| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 18M.2.SL.TZ2.4 |
| Level | Standard level | Paper | Paper 2 | Time zone | Time zone 2 |
| Command term | Show that | Question number | 4 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
The diagram shows a potential divider circuit used to measure the emf E of a cell X. Both cells have negligible internal resistance.
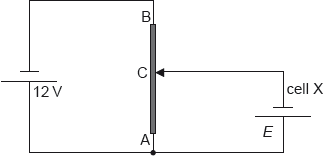
AB is a wire of uniform cross-section and length 1.0 m. The resistance of wire AB is 80 Ω. When the length of AC is 0.35 m the current in cell X is zero.
State what is meant by the emf of a cell.
Show that the resistance of the wire AC is 28 Ω.
Determine E.
Markscheme
the work done per unit charge
in moving charge from one terminal of a cell to the other / all the way round the circuit
Award [1] for “energy per unit charge provided by the cell”/“power per unit current”
Award [1] for “potential difference across the terminals of the cell when no current is flowing”
Do not accept “potential difference across terminals of cell”
[2 marks]
the resistance is proportional to length / see 0.35 AND 1«.00»
so it equals 0.35 × 80
«= 28 Ω»
[2 marks]
current leaving 12 V cell is \(\frac{{12}}{{80}}\) = 0.15 «A»
OR
E = \(\frac{{12}}{{80}}\) × 28
E = «0.15 × 28 =» 4.2 «V»
Award [2] for a bald correct answer
Allow a 1sf answer of 4 if it comes from a calculation.
Do not allow a bald answer of 4 «V»
Allow ECF from incorrect current
[2 marks]
Examiners report
Syllabus sections
- 18M.2.SL.TZ2.4b.ii: Determine E.
- 18M.2.HL.TZ2.4c: Cell X is replaced by a second cell of identical emf E but with internal resistance 2.0...
- 18M.1.SL.TZ2.19: A cell with negligible internal resistance is connected as shown. The ammeter and the...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.16: A cell of emf 6.0 V and negligible internal resistance is connected to three resistors as...
- 18M.2.SL.TZ1.4a: Calculate the resistance of the conductor.
- 18M.1.SL.TZ1.21: Two resistors X and Y are made of uniform cylinders of the same material. X and Y are...
- 18M.1.SL.TZ1.18: Three resistors are connected as shown. What is the value of the total resistance between X...
- 17N.2.SL.TZ0.3c: Draw a circuit diagram to show how you could measure the resistance of the carbon-film...
- 17N.2.SL.TZ0.3b: The current direction is now changed so that charge flows vertically through the...
- 17N.2.SL.TZ0.3a.iii: State why knowledge of quantities such as resistivity is useful to scientists.
- 17N.2.SL.TZ0.3a.ii: The film must dissipate a power less than 1500 W from each square metre of its surface to...
- 17N.2.SL.TZ0.3a.i: The resistance of the carbon film is 82 Ω. The resistivity of carbon is 4.1 x 10–5 Ω m....
- 17N.1.SL.TZ0.18: Kirchhoff’s laws are applied to the circuit shown. What is the equation for the dotted...
- 17N.1.SL.TZ0.17: In the circuit shown, the fixed resistor has a value of 3 Ω and the variable resistor can be...
- 17M.3.SL.TZ2.2a: An ammeter and a voltmeter are connected in the circuit. Label the ammeter with the letter A...
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.6b.iii: Determine the power dissipated in the cable per unit length.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.6b.ii: Calculate the peak current in the cable.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.6b.i: Calculate the radius of each wire.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.4a.iii: Calculate the power dissipated in the cable.
- 17M.2.SL.TZ2.5b.ii: There is a current of 730 A in the cable. Show that the power loss in 1 m of the cable is...
- 17M.2.SL.TZ1.4c: The heater changes the temperature of the water by 35 K. The specific heat capacity of water...
- 17M.2.SL.TZ1.4b: Explain, in terms of electrons, what happens to the resistance of the cable as the...
- 17M.2.SL.TZ1.4a.ii: Calculate the resistance of the cable.
- 17M.2.SL.TZ1.4a.i: Calculate the current in the copper cable.
- 17M.1.SL.TZ2.20: A circuit contains a cell of electromotive force (emf) 9.0 V and internal resistance 1.0 Ω...
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.15: Two pulses are travelling towards each other. What is a possible pulse shape when the...
- 16N.2.SL.TZ0.7b: Components R and T are placed in a circuit. Both meters are ideal. Slider Z of the...
- 16N.2.SL.TZ0.7a: (i) State how the resistance of T varies with the current going through T. (ii) Deduce,...
- 16M.2.HL.TZ0.6a: Two cells of negligible internal resistance are connected in a circuit. The top cell has...
