| Date | May 2015 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 15M.3.sl.TZ1.13 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Compare | Question number | 13 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
The properties of four analgesics are summarized below.
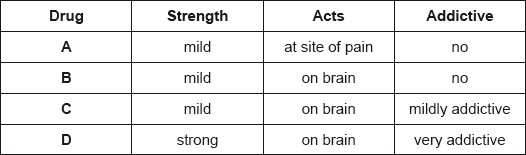
Deduce which drugs could be morphine, aspirin and codeine.
Morphine:
Aspirin:
Codeine:
Compare the structures of diamorphine (heroin) and morphine. Their structures are given in table 20 of the data booklet.
Two similarities:
One difference:
Markscheme
Morphine: D;
Aspirin: A;
Codeine: C;
Award [2] for all three correct, [1] for two correct.
Similarities:
Award [1 max] for any two:
benzene ring/aromatic ring/−C6H2;
Accept “phenyl” or “arene” but not C6H5- or benzene/C6H6.
(tertiary) amino/−NRR'/NRR'R'';
Accept “(tertiary) amine”.
carbon−carbon double bond/C=C;
Accept “alkene” or “alkenyl”.
ether/C−O−C;
Accept “both have the same ring structure / OWTTE”.
Difference:
ester/CH3COO in diamorphine/heroin and hydroxyl/OH in morphine;
Accept “ethanoate” for ester.
Accept “alcohol” or “hydroxy” for hydroxyl but not hydroxide.
Examiners report
Most candidates matched the analgesics to the properties successfully.
Most candidates identified two similarities and one difference between diamorphine and morphine. For the difference, it was necessary to mention both the hydroxyl groups in morphine and the ester groups in diamorphine.

