| Date | November 2011 | Marks available | 3 | Reference code | 11N.3.sl.TZ0.D4 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | Discuss and Explain | Question number | D4 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Antibiotics treat infections by stopping the growth of bacteria or destroying them.
Identify the side-chain by drawing a circle around the side-chain in the structure of benzyl penicillin given below (the structure of penicillin is given in Table 20 of the Data Booklet).
Discuss two problems associated with the overprescription of penicillin and explain how these are overcome.
Markscheme
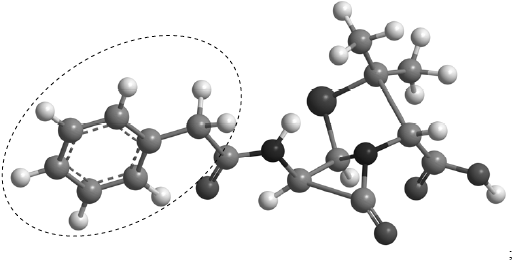
No mark if circle includes CO or just O.
Award [1] if it includes 7 C atoms but misses out on attached H atoms.
overprescription can lead to allergic reaction;
may wipe-out harmless/helpful/beneficial bacteria (in the alimentary canal)/destroyed bacteria may be replaced by more harmful bacteria;
(may pass on genetic) resistance/immunity;
[1] each for any two.
modify R group/side chain to change penicillin effectiveness / form penicillin that is more resistant to penicillinase enzyme;
Examiners report
Many candidates scored the mark in (a) by correctly identifying the side-chain, but a surprising number of candidates only circled the aromatic ring without including the \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\). The general structure of penicillin is given in Table 20 of the Data Booklet, so if all candidates referred to the table they should have scored the mark.
Many candidates did not recognise the loss of beneficial bacteria in the problems associated with over prescription of penicillin. A surprising number were not able to explain the modification of the side chain/R group to change the effectiveness of penicillin.

