| Date | May 2009 | Marks available | 5 | Reference code | 09M.3.hl.TZ2.D4 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Describe and Explain | Question number | D4 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Antibacterials are drugs that kill or inhibit the growth of microorganisms that cause infectious diseases. The general structure of penicillin, an antibacterial, is given below.
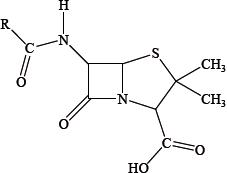
Describe the composition and structure of the beta-lactam ring in penicillin and explain its importance.
Markscheme
ring consists of one nitrogen atom and three carbon atoms (and three hydrogen atoms);
4 membered/square ring structure / bond angles of 90°;
ring under stress/strain / increased (chemical) reactivity / ring opens (due to angle of 90° instead of about 109°);
bonds to/blocks action of enzyme/transpeptidase;
reaction with the enzyme not reversible / prevents cross linking of peptides / inhibits synthesis and growth of bacterial cell walls / OWTTE;
Examiners report
Many candidates were unable to explain the importance of the beta-lactam ring in penicillin. The bonds in the opened structure blocks the action of the enzyme, transpeptidase, a non-reversible reaction that prevents cross linkage of peptides in the bacteria, which inhibits the synthesis and growth of bacterial cell walls.

