| Date | May 2017 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 17M.1.SL.TZ1.19 |
| Level | Standard level | Paper | Paper 1 | Time zone | 1 |
| Command term | Question number | 19 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
An electron is accelerated through a potential difference of 2.5 MV. What is the change in kinetic energy of the electron?
A. 0.4μJ
B. 0.4 nJ
C. 0.4 pJ
D. 0.4 fJ
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
Syllabus sections
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.16:
Two parallel plates are a distance apart with a potential difference between them. A point charge moves from the negatively charged plate to the positively charged plate. The charge gains kinetic energy W. The distance between the plates is doubled and the potential difference between them is halved. What is the kinetic energy gained by an identical charge moving between these plates?
A.
B. W
C. 2W
D. 4W
- 22M.1.SL.TZ2.19: A charge Q is at a point between two electric charges Q1 and Q2. The net electric force on...
- 22M.2.HL.TZ1.7c.i: Identify the direction of the resultant force acting on Z as it oscillates.
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.9a.ii: Show that the energy E of each electron in the beam is about 7 × 10−11 J.
- 17M.1.SL.TZ2.19: A wire has variable cross-sectional area. The cross-sectional area at Y is double that at...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.15: Positive charge is uniformly distributed on a semi-circular plastic rod. What is the...
-
22M.1.SL.TZ1.19:
P and Q are two opposite point charges. The force F acting on P due to Q and the electric field strength E at P are shown.
Which diagram shows the force on Q due to P and the electric field strength at Q?
- 22M.1.SL.TZ1.20: Three point charges of equal magnitude are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle....
-
22M.1.SL.TZ1.22:
Two cylinders, X and Y, made from the same material, are connected in series.
The cross-sectional area of Y is twice that of X. The drift speed of the electrons in X is and in Y it is .
What is the ratio ?
A. 4
B. 2
C. 1
D.
- 21N.2.SL.TZ0.4b.ii: Describe the motion of Q after release.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.3a.ii: State the direction of the resultant electric field at P.
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.15: Two pulses are travelling towards each other. What is a possible pulse shape when the...
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.1c.i:
Outline why the ions are likely to spread out.
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.30:
Two point charges Q1 and Q2 are one metre apart. The graph shows the variation of electric potential V with distance from Q1.
What is ?
A.
B.
C. 4
D. 16
-
18N.2.SL.TZ0.1c.i:
Outline why the ions are likely to spread out.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ2.16:
Four particles, two of charge +Q and two of charge −Q, are positioned on the -axis as shown. A particle P with a positive charge is placed on the -axis. What is the direction of the net electrostatic force on this particle?
- 18N.2.SL.TZ0.2c: One advantage of this system is that if one lamp fails then the other lamps in the...
- 19N.1.SL.TZ0.17: A negatively charged particle in a uniform gravitational field is positioned mid-way between...
- 19N.1.SL.TZ0.18: A thin copper wire and a thick copper wire are connected in series to an electric cell. Which...
-
19M.1.SL.TZ2.18:
A particle with a charge ne is accelerated through a potential difference V.
What is the magnitude of the work done on the particle?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 19M.1.SL.TZ1.22: Charge flows through a liquid. The charge flow is made up of positive and negative ions. In...
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.31: A proton of velocity v enters a region of electric and magnetic fields. The proton is not...
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.8a: Outline what is meant by electric field strength.
-
21N.1.SL.TZ0.18:
A charge +Q and a charge −2Q are a distance 3x apart. Point P is on the line joining the charges, at a distance x from +Q.
The magnitude of the electric field produced at P by the charge +Q alone is .
What is the total electric field at P?
A. to the rightB. to the left
C. to the right
D. to the left
- 16N.1.SL.TZ0.18: A –5µC charge and a +10µC charge are a fixed distance apart. Where can the electric field...
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.18: The graph shows the variation of current with potential difference for a filament...
-
17M.1.HL.TZ1.17:
Electrons, each with a charge e, move with speed v along a metal wire. The electric current in the wire is I.
Plane P is perpendicular to the wire. How many electrons pass through plane P in each second?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.2d: Satellite X must release ions into the space between the satellites. Explain why the current...
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.8b: An electron is placed at X and released from rest. Draw, on the diagram, the direction of the...
