheme
H2O AND (l)
Do not accept H2O (aq).
SO2 (g) is an irritant/causes breathing problems
OR
SO2 (g) is poisonous/toxic
Accept SO2 (g) is acidic, but do not accept “causes acid rain”.
Accept SO2 (g) is harmful.
Accept SO2 (g) has a foul/pungent smell.
n(HCl) = «dm3 × 2.00 mol dm-3 =» 0.0200 / 2.00 × 10-2«mol»
AND
n(Na2S2O3) = «dm3 × 0.150 mol × dm-3 =» 0.00750 / 7.50 × 10-3 «mol»
0.0200 «mol» > 0.0150 «mol»
OR
2.00 × 10-2«mol» > 2 × 7.50 × 10-3 «mol»
OR
× 2.00 × 10-2 «mol» > 7.50 × 10-3 «mol»
Accept answers based on volume of solutions required for complete reaction.
Award [2] for second marking point.
Do not award M2 unless factor of 2 (or half) is used.
five points plotted correctly
best fit line drawn with ruler, going through the origin
22.5 × 10-3 «s-1»
«Time = =» 44.4 «s»
Award [2] for correct final answer.
Accept value based on candidate’s graph.
Award M2 as ECF from M1.
Award [1 max] for methods involving taking mean of appropriate pairs of values.
Award [0] for taking mean of pairs of time values.
Award [2] for answers between 42.4 and 46.4 «s».
(i)
correctly labelled axes
peak of T2 curve lower AND to the right of T1 curve
Accept “probability «density» / number of particles / N / fraction” on y-axis.
Accept “kinetic E/KE/EK” but not just “Energy/E” on x-axis.
(ii)
greater proportion of molecules have E ≥ Ea or E > Ea
OR
greater area under curve to the right of the Ea
greater frequency of collisions «between molecules»
OR
more collisions per unit time/second
Accept more molecules have energy greater than Ea.
Do not accept just “particles have greater kinetic energy”.
Accept “rate/chance/probability/likelihood/” instead of “frequency”.
Accept suitably shaded/annotated diagram.
Do not accept just “more collisions”.
shorter reaction time so larger «%» error in timing/seeing when mark disappears
Accept cooling of reaction mixture during course of reaction.