DP Chemistry Questionbank

4.2 Covalent bonding
Description
[N/A]Directly related questions
-
16N.3.sl.TZ0.6c:
(i) Suggest why incomplete combustion of plastic, such as polyvinyl chloride, is common in industrial and house fires.
(ii) Phthalate plasticizers such as DEHP, shown below, are frequently used in polyvinyl chloride.
With reference to bonding, suggest a reason why many adults have measurable levels of phthalates in their bodies.
- 16N.1.hl.TZ0.11: How many electrons form the carbon–oxygen bond in methanal, HCHO? A. 2 B. 4 C. 8 D. 12
- 16N.3.sl.TZ0.3b: Predict the predominant type of bonding for a binary compound AB in which the electronegativity...
-
17M.2.sl.TZ1.2e.ii:
A chloride of titanium, TiCl4, melts at 248 K. Suggest why the melting point is so much lower than that of KCl.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.6a:
Determine the type of bond present in SbBr3, showing your method. Use sections 8 and 29 of the data booklet.
- 17M.1.sl.TZ1.10: Which two atoms form the most polar bond? A. C and F B. C and Cl C. Si and F D. ...
-
17M.1.sl.TZ2.10:
Which bonds cause the boiling point of water to be significantly greater than that of hydrogen sulfide?
A. London (dispersion)
B. Covalent
C. Ionic
D. Hydrogen
- 17M.1.sl.TZ2.9: How many bonding electrons are there in the urea molecule? A. 8 B. 16 C. 20 D....
-
17M.2.sl.TZ2.4a.i:
State and explain the difference in bond strength between the nitrogen atoms in a hydrazine and nitrogen molecule.
-
20N.1.hl.TZ0.9:
Which of these species contains the shortest carbon to oxygen bond length?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
17N.1.sl.TZ0.10:
Which compound has the shortest C–N bond?
A. CH3NH2
B. (CH3)3CNH2
C. CH3CN
D. CH3CHNH
- 17N.1.sl.TZ0.9: The electronegativity values of four elements are given. What is the order of increasing...
-
21M.1.sl.TZ1.10:
Which compound contains both ionic and covalent bonds?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 21M.1.sl.TZ2.12: Which is the correct order based on increasing strength? A. covalent bonds < hydrogen bonds...
-
21M.1.sl.TZ2.10:
Which compound has the shortest C to N bond?
A. HCN
B. CH3CH2NH2
C. CH3CHNH
D. (CH3)2NH
- 21M.2.sl.TZ1.1c(iv): Suggest why chemists find it convenient to classify bonding into ionic, covalent and metallic.
- 21M.2.hl.TZ1.1d(v): Suggest why chemists find it convenient to classify bonding into ionic, covalent and metallic.
- 18M.1.sl.TZ2.10: Which species has the longest carbon to oxygen bond length? A. CO B. CH3OH C. ...
-
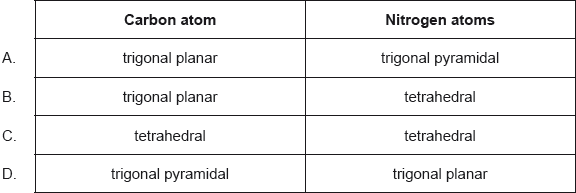
18M.1.sl.TZ2.11:
What are the predicted electron domain geometries around the carbon and both nitrogen atoms in urea, (NH2)2CO, applying VSEPR theory?
-
18M.2.sl.TZ2.6a.i:
Explain why the hydrides of group 16 elements (H2O, H2S, H2Se and H2Te) are polar molecules.
-
18M.2.sl.TZ2.6a.ii:
The graph shows the boiling points of the hydrides of group 16 elements.
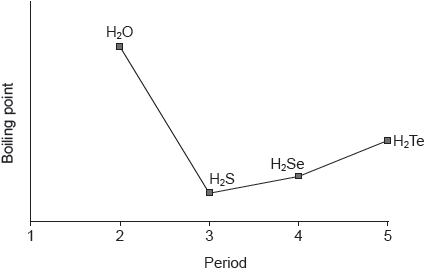
Explain the increase in the boiling point from H2S to H2Te.
- 21N.1.sl.TZ0.9: Which molecule has the weakest nitrogen to nitrogen bond? A. N2 B. N2H2 C. N2H4 D.
- 21N.1.sl.TZ0.11: Which compound contains both ionic and covalent bonds? A. CH3COONa B. CH3COOH C. K2O D. ...
- 21N.2.hl.TZ0.3b(ii): Outline the reason why PCl5 is a non-polar molecule, while PCl4F is polar.
- 22M.1.sl.TZ1.10: What is the explanation for the high melting point of sodium chloride? A. The covalent bond...
- 22M.1.hl.TZ2.9: In which of the following compounds does ionic bonding predominate? A. HCl B. NaF C. ...
- 22M.2.sl.TZ2.4a(i): Outline one difference between the bonding of carbon atoms in C60 and diamond.
-
22M.2.hl.TZ2.8a(i):
Outline two differences between the bonding of carbon atoms in C60 and diamond.
-
22M.2.hl.TZ2.8a(ii):
Explain why C60 and diamond sublime at different temperatures and pressures.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ2.1b(ii):
Compare, giving a reason, the length of the bond between the carbon atoms in ethyne with that in ethane, C2H6.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ2.5d(i):
Identify the type of bonding in sodium hydrogencarbonate.
Between sodium and hydrogencarbonate:
Between hydrogen and oxygen in hydrogencarbonate:
-
19M.2.sl.TZ2.1b(ii):
Compare, giving a reason, the length of the bond between the carbon atoms in ethyne with that in ethane, C2H6.
-
19M.2.sl.TZ2.5b(iii):
Identify the type of bonding in sodium hydrogencarbonate.
Between sodium and hydrogencarbonate:
Between hydrogen and oxygen in hydrogencarbonate:
- 19N.2.hl.TZ0.1c: Predict the bond angle in the ozone molecule.
- 19N.2.sl.TZ0.1d: Discuss how the different bond strengths between the oxygen atoms in O2 and O3 in the ozone layer...
- 19N.1.sl.TZ0.10: Which compound has the shortest C to O bond? A. CH3CHO B. CO C. CO2 D. C2H5OC2H5
-
19N.3.sl.TZ0.5b(i):
Determine the percentage of ionic bonding in alumina using sections 8 and 29 of the data booklet.
- 19N.2.hl.TZ0.1a: Draw the Lewis structures of oxygen, O2, and ozone, O3.
- 19N.2.hl.TZ0.1d: Discuss how the different bond strengths between the oxygen atoms in O2 and O3 in the ozone layer...
- 19N.2.hl.TZ0.1b: Outline why both bonds in the ozone molecule are the same length and predict the bond length in...
- 19N.2.sl.TZ0.1b: Outline why both bonds in the ozone molecule are the same length and predict the bond length in...