- 16M.2.SL.TZ0.5a: State what is meant by an ideal voltmeter.
- 16M.2.SL.TZ0.1e: The electric motor is connected to a source of potential difference 120V and draws a current...
- 16N.1.SL.TZ0.20: A cell of emf 4V and negligible internal resistance is connected to three resistors as shown....
- 16N.1.SL.TZ0.19: An electrical circuit is shown with loop X and junction Y. What is the correct expression...
- 16M.1.HL.TZ0.12: A circuit consists of a cell of electromotive force (emf) 6.0V and negligible...
- 16M.1.SL.TZ0.20: A circuit consists of a cell of electromotive force (emf) 6.0V and negligible internal...
- 16M.1.SL.TZ0.19: The graph shows the variation of current I in a device with potential difference V across...
- 15M.1.SL.TZ2.18: The diagram shows a circuit used to investigate internal resistance of a cell. The...
- 15M.1.SL.TZ1.18: Four resistors are connected as shown. What is the total resistance between X and Y? A. 3...
- 15M.1.HL.TZ2.17: The diagram shows an electric circuit containing a potentiometer of maximum resistance R. The...
- 15M.2.SL.TZ2.5f: An electric circuit consists of a supply connected to a 24Ω resistor in parallel with a...
- 15M.2.HL.TZ2.9a: A 24Ω resistor is made from a conducting wire. (i) The diameter of the wire is 0.30 mm and...
- 15M.2.HL.TZ2.9b: An electric circuit consists of a supply connected to a 24Ω resistor in parallel with a...
- 14M.1.SL.TZ1.16: Each of the resistors in the arrangements below has resistance R. Each arrangement is...
- 14M.1.SL.TZ1.17: Two resistors of resistance 10 Ω and 20 Ω are connected in parallel to a cell of negligible...
- 14M.1.SL.TZ1.18: A battery of emf 12 V and negligible internal resistance is connected to a resistor of...
- 14M.1.SL.TZ2.17: Which of the following is a statement of Ohm’s law? A. The resistance of a conductor is...
- 14M.1.SL.TZ2.18: Three identical filament lamps W, X and Y are connected in the circuit as shown. The cell has...
- 15N.1.HL.TZ0.18: A filament lamp and a semiconducting diode have the voltage–current (\(V\)–\(I\))...
- 15N.2.HL.TZ0.8f.ii: Calculate the power supplied to the transformer.
- 15N.1.SL.TZ0.20: Three resistors of resistance \(R\) are connected in parallel across a cell of electromotive...
- 15N.2.HL.TZ0.8f.i: Calculate the current in the cables connected to the town
- 15N.2.HL.TZ0.8f.iii: Determine the input voltage to the transformer if the power loss in the cables from the power...
- 15N.1.SL.TZ0.19: A cylindrical resistor of length \(l\) is made from a metal of mass \(m\). It has a...
- 15N.2.HL.TZ0.9g.ii: Each cubic metre of the wire contains approximately \(8.5 \times {10^{28}}\) free electrons....
- 14N.1.SL.TZ0.16: A cylindrical resistor of volume V and length l has resistance R. The resistor has a uniform...
- 15N.2.SL.TZ0.6d: An ammeter and a voltmeter are used to investigate the characteristics of a variable resistor...
- 15N.2.SL.TZ0.6e: Show that the current in the circuit is approximately 0.70 A when \(R = 0.80{\text{ }}\Omega \).
- 14N.1.SL.TZ0.18: A lamp is connected to an electric cell and it lights at its working voltage. The lamp is...
- 14N.1.HL.TZ0.19: A voltmeter of resistance 50kΩ is used to measure the electric potential difference in a...
- 14N.1.HL.TZ0.18: A lamp is connected to an electric cell and it lights at its working voltage. The lamp is...
- 14N.2.HL.TZ0.8d.i: On the graph, sketch the variation of \(V\) with \(I\) for the cell.
- 14N.2.HL.TZ0.8d.ii: Using the graph, determine the current in the circuit.
- 14N.2.SL.TZ0.2b.i: Draw on the diagram the positions of the ammeter and voltmeter.
- 14N.2.SL.TZ0.2b.ii: Show that the emf of the cell is 1.25 V.
- 14N.2.SL.TZ0.2b.iv: Calculate the energy dissipated per second in the variable resistor.
- 11N.1.SL.TZO.16: A cell is connected in series with a 2.0Ω resistor and a switch. The voltmeter is connected...
- 11N.1.HL.TZ0.21: A resistor has a resistance R. The potential difference across the resistor is V. Which of...
- 12N.1.SL.TZ0.19: An ideal ammeter is used to measure the current in a resistor. Which of the following gives...
