Half wave
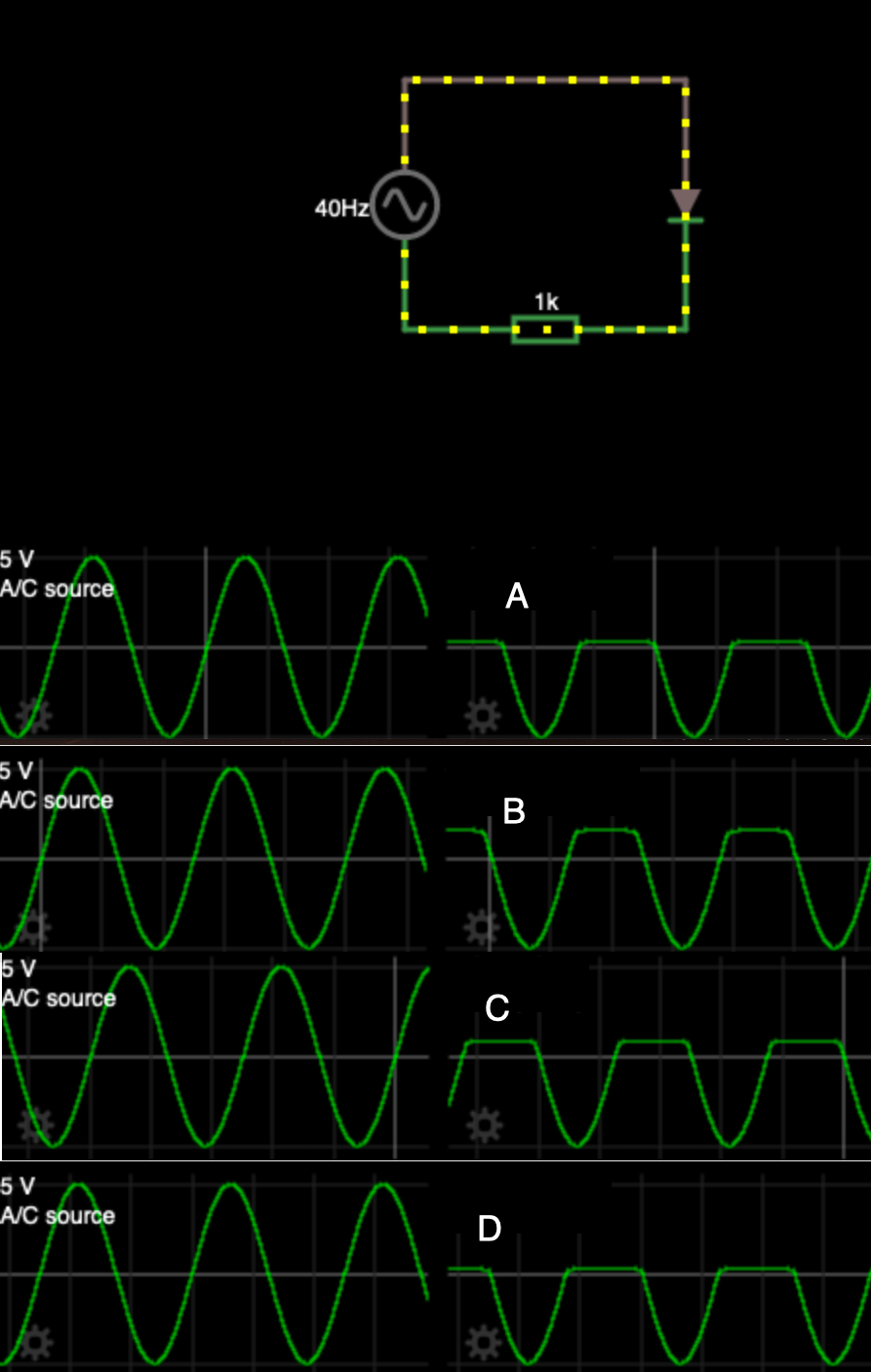
The simplest form of rectification is the insertion of a diode in the series circuit. All current in the forward direction is transmitted; no current flows in reverse bias.
Notice that the diode symbol acts as an arrow to show the direction in which conventional current will flow.

This circuit has the downside that current is only flowing for half of the time.
Full wave
Full wave rectification uses two diode pathways (in opposite directions) to enable the current to flow at all times. Each diode path runs through the same resistor (or desired electrical component).
See if you can trace a finger around the following circuit diagram, first starting upwards from the power supply and then downwards.
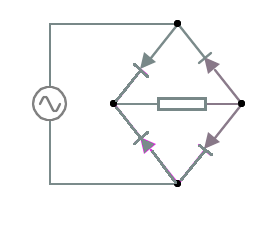
While an improvement on half wave rectification, the output is still sinusoidal in magnitude.
 With most electricity generated to have alternating current, it is useful in some cases for this to be converted into direct current. This process is called rectification.
With most electricity generated to have alternating current, it is useful in some cases for this to be converted into direct current. This process is called rectification.










 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn