| Date | May 2013 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 13M.3.sl.TZ2.D3 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | State | Question number | D3 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Two different antibacterials are sodium piperacillin and doxycycline. Sodium piperacillin is a type of penicillin and doxycycline belongs to a class of drugs known as the tetracyclines.
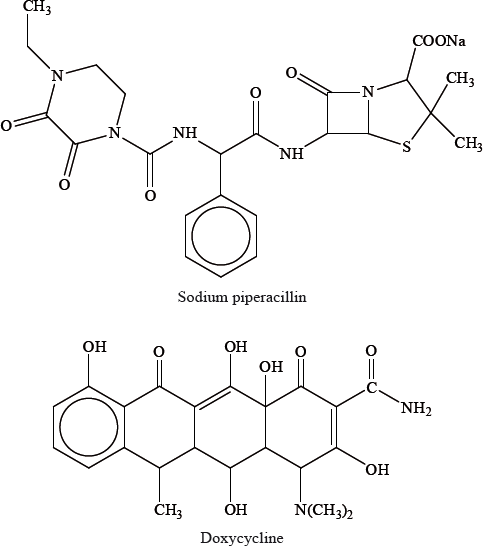
Explain how penicillins are able to cure certain diseases caused by bacteria.
Sodium piperacillin has a different side chain to the original penicillin developed by Florey and Chain. State one advantage of changing the side chain.
Explain why it may be necessary to give a mixture of several different types of antibacterials (such as penicillins and tetracyclines) to patients suffering from diseases such as tuberculosis (TB) or MRSA (a disease caused by the presence of the staphylococcus aureus bacterium).
Markscheme
prevents the growth/ multiplication of bacteria (causing disease);
Accept “kills bacteria”.
interferes with the enzymes that bacteria need to make normal cell walls / prevents normal cell wall formation;
Do not accept “Destroys cell walls”.
cells absorbs water (by osmosis) and ruptures/bursts;
does not need to be injected / not broken down by stomach acid / resistant to penicillinase;
Accept “overcomes resistance of bacteria” / OWTTE;
Do not accept “immune” rather than “resistant”.
some bacteria may be resistant to just one antibiotic / can make \(\beta \)-lactamase/penicillinase (which can degrade penicillin);
few bacteria resistant to all the antibiotics / prevents the risk of further resistance developing;
Unless penalised in D3 (b), do not accept “immune” rather than “resistant”.
Examiners report
Many students knew that penicillins affected the walls of bacteria, though many wrongly stated that it destroyed the cell wall, rather than hindering its formation. The effects of changing the side chain were generally appreciated, but once again, in the final part of the question, students often failed to express the reasons for using multiple antibacterials clearly enough to gain full credit. In the last two parts candidates often, incorrectly, referred to bacteria being “immune” or “tolerant” rather than “resistant” - another example of a failure to use precise vocabulary correctly.
Many students knew that penicillins affected the walls of bacteria, though many wrongly stated that it destroyed the cell wall, rather than hindering its formation. The effects of changing the side chain were generally appreciated, but once again, in the final part of the question, students often failed to express the reasons for using multiple antibacterials clearly enough to gain full credit. In the last two parts candidates often, incorrectly, referred to bacteria being “immune” or “tolerant” rather than “resistant” - another example of a failure to use precise vocabulary correctly.
Many students knew that penicillins affected the walls of bacteria, though many wrongly stated that it destroyed the cell wall, rather than hindering its formation. The effects of changing the side chain were generally appreciated, but once again, in the final part of the question, students often failed to express the reasons for using multiple antibacterials clearly enough to gain full credit. In the last two parts candidates often, incorrectly, referred to bacteria being “immune” or “tolerant” rather than “resistant” - another example of a failure to use precise vocabulary correctly.

