| Date | November 2019 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 19N.3.hl.TZ0.14 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | State | Question number | 14 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Changes in physiology can impact living creatures.
The graph shows the change in oxygen partial pressure in blood, measured at different pH values.
Explain the effect of changing pH on the percentage saturation of hemoglobin at a given partial pressure of oxygen.
Explain the biomagnification of the pesticide DDT.
Vitamins are organic compounds essential in small amounts.
State the name of one functional group common to all three vitamins shown in section 35 of the data booklet.
Markscheme
as pH decreases, protons/CO2 bind to allosteric sites
OR
as pH decreases, protons/CO2 act as non-competitive inhibitor
OR
active/binding site changes shape ✔
saturation decreases
OR
more oxygen released
OR
affinity to oxygen decreases ✔
accumulates in fat/tissues/living organisms
OR
cannot be metabolized/does not break down «in living organisms»
OR
not excreted / excreted «very» slowly ✔
passes «unchanged» up the food chain
OR
increased concentration as one species feeds on another «up the food chain» ✔
NOTE: Accept “lipids” for “fat”.
hydroxyl ✔
NOTE: Accept “hydroxy” but not “hydroxide”.
Accept “alkenyl”.
Do not accept formula.
Examiners report
Syllabus sections
- 18M.1.sl.TZ1.24: What are possible names of a molecule with molecular formula C4H10O? I. ...
- 22M.1.sl.TZ1.24: Which functional groups are present in serine? A. nitro, carbonyl and carboxyl B. ...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ2.24: Which compounds belong to the same homologous series? A. CHCCH2CH3, CHCCH2CH2CH3 B. ...
-
22M.2.hl.TZ1.5a(i):
State the name of Compound B, applying International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) rules.
- 22M.2.hl.TZ1.5b(i): Draw the structural formula of the alkene required.
- 17N.1.sl.TZ0.28: How many structural isomers of C6H14 exist? A. 4 B. 5 C. 6 D. 7
-
16N.3.sl.TZ0.9b:
The structures of two molecules, X and Y, are shown below.
(i) Justify why both these molecules are carbohydrates.
(ii) Distinguish between these molecules in terms of their functional groups.
- 22M.2.sl.TZ1.3d(i): Draw the structural formula of the alkene required.
- 19N.2.sl.TZ0.3e: Ethene is often polymerized. Draw a section of the resulting polymer, showing two repeating...
- 17N.1.sl.TZ0.26: What is the name of this compound, using IUPAC rules? A. 3-methylbutan-3-ol B....
- 16N.2.sl.TZ0.1b: Determine the average oxidation state of carbon in ethene and in...
- 22M.1.sl.TZ2.24: How many dichlorinated butane isomers can be formed by the halogenation of CH3CH2CH2CH3 with...
- 17M.1.sl.TZ1.24: What is the order of increasing boiling point? A. C4H10 < CH3COOH < CH3CH2CHO <...
-
17M.3.sl.TZ2.10a:
Identify the functional groups which are present in only one structure of glucose.
- 18M.1.hl.TZ1.34: Which is a secondary alcohol?
- 16N.2.sl.TZ0.5a: Draw the full structural formulas of propane and propene.
-
17M.2.sl.TZ1.5d:
Chloroethene, C2H3Cl, can undergo polymerization. Draw a section of the polymer with three repeating units.
- 17M.1.hl.TZ2.36: Which compounds can be reduced? I. C2H4II. CH3COOHIII. CH3CHO A. I and II...
- 16N.1.sl.TZ0.23: The structure of a drug used to treat symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease is shown below. Which...
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.6b:
The overall equation for monochlorination of methane is:
CH4(g) + Cl2(g) → CH3Cl(g) + HCl(g)
Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the reaction, ΔH θ, using section 12 of the data booklet.
-
19N.3.hl.TZ0.10a:
Draw the structure of the dipeptide Asp–Phe using section 33 of the data booklet.
- 19N.3.hl.TZ0.15c: Explain why maltose, C12H22O11, is soluble in water.
-
18M.2.hl.TZ2.9a.i:
Deduce the structural formulas of the two possible isomers.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.10b.ii:
Explain why the difference in their structures affects their melting points.
