| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 18M.2.sl.TZ2.6 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Explain | Question number | 6 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Some physical properties of molecular substances result from the different types of forces between their molecules.
Explain why the hydrides of group 16 elements (H2O, H2S, H2Se and H2Te) are polar molecules.
The graph shows the boiling points of the hydrides of group 16 elements.
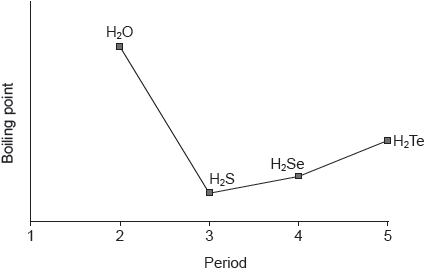
Explain the increase in the boiling point from H2S to H2Te.
Lewis structures show electron domains and are used to predict molecular geometry.
Deduce the electron domain geometry and the molecular geometry for the NH2− ion.
Markscheme
polar bonds «between H and group 16 element»
OR
difference in electronegativities «between H and group 16 element»
uneven distribution of charge/electron cloud
OR
non-linear/bent/V-shaped/angular shape «due to lone pairs»
OR
polar bonds/dipoles do not cancel out
M2:
Do not accept “net/overall dipole moment” without further explanation.
Accept “non-symmetrical «shape/distribution of charge»”.
[2 marks]
number of electrons increases
London/dispersion/instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole forces increase
M1: Accept “Mr/Ar increases” or “molecules become larger in size/mass/surface area”.
[2 marks]
Electron domain geometry:
tetrahedral
Molecular geometry:
bent/V-shaped/angular
Both marks can be awarded for clear diagrams. Electron domain geometry requires a 3-D diagram showing the tetrahedral arrangement.
[2 marks]