- 19M.1.SL.TZ2.2: What is the unit of electrical potential difference expressed in fundamental SI units? A. kg...
-
19N.2.SL.TZ0.5b(i):
Calculate the magnitude of the initial acceleration of the electron.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.4c.i:
Determine the electric field strength E.
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.8c:
The electron is replaced by a proton which is also released from rest at X. Compare, without calculation, the motion of the electron with the motion of the proton after release. You may assume that no frictional forces act on the electron or the proton.
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.20: A cell is connected in series with a resistor and supplies a current of 4.0 A for a time of...
-
18N.1.SL.TZ0.18:
Two copper wires X and Y are connected in series. The diameter of Y is double that of X. The drift speed in X is v. What is the drift speed in Y?
A.
B.
C. 2v
D. 4v
- 18M.1.SL.TZ2.20: An electron enters the region between two charged parallel plates initially moving parallel...
-
20N.1.SL.TZ0.18:
A metal wire has free charge carriers per unit volume. The charge on the carrier is . What additional quantity is needed to determine the current per unit area in the wire?
A. Cross-sectional area of the wire
B. Drift speed of charge carriers
C. Potential difference across the wire
D. Resistivity of the metal
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.4b:
Calculate the drift speed v of the electrons in the conductor in cm s–1.
-
18M.2.SL.TZ1.4b:
Calculate the drift speed v of the electrons in the conductor in cm s–1. State your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
19N.1.HL.TZ0.31:
The force acting between two point charges is when the separation of the charges is . What is the force between the charges when the separation is increased to ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.8c(i):
Calculate the electric potential difference between points A and B.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.4c.ii:
Show that .
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8c.ii:
Calculate, in A, the average current during the discharge.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.3b.ii:
The charge on the ball is 1.2 × 10−6 C. Determine σ.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.8c.ii:
An electron is emitted from the photoelectric surface with kinetic energy 2.1 eV. Calculate the speed of the electron at the collecting plate.
- 21M.1.SL.TZ1.18: Two charges Q1 and Q2, each equal to 2 nC, are separated by a distance 3 m in a vacuum. What...
-
21M.2.SL.TZ2.3c:
The centre of the ball, still carrying a charge of , is now placed from a point charge Q. The charge on the ball acts as a point charge at the centre of the ball.
P is the point on the line joining the charges where the electric field strength is zero.
The distance PQ is .Calculate the charge on Q. State your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
19N.2.SL.TZ0.5a:
Show that the electric field strength due to the point charge at the position of the electron is 3.4 × 108 N C–1.
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.15:
Two wires, X and Y, are made from the same metal. The wires are connected in series. The radius of X is twice that of Y. The carrier drift speed in X is vX and in Y it is vY.
What is the value of the ratio ?A. 0.25
B. 0.50
C. 2.00
D. 4.00
-
21M.2.SL.TZ2.3b.ii:
The charge on the ball is 1.2 × 10−6 C. Determine σ.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.3d.i:
Calculate the charge on Q. State your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
19M.2.SL.TZ1.1a.i:
Show that the time taken for the battery to discharge is about 3 × 103 s.
- 17M.2.SL.TZ2.5a: The copper wires and insulator are both exposed to an electric field. Discuss, with reference...
- 17M.1.SL.TZ2.18: The diagram shows two equal and opposite charges that are fixed in place. At which points...
-
18M.1.HL.TZ1.15:
An ion of charge +Q moves vertically upwards through a small distance s in a uniform vertical electric field. The electric field has a strength E and its direction is shown in the diagram.
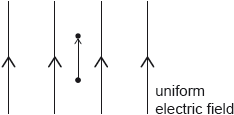
What is the electric potential difference between the initial and final position of the ion?
A.
B. EQs
C. Es
D.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.9c.i:
Show that the speed v of an electron in the hydrogen atom is related to the radius r of the orbit by the expression
where k is the Coulomb constant.
-
21N.2.SL.TZ0.4a:
The work done to move a particle of charge 0.25 μC from one point in an electric field to another is 4.5 μJ. Calculate the magnitude of the potential difference between the two points.
-
21N.2.SL.TZ0.4b.i:
Determine the force on Q at the instant it is released.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.3a.i:
Show that the magnitude of the resultant electric field at P is 3 MN C−1
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.7c.ii:
Deduce whether the motion of Z is simple harmonic.