- 12N.1.HL.TZ0.20: An ideal ammeter is used to measure the current in a resistor. Which of the following gives...
- 13N.1.SL.TZ0.17: A resistor X of resistance R is made of wire of length L and cross-sectional area A. Resistor...
- 13N.1.SL.TZ0.19: Each of the resistors in the circuit has a resistance of 2.0 Ω. The cell has an emf of 3.0 V...
- 12M.1.SL.TZ2.16: A metal wire X with length L and radius r has a resistance R. A wire Y of length 4L made from...
- 13M.2.SL.TZ1.8d: The diagram shows 12 photovoltaic cells connected in series and in parallel to form a module...
- 12M.1.SL.TZ2.17: Three identical filament lamps, X, Y and Z, are connected as shown to a battery of...
- 12M.1.SL.TZ2.18: Which of the following is the correct way of connecting an ammeter and of connecting a...
- 12M.1.SL.TZ1.18: Which of the following gives the resistances of an ideal ammeter and an ideal voltmeter?
- 11M.1.SL.TZ2.17: The graph shows the I–V characteristics of two resistors. When resistors X and Y...
- 11M.1.HL.TZ2.20: Two resistors, of resistance R1 and...
- 13M.1.SL.TZ2.16: A copper wire with length L and radius r has a resistance R. What is the radius of a copper...
- 13M.1.SL.TZ2.17: An electric circuit consists of three identical resistors of resistance R connected to a cell...
- 13M.1.SL.TZ2.18: A proton is accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 1000 V. What is the...
- 13M.1.HL.TZ2.20: A copper wire with length L and radius r has a resistance R. What is the radius of a copper...
- 12M.2.SL.TZ2.7b: The plates in (a) are replaced by a cell that has an emf of 12.0 V and internal...
- 11M.2.SL.TZ2.9a: ...
- 11M.2.SL.TZ2.9b: ...
- 12M.2.SL.TZ1.9b: (i) Calculate the resistance of the filament lamp when the potential difference across it is...
- 12M.2.SL.TZ1.9c: Two identical filament lamps are connected in series with a cell of emf 6.0 V and negligible...
- 11N.2.SL.TZ0.2b: A tungsten filament lamp is marked 6.0 V, 15 W. (i) Show that the resistance of the lamp at...
- 11N.2.HL.TZ0.10d: (d) The diagram shows part of a potential divider circuit used to measure the...
- 11N.2.SL.TZ0.2c: The diagram shows part of a potential divider circuit used to measure the current-potential...
- 11N.2.SL.TZ0.9b: The electric motor can be adjusted such that, after an initial acceleration, the load moves...
- 11N.2.HL.TZ0.10e: A student sets up a different circuit to measure the I–V graph. The cell has an emf of 6.0 V...
- 13N.2.SL.TZ0.5d: Outline, with reference to the graph and to Ohm’s law, whether or not each component is ohmic.
- 13N.2.SL.TZ0.5e: Components X and Y are connected in parallel. The parallel combination is then connected in...
- 11M.2.SL.TZ1.8b: A battery of emf ε and negligible internal resistance is connected in series to two...
- 11M.2.SL.TZ1.8c: The graph shows the I-V characteristics of two conductors, X and Y. On the axes below,...
- 11M.2.SL.TZ1.8d: The conductors in (c) are connected in series to a battery of emf ε and negligible...
- 11M.2.SL.TZ1.8a: Define (i) electromotive force (emf ) of a battery. (ii) electrical resistance of a...
- 09M.1.SL.TZ1.17: Two \(6{\text{ }}\Omega \) resistors are connected in series with a 6 V cell. A student...
- 09M.1.SL.TZ1.16: Two rectangular blocks, \(X\) and \(Y\), of the same material have different dimensions but...
- 09N.1.SL.TZ0.17: A cylindrical conductor of length \(l\), diameter \(D\) and resistivity \(\rho \) has...
- 09N.1.SL.TZ0.18: In the circuits below the cells have the same emf and zero internal resistance. The resistors...
- 10M.1.SL.TZ1.17: A resistor of resistance \({\text{12 }}\Omega \) is connected in series with a cell of...
- 10N.1.SL.TZ0.17: The circuit shows a resistor R connected in series with a battery and a resistor of...
- 10N.1.SL.TZ0.18: Three identical resistors are connected to a battery as shown. Which of the following is a...
- 10N.1.SL.TZ0.16: Two resistors, made of the same material, are connected in series to a battery. The length of...
- 10N.2.SL.TZ0.A3a: Draw the complete diagram of the circuit that uses a potential divider, ammeter, voltmeter...
- 10N.2.SL.TZ0.A3b: The graph shows the current-voltage characteristics for the component X. Component X is...

