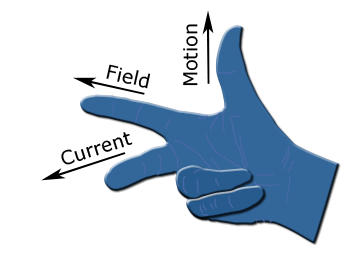
 Electromagnetic induction is the process by which kinetic energy is converted into electrical energy in the presence of a magnetic field.
Electromagnetic induction is the process by which kinetic energy is converted into electrical energy in the presence of a magnetic field.
How can we determine the magnitude and direction of induced EMF? What is involved in the construction and operation of an AC generator? How is electrical power transmitted across countries? What can we do to convert AC to DC? What is a capacitor?
Key Concepts
Electromagnetic induction is the process by which an EMF is induced due to the relative motion of a magnetic field and conductor.
Faraday's law and Lenz's law can be combined to determine the magnitude and direction of the induced EMF:
\(\varepsilon =-{\mathrm{d}N\Phi\over \mathrm{d}t}\)
- \(\varepsilon \) is the induced EMF (V)
- \(N\Phi\) is the magnetic flux linkage (Tm2 or Wb)
- \({\mathrm{d}N\Phi\over \mathrm{d}t}\) is the rate of change of magnetic flux linkage (Tm2s-1 or Wb s-1)
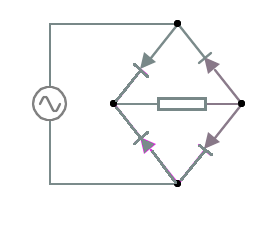
Alternating current can be converted into direct current by rectification:
- In half wave rectification, a diode is inserted. Current will only pass in forward bias.
- In full wave rectification, two diode pathways are inserted. Current will pass in either direction, but will always enter the load resistor at the same side.
- The addition of a capacitor to a diode bridge rectification circuit creates a smoothing effect.

Diodes are made from semiconducting materials containing a p-n junction.
How much of AHL EM induction have you understood?




 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn