| Date | November 2016 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 16N.2.HL.TZ0.9 |
| Level | Higher level | Paper | Paper 2 | Time zone | 0 - no time zone |
| Command term | Explain | Question number | 9 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
A beam of electrons e– enters a uniform electric field between parallel conducting plates RS. RS are connected to a direct current (dc) power supply. A uniform magnetic field B is directed into the plane of the page and is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the electrons.
The magnetic field is adjusted until the electron beam is undeflected as shown.
Identify, on the diagram, the direction of the electric field between the plates.
The following data are available.
Separation of the plates RS = 4.0 cm Potential difference between the plates = 2.2 kV Velocity of the electrons = 5.0×105 m s–1
Determine the strength of the magnetic field B.
The velocity of the electrons is now increased. Explain the effect that this will have on the path of the electron beam.
Markscheme
direction indicated downwards, perpendicular to plates
Arrows must be between plates but allow edge effects if shown. Only one arrow is required.
«Vm–1»
B = «» 0.11 «T»
ECF applies from MP1 to MP2 due to math error.
Award [2] for a bald correct answer.
ALTERNATIVE 1
magnetic force increases
OR
magnetic force becomes greater than electric force
electron beam deflects “downwards” / towards S
OR
path of beam is downwards
ALTERNATIVE 2
when v increases, the B required to maintain horizontal path decreases
«but B is constant» so path of beam is downwards
Do not apply an ecf from (a).
Award [1 max] if answer states that magnetic force decreases and therefore path is upwards.
Ignore any statement about shape of path
Do not allow “path deviates in direction of magnetic force” without qualification.
Examiners report
Syllabus sections
- 19M.2.SL.TZ2.5aii: Label with arrows on the velocity vector v of the proton.
- 17N.2.SL.TZ0.3a.iii: State why knowledge of quantities such as resistivity is useful to scientists.
-
17N.2.SL.TZ0.3b:
The current direction is now changed so that charge flows vertically through the film.
Deduce, without calculation, the change in the resistance.
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.16:
Two parallel plates are a distance apart with a potential difference between them. A point charge moves from the negatively charged plate to the positively charged plate. The charge gains kinetic energy W. The distance between the plates is doubled and the potential difference between them is halved. What is the kinetic energy gained by an identical charge moving between these plates?
A.
B. W
C. 2W
D. 4W
- 18M.1.SL.TZ1.18: Three resistors are connected as shown. What is the value of the total resistance between X...
- 22M.1.SL.TZ2.19: A charge Q is at a point between two electric charges Q1 and Q2. The net electric force on...
- 22M.1.SL.TZ2.20: A battery of negligible internal resistance is connected to a lamp. A second identical lamp...
- 22M.1.SL.TZ2.22: A rectangular coil of wire RSTU is connected to a battery and placed in a magnetic field Z...
-
22M.1.SL.TZ2.21:
A circuit consists of a cell of emf E = 3.0 V and four resistors connected as shown. Resistors R1 and R4 are 1.0 Ω and resistors R2 and R3 are 2.0 Ω.
What is the voltmeter reading?
A. 0.50 V
B. 1.0 V
C. 1.5 V
D. 2.0 V
- 18M.1.SL.TZ2.19: A cell with negligible internal resistance is connected as shown. The ammeter and the...
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.2c: The cable between the satellites cuts the magnetic field lines of the Earth at right...
- 19M.1.HL.TZ1.19: A horizontal electrical cable carries a steady current out of the page. The Earth’s magnetic...
- 19M.1.HL.TZ1.18: Two currents of 3 A and 1 A are established in the same direction through two parallel...
- 22M.2.SL.TZ2.4b.i: State the emf of the cell.
-
22M.2.SL.TZ2.4b.ii:
Deduce the internal resistance of the cell.
- 16N.1.SL.TZ0.19: An electrical circuit is shown with loop X and junction Y. What is the correct expression...
- 22M.2.HL.TZ1.7c.i: Identify the direction of the resultant force acting on Z as it oscillates.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.4c.ii:
Comment on the implications of your answer to (c)(i) for cell B.
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.4b.i: State the emf of the cell.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.4b.ii:
Deduce the internal resistance of the cell.
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.9a.ii: Show that the energy E of each electron in the beam is about 7 × 10−11 J.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.6d:
The two cables in part (c) are suspended a constant distance apart. Explain how the magnetic forces acting between the cables vary during the course of one cycle of the alternating current (ac).
-
22M.2.SL.TZ2.4c:
The voltmeter is used in another circuit that contains two secondary cells.
Cell A has an emf of 10 V and an internal resistance of 1.0 Ω. Cell B has an emf of 4.0 V and an internal resistance of 2.0 Ω.
Calculate the reading on the voltmeter.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.4e.i:
A fully charged cell of emf 6.0 V delivers a constant current of 5.0 A for a time of 0.25 hour until it is completely discharged.
The cell is then re-charged by a rectangular solar panel of dimensions 0.40 m × 0.15 m at a place where the maximum intensity of sunlight is 380 W m−2.
The overall efficiency of the re-charging process is 18 %.
Calculate the minimum time required to re-charge the cell fully.
- 17N.2.SL.TZ0.3c: Draw a circuit diagram to show how you could measure the resistance of the carbon-film...
- 17N.3.SL.TZ0.2b: State the value of the intercept on the R axis.
- 17M.1.SL.TZ2.19: A wire has variable cross-sectional area. The cross-sectional area at Y is double that at...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.15: Positive charge is uniformly distributed on a semi-circular plastic rod. What is the...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.17: The diagram shows the path of a particle in a region of uniform magnetic field. The field is...
- 17M.2.SL.TZ1.5b.i: Explain which interaction is responsible for this decay.
-
17M.3.SL.TZ2.2a:
An ammeter and a voltmeter are connected in the circuit. Label the ammeter with the letter A and the voltmeter with the letter V.
-
22M.1.SL.TZ1.19:
P and Q are two opposite point charges. The force F acting on P due to Q and the electric field strength E at P are shown.
Which diagram shows the force on Q due to P and the electric field strength at Q?
-
22M.1.SL.TZ1.21:
Three identical resistors each of resistance R are connected with a variable resistor X as shown. X is initially set to R. The current in the cell is 0.60 A.
The cell has negligible internal resistance.
X is now set to zero. What is the current in the cell?
A. 0.45 A
B. 0.60 A
C. 0.90 A
D. 1.80 A
- 22M.1.SL.TZ1.20: Three point charges of equal magnitude are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle....
-
22M.1.SL.TZ1.22:
Two cylinders, X and Y, made from the same material, are connected in series.
The cross-sectional area of Y is twice that of X. The drift speed of the electrons in X is and in Y it is .
What is the ratio ?
A. 4
B. 2
C. 1
D.
- 22M.1.HL.TZ1.22: A conductor is placed in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the paper. A...
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.21:
Two cells are connected in parallel as shown below. Each cell has an emf of 5.0 V and an internal resistance of 2.0 Ω. The lamp has a resistance of 4.0 Ω. The ammeter is ideal.
What is the reading on the ammeter?
A. 1.0 A
B. 1.3 A
C. 2.0 A
D. 2.5 A
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.20:
In the circuit shown, the battery has an emf of 12 V and negligible internal resistance. Three identical resistors are connected as shown. The resistors each have a resistance of 10 Ω.
The resistor L is removed. What is the change in potential at X?
A. Increases by 2 V
B. Decreases by 2 V
C. Increases by 4 V
D. Decreases by 4 V
-
16N.2.SL.TZ0.7b:
Components R and T are placed in a circuit. Both meters are ideal.
Slider Z of the potentiometer is moved from Y to X.
(i) State what happens to the magnitude of the current in the ammeter.
(ii) Estimate, with an explanation, the voltmeter reading when the ammeter reads 0.20 A.
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.17: A cell has an emf of 3.0 V and an internal resistance of 2.0 Ω. The cell is connected in...
-
18M.2.SL.TZ2.4b.i:
Show that the resistance of the wire AC is 28 Ω.
- 21N.2.SL.TZ0.4b.ii: Describe the motion of Q after release.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.3a.ii: State the direction of the resultant electric field at P.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.16: A cell of emf 6.0 V and negligible internal resistance is connected to three resistors as...
-
18M.1.HL.TZ1.17:
When an electric cell of negligible internal resistance is connected to a resistor of resistance 4R, the power dissipated in the resistor is P.
What is the power dissipated in a resistor of resistance value R when it is connected to the same cell?
A.
B. P
C. 4P
D. 16P
-
17M.3.SL.TZ2.2b:
In one experiment a student obtains the following graph showing the variation with current I of the potential difference V across the cell.
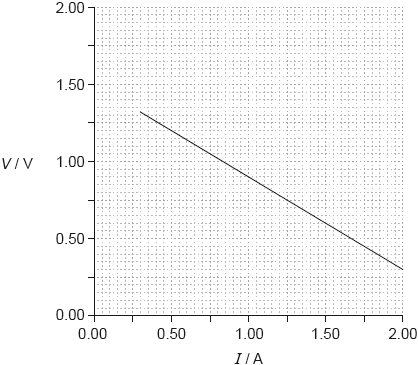
Using the graph, determine the best estimate of the internal resistance of the cell.
- 17N.1.SL.TZ0.18: Kirchhoff’s laws are applied to the circuit shown. What is the equation for the dotted...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.4b.i:
Show that the resistance of the wire AC is 28 Ω.
- 17N.1.SL.TZ0.20: The diagram shows two current-carrying wires, P and Q, that both lie in the plane of the...
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.18: The diagram shows the magnetic field surrounding two current-carrying metal wires P and...
-
22M.2.SL.TZ1.4c.i:
Deduce the resistance of this new cylinder when it has been reshaped.
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.15: Two pulses are travelling towards each other. What is a possible pulse shape when the...
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.19: An electron is accelerated through a potential difference of 2.5 MV. What is the change in...
-
17M.1.SL.TZ2.20:
A circuit contains a cell of electromotive force (emf) 9.0 V and internal resistance 1.0 Ω together with a resistor of resistance 4.0 Ω as shown. The ammeter is ideal. XY is a connecting wire.
What is the reading of the ammeter?
A. 0 A
B. 1.8 A
C. 9.0 A
D. 11 A
- 16N.1.SL.TZ0.20: A cell of emf 4V and negligible internal resistance is connected to three resistors as shown....
- 18N.1.SL.TZ0.22: A particle of mass m and charge of magnitude q enters a region of uniform magnetic field B...
- 18N.1.SL.TZ0.19: A wire of length L is used in an electric heater. When the potential difference across the...
- 18N.1.HL.TZ0.18: Two parallel wires P and Q are perpendicular to the page and carry equal currents. Point S is...
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.1c.i:
Outline why the ions are likely to spread out.
-
18N.1.SL.TZ0.20:
A combination of four identical resistors each of resistance R are connected to a source of emf ε of negligible internal resistance. What is the current in the resistor X?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 18N.1.SL.TZ0.21: Two parallel wires are perpendicular to the page. The wires carry equal currents in opposite...
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.30:
Two point charges Q1 and Q2 are one metre apart. The graph shows the variation of electric potential V with distance from Q1.
What is ?
A.
B.
C. 4
D. 16
-
18N.2.SL.TZ0.1c.i:
Outline why the ions are likely to spread out.
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.2d.i: Outline how eddy currents reduce transformer efficiency.
-
17M.2.SL.TZ1.4a.i:
Calculate the current in the copper cable.
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.18:
An electrical power supply has an internal resistance. It supplies a direct current to an external circuit for a time . What is the electromotive force (emf) of the power supply?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ2.16:
Four particles, two of charge +Q and two of charge −Q, are positioned on the -axis as shown. A particle P with a positive charge is placed on the -axis. What is the direction of the net electrostatic force on this particle?
-
19N.2.SL.TZ0.4b(i):
Show that the radius of the path is about 6 cm.
- 18N.2.SL.TZ0.2c: One advantage of this system is that if one lamp fails then the other lamps in the...
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.2c: One advantage of this system is that if one lamp fails then the other lamps in the...
- 19N.1.SL.TZ0.19: The diagram shows a resistor network. The potential difference between X and Y is 8.0...
- 19N.1.SL.TZ0.17: A negatively charged particle in a uniform gravitational field is positioned mid-way between...
- 19N.1.SL.TZ0.18: A thin copper wire and a thick copper wire are connected in series to an electric cell. Which...
- 19N.1.SL.TZ0.20: When a wire with an electric current I is placed in a magnetic field of strength B it...
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.16: Two power supplies, one of constant emf 24 V and the other of variable emf P, are connected...
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.5c(i):
State the range of current that the ammeter can measure as the slider S of the potential divider is moved from Q to P.
-
18N.2.SL.TZ0.2a:
Each rod is to have a resistance no greater than 0.10 Ω. Calculate, in m, the minimum radius of each rod. Give your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
18M.2.SL.TZ1.4a:
Calculate the resistance of the conductor.
-
16N.2.SL.TZ0.7a:
(i) State how the resistance of T varies with the current going through T.
(ii) Deduce, without a numerical calculation, whether R or T has the greater resistance at I=0.40 A.
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.9b:
The following data are available.
Separation of the plates RS = 4.0 cm Potential difference between the plates = 2.2 kV Velocity of the electrons = 5.0×105 m s–1Determine the strength of the magnetic field B.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.5b(ii):
Calculate the power dissipated in the circuit.
-
19M.1.SL.TZ2.18:
A particle with a charge ne is accelerated through a potential difference V.
What is the magnitude of the work done on the particle?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
19M.2.SL.TZ1.1e.ii:
Calculate the internal resistance of one cell.
-
19M.2.SL.TZ1.1d:
Determine the internal resistance of the battery.
- 19M.2.SL.TZ1.1a.ii: Deduce that the average power output of the battery is about 240 W.
- 17N.1.SL.TZ0.17: In the circuit shown, the fixed resistor has a value of 3 Ω and the variable resistor can be...
- 19M.1.SL.TZ1.21: Two cells each of emf 9.0 V and internal resistance 3.0 Ω are connected in series. A 12.0 Ω...
- 19M.3.SL.TZ2.1c: Outline, without calculation, how the internal resistance can be determined from this graph.
- 19M.1.SL.TZ1.22: Charge flows through a liquid. The charge flow is made up of positive and negative ions. In...
- 19M.1.SL.TZ2.19: The resistance of component X decreases when the intensity of light incident on it increases....
- 19M.1.SL.TZ2.20: Three resistors of resistance 1.0 Ω, 6.0 Ω and 6.0 Ω are connected as shown. The voltmeter is...
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.31: A proton of velocity v enters a region of electric and magnetic fields. The proton is not...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ2.24:
In an experiment to determine the resistivity of a material, a student measures the resistance of several wires made from the pure material. The wires have the same length but different diameters.
Which quantities should the student plot on the -axis and the -axis of a graph to obtain a straight line?
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.4a:
State what is meant by the emf of a cell.
- 19N.2.SL.TZ0.4a: Explain why the path of the proton is a circle.
- 19M.2.SL.TZ2.4bi: The switch is now closed. State, without calculation, why the current in the cell will...
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.8a: Outline what is meant by electric field strength.
-
19M.2.SL.TZ2.4a:
The switch S is initially open. Calculate the total power dissipated in the circuit.
-
19M.2.SL.TZ2.5b:
The speed of the proton is 2.16 × 106 m s-1 and the magnetic field strength is 0.042 T. For this proton, determine, in m, the radius of the circular path. Give your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
17M.2.SL.TZ2.5b.ii:
There is a current of 730 A in the cable. Show that the power loss in 1 m of the cable is about 30 W.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.5bi:
For this proton, determine, in m, the radius of the circular path. Give your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.7b.i: Describe, in terms of electron flow, how the smaller sphere becomes charged.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.6b.iii:
Determine the power dissipated in the cable per unit length.
-
21N.1.SL.TZ0.18:
A charge +Q and a charge −2Q are a distance 3x apart. Point P is on the line joining the charges, at a distance x from +Q.
The magnitude of the electric field produced at P by the charge +Q alone is .
What is the total electric field at P?
A. to the rightB. to the left
C. to the right
D. to the left
- 21N.1.SL.TZ0.21: A variable resistor is connected in series to a cell with internal resistance r as...
- 17N.1.SL.TZ0.19: With reference to internal energy conversion and ability to be recharged, what are...
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.9c:
Suggest why the answers to (a) and (b)(ii) are different.
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.17: A 12V battery has an internal resistance of 2.0Ω. A load of variable resistance is connected...
- 16N.1.SL.TZ0.18: A –5µC charge and a +10µC charge are a fixed distance apart. Where can the electric field...
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.18: The graph shows the variation of current with potential difference for a filament...
-
17M.1.HL.TZ1.17:
Electrons, each with a charge e, move with speed v along a metal wire. The electric current in the wire is I.
Plane P is perpendicular to the wire. How many electrons pass through plane P in each second?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 17M.1.SL.TZ2.21: A positively-charged particle moves parallel to a wire that carries a current...
- 16N.2.HL.TZ0.9a: Identify, on the diagram, the direction of the electric field between the plates.
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.2a:
Each rod is to have a resistance no greater than 0.10 Ω. Calculate, in m, the minimum radius of each rod. Give your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
21N.1.SL.TZ0.19:
Two wires, and , are made of the same material and have equal length. The diameter of is twice that of .
What is ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 21N.1.SL.TZ0.20: An electric motor of efficiency 0.75 is connected to a power supply with an emf of 20 V and...
- 21N.2.SL.TZ0.4c.ii: Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant magnetic field at Q.
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.2d: Satellite X must release ions into the space between the satellites. Explain why the current...
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.8b: An electron is placed at X and released from rest. Draw, on the diagram, the direction of the...
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.5aii: Label with arrows on the diagram the velocity vector v of the proton.
-
19M.2.SL.TZ1.1e.i:
Calculate the emf of one cell.
- 19M.1.HL.TZ1.17: A resistor of resistance R is connected to a fully charged cell of negligible internal...
- 19N.3.SL.TZ0.2a(ii): Explain, by reference to the power dissipated in the wire, the advantage of the fixed...
-
19N.3.SL.TZ0.2b:
The experiment is repeated using a wire made of the same material but of a larger diameter than the wire in part (a). On the axes in part (a), draw the graph for this second experiment.
- 18M.1.SL.TZ2.22: A cell has an emf of 4.0 V and an internal resistance of 2.0 Ω. The ideal voltmeter reads 3.2...
- 19M.1.SL.TZ2.21: A horizontal wire PQ lies perpendicular to a uniform horizontal magnetic field. A length...
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.4bi: The switch is now closed. State, without calculation, why the current in the cell will increase.
-
17N.3.SL.TZ0.2a:
Show that the gradient of the graph is equal to .
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.5ai: Label with arrows on the diagram the magnetic force F on the proton.
- 19M.1.SL.TZ2.2: What is the unit of electrical potential difference expressed in fundamental SI units? A. kg...
-
19N.2.SL.TZ0.5b(i):
Calculate the magnitude of the initial acceleration of the electron.
- 20N.1.SL.TZ0.20: A current in a wire lies between the poles of a magnet. What is the direction of the...
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.5c(ii):
Slider S of the potential divider is positioned so that the ammeter reads . Explain, without further calculation, any difference in the power transferred by the potential divider arrangement over the arrangement in (b).
- 20N.2.HL.TZ0.5a: Outline why component X is considered non-ohmic.
-
18M.2.SL.TZ1.5b:
Calculate, in N, the magnitude of the magnetic force acting on the electron.
-
17M.2.SL.TZ1.4b:
Explain, in terms of electrons, what happens to the resistance of the cable as the temperature of the cable increases.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.4c:
Cell X is replaced by a second cell of identical emf E but with internal resistance 2.0 Ω. Comment on the length of AC for which the current in the second cell is zero.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.4c.i:
Determine the electric field strength E.
-
19M.1.SL.TZ1.23:
A beam of negative ions flows in the plane of the page through the magnetic field due to two bar magnets.
What is the direction in which the negative ions will be deflected?
A. Out of the page
B. Into the page X
C. Up the page ↑
D. Down the page ↓
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.8c:
The electron is replaced by a proton which is also released from rest at X. Compare, without calculation, the motion of the electron with the motion of the proton after release. You may assume that no frictional forces act on the electron or the proton.
-
19M.2.SL.TZ2.4bii:
The switch is now closed. Deduce the ratio .
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.5b(i):
Determine the resistance of the variable resistor.
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.20: A cell is connected in series with a resistor and supplies a current of 4.0 A for a time of...
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.4a.iii:
Calculate the power dissipated in the cable.
-
18N.1.SL.TZ0.18:
Two copper wires X and Y are connected in series. The diameter of Y is double that of X. The drift speed in X is v. What is the drift speed in Y?
A.
B.
C. 2v
D. 4v
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.21: An electron travelling at speed v perpendicular to a magnetic field of strength B experiences...
- 18M.1.SL.TZ2.20: An electron enters the region between two charged parallel plates initially moving parallel...
- 18M.1.SL.TZ2.21: A beam of electrons moves between the poles of a magnet. ...
-
18M.2.SL.TZ2.4b.ii:
Determine E.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.6b.ii:
Calculate the peak current in the cable.
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.35: A capacitor of capacitance 1.0 μF stores a charge of 15 μC. The capacitor is discharged...
-
22M.2.SL.TZ2.4a:
Identify the laws of conservation that are represented by Kirchhoff’s circuit laws.
-
22M.2.SL.TZ2.4e.i:
A fully charged cell of emf 6.0 V delivers a constant current of 5.0 A for a time of 0.25 hour until it is completely discharged.
The cell is then re-charged by a rectangular solar panel of dimensions 0.40 m × 0.15 m at a place where the maximum intensity of sunlight is 380 W m−2.
The overall efficiency of the re-charging process is 18 %.
Calculate the minimum time required to re-charge the cell fully.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.4c.i:
Calculate the reading on the voltmeter.
-
20N.1.SL.TZ0.18:
A metal wire has free charge carriers per unit volume. The charge on the carrier is . What additional quantity is needed to determine the current per unit area in the wire?
A. Cross-sectional area of the wire
B. Drift speed of charge carriers
C. Potential difference across the wire
D. Resistivity of the metal
-
20N.1.SL.TZ0.21:
Four resistors of each are connected as shown.
What is the effective resistance between P and Q?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
20N.1.SL.TZ0.19:
An electric motor raises an object of weight through a vertical distance of in . The current in the electric motor is at a potential difference of . What is the efficiency of the electric motor?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.6b.i:
Calculate the radius of each wire.
-
17N.2.SL.TZ0.3a.ii:
The film must dissipate a power less than 1500 W from each square metre of its surface to avoid damage. Calculate the maximum allowable current for the resistor.
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.16:
What is the relationship between the resistivity of a uniform wire, the radius of the wire and the length of the wire when its resistance is constant?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.4b:
Calculate the drift speed v of the electrons in the conductor in cm s–1.
-
16N.1.SL.TZ0.21:
A wire carrying a current is at right angles to a uniform magnetic field of strength B. A magnetic force F is exerted on the wire. Which force acts when the same wire is placed at right angles to a uniform magnetic field of strength 2B when the current is ?
A.
B.
C. F
D. 2F
-
18M.2.SL.TZ1.4b:
Calculate the drift speed v of the electrons in the conductor in cm s–1. State your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.15:
A cell of electromotive force (emf) and zero internal resistance is in the circuit shown.
What is correct for loop WXYUW?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
19N.1.HL.TZ0.31:
The force acting between two point charges is when the separation of the charges is . What is the force between the charges when the separation is increased to ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.17:
A power station generates of power at a potential difference of . The energy is transmitted through cables of total resistance .
What is the power loss in the cables?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.8c(i):
Calculate the electric potential difference between points A and B.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.4c.ii:
Show that .