-
18M.2.hl.TZ1.7c.iii:
Deduce the name of the class of compound formed when the product of (c)(i) reacts with butanoic acid.
- 18M.1.sl.TZ2.27: Which are structural isomers? I. CH3CH2OH and CH3OCH3 II. HOCH2CH3...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ2.25: What is the name of this compound, using IUPAC rules? A. 1,1-dimethylpropanoic...
- 22M.2.hl.TZ2.8b: State two features showing that propane and butane are members of the same homologous series.
- 18N.1.sl.TZ0.26: Which is correct for benzene? A. It readily undergoes addition reactions and...
-
18N.2.hl.TZ0.2d:
The compound could not be oxidized using acidifi ed potassium dichromate(VI).
Deduce the structural formula of the compound.
- 18N.2.sl.TZ0.2c: Classify propan-2-ol as a primary, secondary or tertiary alcohol, giving a reason.
-
18N.2.sl.TZ0.2a:
Draw the structural formula of propan-2-ol.
-
18N.2.hl.TZ0.8b.i:
Draw two structural isomers of methyloxirane.
- 17M.1.sl.TZ1.26: What is the name of the compound with this molecular structure applying IUPAC rules? A. ...
-
16N.1.sl.TZ0.24:
Which alcohols are oxidized by acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution when heated?
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
- 19N.3.sl.TZ0.10c: Explain why maltose, C12H22O11, is soluble in water.
- 19N.3.sl.TZ0.10a: State the name of one functional group common to all three vitamins shown in section 35 of...
-
19N.2.sl.TZ0.3d(ii):
Explain why the compound C2H6O, produced in (b), has a higher boiling point than compound C2H4O, produced in d(i).
- 19M.1.hl.TZ1.32: What is the IUPAC name of the following molecule? A. 2-bromo-3-ethylbutane B....
- 19M.1.hl.TZ2.34: What is the name of this compound using IUPAC rules? A. 2,3-diethylbutane B....
-
17M.1.hl.TZ2.37:
In which order should the reagents be used to convert benzene into phenylamine (aniline)?
-
19M.2.hl.TZ1.2c:
Outline one piece of physical evidence for the structure of the benzene ring.
-
19M.2.sl.TZ1.1b:
Draw the structure of one other isomer of xylene which retains the benzene ring.
-
19M.3.sl.TZ1.5a:
State the name of the functional group which allows the molecule to be responsive to applied electric fields.
- 19M.1.sl.TZ1.24: Which functional group is surrounded in the molecule? A. hydroxyl B. carboxyl C....
- 19M.1.sl.TZ1.25: What is the IUPAC name of the following molecule? A. 2-bromo-3-ethylbutane B....
- 17N.1.hl.TZ0.38: Which functional group is responsible for the pKb of 4.1 in this compound? A. Amido B....
-
16N.3.sl.TZ0.20a:
Compare and contrast the functional groups present in methadone and diamorphine (heroin), giving their names. Use section 37 of the data booklet.
-
19M.1.sl.TZ2.24:
Which compound has the lowest boiling point?
A. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3
B. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
C. CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH3
D. CH3C(CH3)2CH3
-
19M.1.hl.TZ2.32:
Which compound has the lowest boiling point?
A. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3
B. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
C. CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH3
D. CH3C(CH3)2CH3
- 22M.1.sl.TZ1.25: Which compounds are members of the same homologous series? A. propanal, propanone,...
- 17M.1.sl.TZ2.24: Which functional group is present in paracetamol? A. Carboxyl B. Amino C. ...
- 17M.1.hl.TZ1.35: What is the major product of the reaction between 2-methylbut-2-ene and hydrogen bromide? A....
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.15b:
Deduce the formula of the biodiesel formed when the vegetable oil shown is reacted with the reagents in (a).
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.7c.i:
State the reagents and the name of the mechanism for the nitration of benzene.
-
17M.1.sl.TZ2.27:
Which compound contains a secondary carbon atom?
A. CH3CH(Cl)CH(CH3)2
B. (CH3)2CHCH2Cl
C. (CH3)3CCl
D. CH3CH2Cl
- 16N.3.sl.TZ0.10a: State the IUPAC name for leucine.
