| Date | May 2013 | Marks available | 3 | Reference code | 13M.3.hl.TZ1.C5 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Explain and Predict | Question number | C5 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Poly(propene) has different forms. Isotactic poly(propene) is tough, while atactic poly(propene) is flexible.
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), represented below, is an example of a condensation polymer.
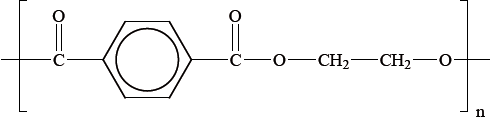
Draw the structures of the monomers that form polyethylene terephthalate.
Predict whether polyethylene terephthalate or isotactic poly(propene) has a higher melting point. Explain your answer in terms of intermolecular forces.
Markscheme
HOOC–\({{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\)–COOH;
\({\text{HOC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}\);
Accept condensed or full structural formulas.
polyethylene terephthalate (PET);
(permanent) dipole-(permanent) dipole interactions in PET;
both polymers contain van der Waals’/London/dispersion forces between chains / polypropene only has van der Waals’/London/dispersion forces which are weaker than dipole-dipole interactions;
Allow vdW as abbreviation for van der Waals’ or FDL for London/dispersion.
M2 and M3 can only be scored if M1 is correct.
Examiners report
In (b), the structures of the monomers that form PET were usually correctly represented, even by the weaker students.
In (b), the structures of the monomers that form PET were usually correctly represented, even by the weaker students.