-
21M.2.SL.TZ1.3d.i:
Show that each resistor has a resistance of about 30 Ω.
- 21M.2.SL.TZ1.3d.ii: Calculate the power transferred by the heater when both switches are closed.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8c.ii:
Calculate, in A, the average current during the discharge.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.4b.ii:
Determine E.
- 20N.2.SL.TZ0.5a: Outline why component X is considered non-ohmic.
-
20N.2.SL.TZ0.5c(i):
State the range of current that the ammeter can measure as the slider S of the potential divider is moved from Q to P.
-
20N.2.SL.TZ0.5b(i):
Determine the resistance of the variable resistor.
-
20N.2.SL.TZ0.5c(ii):
Describe, by reference to your answer for (c)(i), the advantage of the potential divider arrangement over the arrangement in (b).
-
20N.2.SL.TZ0.5b(ii):
Calculate the power dissipated in the circuit.
-
17M.2.SL.TZ1.4a.ii:
Calculate the resistance of the cable.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.3b.ii:
The charge on the ball is 1.2 × 10−6 C. Determine σ.
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.2b:
Calculate the maximum number of lamps that can be connected between the rods. Neglect the resistance of the rods.
-
21M.2.SL.TZ2.6a:
Explain why the output potential difference to the external circuit and the output emf of the photovoltaic cell are different.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.8c.ii:
An electron is emitted from the photoelectric surface with kinetic energy 2.1 eV. Calculate the speed of the electron at the collecting plate.
- 21M.1.SL.TZ1.18: Two charges Q1 and Q2, each equal to 2 nC, are separated by a distance 3 m in a vacuum. What...
- 21M.1.SL.TZ1.19: Two conductors S and T have the V/I characteristic graphs shown below. When the conductors...
- 21M.1.SL.TZ1.21: A long straight vertical conductor carries a current I upwards. An electron moves...
- 21M.1.SL.TZ2.19: An ion moves in a circle in a uniform magnetic field. Which single change would increase...
-
21M.1.SL.TZ2.18:
The diagram shows two cylindrical wires, X and Y. Wire X has a length , a diameter , and a resistivity . Wire Y has a length , a diameter of and a resistivity of .
What is ?
A. 4
B. 2
C. 0.5
D. 0.25
- 21M.1.SL.TZ2.20: In the circuits shown, the cells have the same emf and zero internal resistance. All...
-
21M.1.SL.TZ2.21:
Three identical resistors of resistance R are connected as shown to a battery with a potential difference of and an internal resistance of . A voltmeter is connected across one of the resistors.
What is the reading on the voltmeter?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 21M.1.SL.TZ2.22: Magnetic field lines are an example of A. a discovery that helps us understand...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.17:
A circuit contains a variable resistor of maximum resistance R and a fixed resistor, also of resistance R, connected in series. The emf of the battery is and its internal resistance is negligible.
What are the initial and final voltmeter readings when the variable resistor is increased from an initial resistance of zero to a final resistance of R?
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.18: An electron enters the space inside a current-carrying solenoid. The velocity of the electron...
- 21M.1.SL.TZ1.20: For a real cell in a circuit, the terminal potential difference is at its closest to the emf...
-
21M.2.SL.TZ2.3c:
The centre of the ball, still carrying a charge of , is now placed from a point charge Q. The charge on the ball acts as a point charge at the centre of the ball.
P is the point on the line joining the charges where the electric field strength is zero.
The distance PQ is .Calculate the charge on Q. State your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
19N.2.SL.TZ0.5a:
Show that the electric field strength due to the point charge at the position of the electron is 3.4 × 108 N C–1.
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.15:
Two wires, X and Y, are made from the same metal. The wires are connected in series. The radius of X is twice that of Y. The carrier drift speed in X is vX and in Y it is vY.
What is the value of the ratio ?A. 0.25
B. 0.50
C. 2.00
D. 4.00
-
17N.2.SL.TZ0.3a.i:
The resistance of the carbon film is 82 Ω. The resistivity of carbon is 4.1 x 10–5 Ω m. Calculate the length l of the film.