-
17M.1.sl.TZ1.27:
Which molecule has a tertiary nitrogen?
A. (CH3)2NH
B. (C2H5)4N+I−
C. C3H7N(CH3)2
D. C6H5NH2
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.7a.iii:
Suggest the structural formula of this compound.
-
17M.2.hl.TZ1.7c:
State the reagents used to convert benzene to nitrobenzene and the formula of the electrophile formed.
-
19N.3.sl.TZ0.7a:
Draw the structure of the dipeptide Asp–Phe using section 33 of the data booklet.
- 19N.3.sl.TZ0.9d(i): State one similarity and one difference in composition between phospholipids and...
- 19N.3.hl.TZ0.12c: State one similarity and one difference in composition between phospholipids and...
-
19N.2.hl.TZ0.3d(iii):
Explain why the 1H NMR spectrum of C3H6O, produced in (d)(i), shows only one signal.
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.9b.i:
Hydrogenation of propene produces propane. Calculate the standard entropy change, ΔS θ, for the hydrogenation of propene.
- 19N.2.hl.TZ0.3a(ii): State the IUPAC name of the major product.
- 19N.2.hl.TZ0.3e: Propene is often polymerized. Draw a section of the resulting polymer, showing two repeating...
- 19N.3.sl.TZ0.12b(i): Reforming reactions are used to increase the octane number of a hydrocarbon fuel. Suggest...
- 19N.3.sl.TZ0.12b(ii): The 1H NMR spectrum of one of the products has four signals. The integration trace shows a...
-
19N.3.hl.TZ0.24a:
Infrared (IR) spectroscopy is used to identify functional groups in organic compounds.
Deduce the wavenumber, in cm−1, of an absorption peak found in the IR spectrum of testosterone but not in that of cholesterol.
-
17M.3.hl.TZ2.3c.iii:
Subsequent steps proceed under differing conditions, forming the dendrimer polymer with the following repeating unit.
State the name of one functional group in this repeating unit.
-
19N.2.hl.TZ0.3d(ii):
Explain why the compound C3H8O, produced in (a)(iv), has a higher boiling point than compound C3H6O, produced in d(i).
-
17M.2.sl.TZ1.6b:
State the typical reactions that benzene and cyclohexene undergo with bromine.
-
17M.1.sl.TZ1.25:
What are the functional groups in the aspirin molecule?
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
-
17M.2.sl.TZ1.6a:
Discuss the physical evidence for the structure of benzene.
- 21M.1.sl.TZ2.25: What is the IUPAC name of the molecule shown? A. 2,4-dimethylhexane B. ...
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.7b.i:
Bromine was added to hexane, hex-1-ene and benzene. Identify the compound(s) which will react with bromine in a well-lit laboratory.
-
18N.1.sl.TZ0.25:
What is the order of increasing boiling point for the isomers of C5H12?
A. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 < CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH3 < CH3C(CH3)3
B. CH3C(CH3)3 < CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH3 < CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
C. CH3C(CH3)3 < CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 < CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH3
D. CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH3 < CH3C(CH3)3 < CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
-
19M.2.sl.TZ2.1c(ii):
State the name of product B, applying IUPAC rules.
-
18M.2.hl.TZ1.3d:
One possible Lewis structure for benzene is shown.
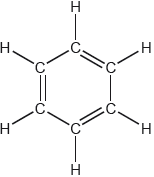
State one piece of physical evidence that this structure is incorrect.
-
17M.2.sl.TZ1.5a:
Ethane, C2H6, reacts with chlorine in sunlight. State the type of this reaction and the name of the mechanism by which it occurs.
-
20N.1.hl.TZ0.40:
Which compound with the molecular formula has this high resolution ?
From: libretexts.org. Courtesy of Chris Schaller, Professor (Chemistry)
at College of Saint Benedict/Saint John’s University.A. but-3-en-2-ol,
B. butanal,
C. butanone,
D. but-3-en-1-ol,
-
17M.2.sl.TZ2.6b:
Bromine was added to hexane, hex-1-ene and benzene. Identify the compound(s) which will react with bromine in a well-lit laboratory.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.10b.i:
Describe the difference in their structures.
