| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 18M.2.hl.TZ1.3 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | State | Question number | 3 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
This question is about ethene, C2H4, and ethyne, C2H2.
Ethyne, like ethene, undergoes hydrogenation to form ethane. State the conditions required.
Outline the formation of polyethene from ethene by drawing three repeating units of the polymer.
Ethyne reacts with chlorine in a similar way to ethene. Formulate equations for the following reactions.
Under certain conditions, ethyne can be converted to benzene.
Determine the standard enthalpy change, ΔHΘ, for the reaction stated, using section 11 of the data booklet.
3C2H2(g) → C6H6(g)
Determine the standard enthalpy change, ΔHΘ, for the following similar reaction, using ΔHf values in section 12 of the data booklet.
3C2H2(g) → C6H6(l)
Explain, giving two reasons, the difference in the values for (c)(i) and (ii). If you did not obtain answers, use −475 kJ for (i) and −600 kJ for (ii).
Calculate the standard entropy change, ΔSΘ, in J K−1, for the reaction in (ii) using section 12 of the data booklet.
Determine, showing your working, the spontaneity of the reaction in (ii) at 25 °C.
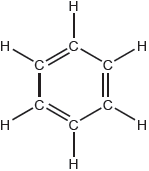
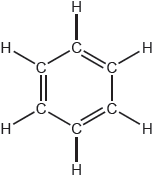
One possible Lewis structure for benzene is shown.
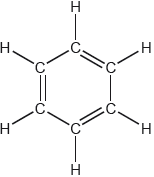
State one piece of physical evidence that this structure is incorrect.
Markscheme
nickel/Ni «catalyst»
high pressure
OR
heat
Accept these other catalysts: Pt, Pd, Ir, Rh, Co, Ti.
Accept “high temperature” or a stated temperature such as “150 °C”.
[2 marks]
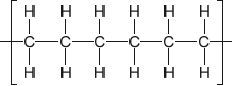
Ignore square brackets and “n”.
Connecting line at end of carbons must be shown.
[1 mark]
ethyne: C2H2 + Cl2 → CHClCHCl
benzene: C6H6 + Cl2 → C6H5Cl + HCl
Accept “C2H2Cl2”.
[2 marks]
ΔHΘ = bonds broken – bonds formed
«ΔHΘ = 3(C≡C) – 6(CC)benzene / 3 839 – 6 507 / 2517 – 3042 =» –525 «kJ»
Award [2] for correct final answer.
Award [1 max] for “+525 «kJ»”.
Award [1 max] for:
«ΔHΘ = 3(C≡C) – 3(C–C) – 3(C=C) / 3 839 – 3 346 – 3 614 / 2517 – 2880 =» –363 «kJ».
[2 marks]
ΔHΘ = ΣΔHf (products) – ΣΔHf (reactants)
«ΔHΘ = 49 kJ – 3 228 kJ =» –635 «kJ»
Award [2] for correct final answer.
Award [1 max] for “+635 «kJ»”.
[2 marks]
ΔHf values are specific to the compound
OR
bond enthalpy values are averages «from many different compounds»
condensation from gas to liquid is exothermic
Accept “benzene is in two different states «one liquid the other gas»” for M2.
[2 marks]
«ΔSΘ = 173 – 3 201 =» –430 «J K–1»
[1 mark]
T = «25 + 273 =» 298 «K»
ΔGϴ «= –635 kJ – 298 K × (–0.430 kJ K–1)» = –507 kJ
ΔGϴ < 0 AND spontaneous
ΔGϴ < 0 may be inferred from the calculation.
[3 marks]
equal C–C bond «lengths/strengths»
OR
regular hexagon
OR
«all» C–C have bond order of 1.5
OR
«all» C–C intermediate between single and double bonds
Accept “all C–C–C bond angles are equal”.
[1 mark]