-
21M.2.SL.TZ2.3b.ii:
The charge on the ball is 1.2 × 10−6 C. Determine σ.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.3d.i:
Calculate the charge on Q. State your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
18N.2.SL.TZ0.2b:
Calculate the maximum number of lamps that can be connected between the rods. Neglect the resistance of the rods.
-
18M.2.SL.TZ2.4a:
State what is meant by the emf of a cell.
-
17M.2.SL.TZ1.4c:
The heater changes the temperature of the water by 35 K. The specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J kg–1 K–1.
Determine the rate at which water flows through the shower. State an appropriate unit for your answer.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.7a.ii:
Determine the total resistance of the lamps when they are working normally.
-
19M.2.SL.TZ1.1a.i:
Show that the time taken for the battery to discharge is about 3 × 103 s.
- 18M.1.SL.TZ1.19: A liquid that contains negative charge carriers is flowing through a square pipe with sides...
-
18M.2.SL.TZ1.5a:
State the direction of the magnetic field.
- 17M.2.SL.TZ2.5a: The copper wires and insulator are both exposed to an electric field. Discuss, with reference...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.4a:
Calculate the resistance of the conductor.
- 17M.1.SL.TZ2.18: The diagram shows two equal and opposite charges that are fixed in place. At which points...
- 18M.1.SL.TZ1.20: Five resistors of equal resistance are connected to a cell as shown. ...
-
18M.1.HL.TZ1.15:
An ion of charge +Q moves vertically upwards through a small distance s in a uniform vertical electric field. The electric field has a strength E and its direction is shown in the diagram.
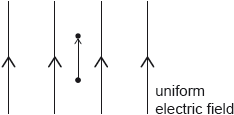
What is the electric potential difference between the initial and final position of the ion?
A.
B. EQs
C. Es
D.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.9c.i:
Show that the speed v of an electron in the hydrogen atom is related to the radius r of the orbit by the expression
where k is the Coulomb constant.
-
18M.1.SL.TZ1.21:
Two resistors X and Y are made of uniform cylinders of the same material. X and Y are connected in series. X and Y are of equal length and the diameter of Y is twice the diameter of X.
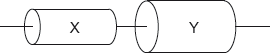
The resistance of Y is R.
What is the resistance of this series combination?
A.
B.
C. 3R
D. 5R
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.4a:
The switch S is initially open. Calculate the total power dissipated in the circuit.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.4bii:
The switch is now closed. .
-
21M.2.SL.TZ2.6b:
Calculate the internal resistance of the photovoltaic cell for the maximum intensity condition using the model for the cell.
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.18: Two parallel wires carry equal currents in the same direction out of the paper. Which diagram...
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.5d.i:
Show that the energy dissipated in the loop from t = 0 to t = 3.5 s is 0.13 J.
-
21N.2.SL.TZ0.4a:
The work done to move a particle of charge 0.25 μC from one point in an electric field to another is 4.5 μJ. Calculate the magnitude of the potential difference between the two points.
-
21N.2.SL.TZ0.4b.i:
Determine the force on Q at the instant it is released.
- 21N.2.SL.TZ0.4c.i: On the diagram draw an arrow to show the direction of the magnetic field at Q due to wire X...
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.3a.i:
Show that the magnitude of the resultant electric field at P is 3 MN C−1
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.5c.ii:
The resistance of the loop is 2.4 Ω. Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic force on the loop as it enters the region of magnetic field.
-
22M.2.SL.TZ1.4b:
The voltmeter reads zero. Determine the resistance of S.
-
22M.2.SL.TZ1.4c.ii:
Outline, without calculation, the change in the total power dissipated in Q and the new cylinder after it has been reshaped.
-
22M.2.SL.TZ1.4a:
Calculate the potential difference across P.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.7c.ii:
Deduce whether the motion of Z is simple harmonic.
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.19: The coil of a direct current electric motor is turning with a period T. At t = 0 the coil is...
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.4a:
Identify the laws of conservation that are represented by Kirchhoff’s circuit laws.