- 19N.1.sl.TZ0.25: Which compound is not in the same homologous series as the others? A. C5H12 B. C6H12 C. ...
- 21N.1.sl.TZ0.26: Which pair of compounds are structural isomers? A. Propane and propene B. Propanal and...
- 21N.1.sl.TZ0.27: What is the general formula of alkynes? A. CnH2n+2 B. CnH2n C. CnH2n−2 D. CnHn
-
18M.3.sl.TZ2.2a:
Describe two differences, other than the number of atoms, between the models of ethane and ethene constructed from the kit shown.
- 19N.3.sl.TZ0.15a: State the names of two functional groups present in all three molecules, using section 37 of...
- 19N.3.sl.TZ0.9b: State one impact on health of the increase in LDL cholesterol concentration in blood.
-
20N.2.hl.TZ0.2e:
Compound A and B are isomers. Draw two other structural isomers with the formula .
- 20N.1.sl.TZ0.24: Which functional groups are present in this molecule? A. carbonyl, ether, nitrile B. ...
-
18M.3.sl.TZ2.2b.i:
The above ball and stick model is a substituted pyridine molecule (made of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, bromine and chlorine atoms). All atoms are shown and represented according to their relative atomic size.
Label each ball in the diagram, excluding hydrogens, as a carbon, C, nitrogen, N, bromine, Br, or chlorine, Cl.
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.2a.v:
Identify one organic functional group that can react with acidified K2Cr2O7(aq).
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.7a.ii:
Identify the functional group that shows stretching at 1710 cm–1 in the infrared spectrum of this compound using section 26 of the data booklet and the 1H NMR.
-
17M.2.hl.TZ1.6c.i:
One possible product, X, of the reaction of ethane with chlorine has the following composition by mass:
carbon: 24.27%, hydrogen: 4.08%, chlorine: 71.65%
Determine the empirical formula of the product.
- 20N.3.sl.TZ0.9b: State a class of organic compounds found in gasoline.
-
19N.3.hl.TZ0.24b:
Describe a technique for the detection of steroids in blood and urine.
- 20N.1.sl.TZ0.26: What is the IUPAC name of this molecule? A. 1,1,2,4-tetramethylpent-1-ene B. ...
-
22M.2.sl.TZ1.3c(i):
State the name of Compound A, applying International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) rules.
-
17M.3.hl.TZ2.20a.iii:
Suggest two absorbances, other than the absorbances due to the ring structure and C–H bonds, that would be present in the infrared (IR) spectrum of aspirin.
-
17M.2.sl.TZ1.5c.i:
One possible product, X, of the reaction of ethane with chlorine has the following composition by mass:
carbon: 24.27%, hydrogen: 4.08%, chlorine: 71.65%
Determine the empirical formula of the product.
-
20N.2.sl.TZ0.1d(v):
Ethoxyethane (diethyl ether) can be used as a solvent for this conversion. Draw the structural formula of ethoxyethane
-
19N.3.hl.TZ0.24c:
Explain how redox chemistry is used to measure the ethanol concentration in a breathalyser.
- 21M.1.sl.TZ1.25: What is the name of this compound, applying IUPAC rules? A. 4-methylhex-2-ene B. ...
-
18M.3.sl.TZ2.2b.iii:
Pyridine, like benzene, is an aromatic compound.
Outline what is meant by an aromatic compound.
- 20N.3.hl.TZ0.11b: State a class of organic compounds found in gasoline.
-
20N.3.hl.TZ0.11e(iii):
Suggest a wavenumber absorbed by methane gas.
- 21M.2.hl.TZ1.5a(ii): State the molecular formula of the next member of the homologous series to which ethene belongs.
- 21M.2.hl.TZ1.5a(i): State the class of compound to which ethene belongs.
- 21M.1.sl.TZ2.24: Which is in the same homologous series as CH3OCH3? A. CH3COCH3 B. CH3COOCH3 C. ...
-
21M.1.sl.TZ2.28:
Which spectra would show the difference between propan-2-ol, CH3CH(OH)CH3, and propanal, CH3CH2CHO?
I. mass
II. infrared
III. 1H NMRA. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
-
18M.2.sl.TZ2.7a:
The Kekulé structure of benzene suggests it should readily undergo addition reactions.
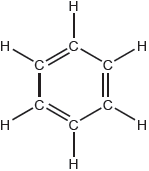
Discuss two pieces of evidence, one physical and one chemical, which suggest this is not the structure of benzene.
- 21M.2.sl.TZ1.5a(i): State the class of compound to which ethene belongs.
- 21M.2.sl.TZ1.5a(ii): State the molecular formula of the next member of the homologous series to which ethene belongs.
- 20N.2.sl.TZ0.4c: Discuss, referring to intermolecular forces present, the relative volatility of propanone and...
-
21M.2.sl.TZ2.4c:
Write the equation and name the organic product when ethanol reacts with methanoic acid.
-
20N.2.sl.TZ0.2c:
Compound A and B are isomers. Draw two other structural isomers with the formula .
-
17M.2.sl.TZ2.6a:
Using relevant equations, show the initiation and the propagation steps for this reaction.
-
20N.2.hl.TZ0.1d(iv):
Ethoxyethane (diethyl ether) can be used as a solvent for this conversion.
Draw the structural formula of ethoxyethane -
20N.2.hl.TZ0.2d:
The IR spectrum of one of the compounds is shown:
COBLENTZ SOCIETY. Collection © 2018 copyright by the U.S. Secretary of Commerce on behalf of the United States of America. All rights reserved.
Deduce, giving a reason, the compound producing this spectrum.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ1.1b:
Draw the structure of one other isomer of xylene which retains the benzene ring.
- 20N.2.hl.TZ0.4c: Discuss, referring to intermolecular forces present, the relative volatility of propanone and...
-
20N.2.sl.TZ0.2b:
The IR spectrum of one of the compounds is shown:
COBLENTZ SOCIETY. Collection © 2018 copyright by the U.S. Secretary of Commerce on behalf of the United States of America. All rights reserved.
Deduce, giving a reason, the compound producing this spectrum. -
20N.3.sl.TZ0.9f(iii):
Suggest a wavenumber absorbed by methane gas.
- 20N.3.sl.TZ0.14a(i): Name two functional groups that both zanamivir and oseltamivir contain.
-
22M.2.hl.TZ2.8d(iv):
Suggest two differences in the 1H NMR of but-2-ene and the organic product from (d)(ii).
-
22M.2.hl.TZ2.8e(ii):
Deduce the splitting pattern in the 1H NMR spectrum for 1-bromopropane.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ2.1c(ii):
Determine the enthalpy change for the reaction, in kJ, to produce A using section 11 of the data booklet.
- 22M.2.sl.TZ2.4b: State two features showing that propane and butane are members of the same homologous series.
- 22M.2.sl.TZ2.4d(i): Draw the full structural formula of but-2-ene.
-
22M.2.sl.TZ2.4d(iv):
Suggest two differences in the 1H NMR of but-2-ene and the organic product from (d)(ii).
-
17M.2.hl.TZ1.6c.ii:
The mass and 1H NMR spectra of product X are shown below. Deduce, giving your reasons, its structural formula and hence the name of the compound.
-
18M.2.sl.TZ1.3c:
One possible Lewis structure for benzene is shown.
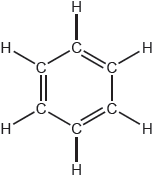
State one piece of physical evidence that this structure is incorrect.
-
17M.2.sl.TZ1.5c.ii:
The mass and 1HNMR spectra of product X are shown below. Deduce, giving your reasons, its structural formula and hence the name of the compound.
- 21M.1.sl.TZ1.24: Which series is in order of increasing boiling point? A. CH2CH2CH3OH CH3COCH3 ...
-
22M.1.sl.TZ2.26:
Which is a homologous series?
A. C2H4, C3H5, C4H6
B. C2H2, C3H4, C4H6
C. C2H2, C2H4, C2H6
D. C2H2, C4H4, C6H6
- 21N.1.sl.TZ0.25: What is the name of this substance using IUPAC rules? A. 2-ethyl-1-methylbutan-1-ol B. ...

