| Date | May 2014 | Marks available | 5 | Reference code | 14M.3.hl.TZ1.10 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Deduce, Describe, and Outline | Question number | 10 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Liquid crystals are widely used in devices such as calculators, laptop computers and advanced optical materials.
Kevlar® is a material used in bullet-proof vests.
(i) Deduce the products formed by a condensation polymerization reaction of the monomers benzene-1,4-diamine and benzene-1,4-dicarbonyl chloride to form Kevlar®.
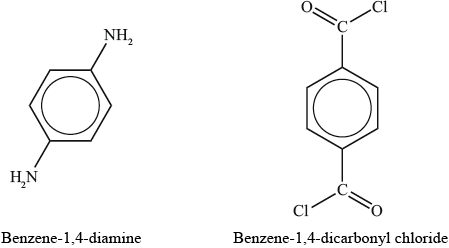
(ii) Describe the factors which account for the inherent strength of Kevlar®.
(iii) Outline why Kevlar® can dissolve in concentrated sulfuric acid.
Markscheme
(i) 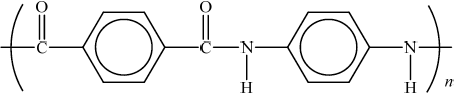 ;
;
Brackets or n not necessary but continuation bonds must be shown.
Do not penalise if CO and NH are in cis configuration.
HCl;
Allow correct name for M2.
(ii) Kevlar® (molecules) have strong covalent bonds (so hard to break);
(large number of) hydrogen bonds between C=O and NH groups;
CO/NH groups trans to each other so orientation maximizes interactions/helps packing/produces more ordered structure / \(\pi \)-bonding/aromatic stacking interactions between benzene rings in neighbouring strands / OWTTE;
(iii) intermolecular forces/hydrogen bonds broken / nitrogen and oxygen atoms become protonated / reverses condensation process / OWTTE;
Examiners report
In (c) (i), continuation bonds were frequently omitted and \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\) was often stated incorrectly instead of HCl. In (ii) although some candidates mentioned the hydrogen bonding network in Kevlar® often they did not state that these intermolecular forces are between the C=O and NH groups. (iii) was generally answered correctly.

