 A wave is a transfer of energy or information using oscillations of a medium, without moving the particles of the medium themselves.
A wave is a transfer of energy or information using oscillations of a medium, without moving the particles of the medium themselves.
Waves can be modelled mathematically and have a number of different properties.
Key Concepts
All waves have the following chracteristics:
Reflection: When a wave hits a barrier it comes back. The angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence.
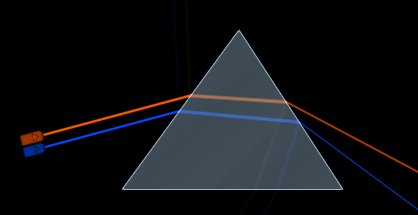
Refraction: When a wave passes into another medium, it changes direction due to a change in speed.
Interference: When two waves of the same type meet, they combine to construct and destruct one another.
Superposition: The total displacement of interfering waves is the vector sum of the individual displacements.
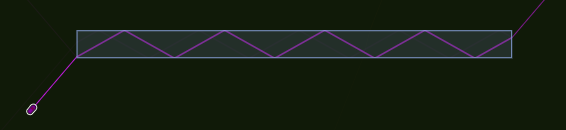
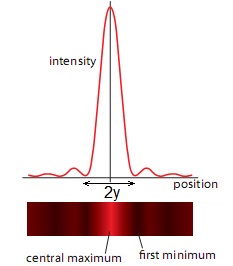
Diffraction: When a wave passes through a narrow opening it spreads out. A wave will also pass around the edge of a barrier.
When air is disturbed it causes a change in pressure. This in turn disturbs the surrounding air, resulting in propagation of changing pressure throughout the medium.
Sound waves can be simulated using Algodoo.
Sound changes speed when it enters a new material (the denser the material, the more particles present, and the faster the propagation of pressure. In fact, sound will not travel through a vacuum.
Sound is also refracted as it passes through air of a different temperature.
There are some key differences between progressive and standing waves:
| Progressive | Standing |
| Amplitude of all points is equal | Amplitude of all points between a node and antinode different |
| All points within one wavelength out of phase | All points between 2 nodes in phase |
| Energy transfer | No energy transfer |
| Wave profile progresses | Wave profile stationary |
How much of Waves have you understood?


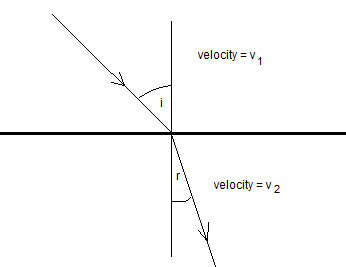
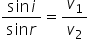

 The Huygens construction explains the properties of a wave by considering the wave front (e.g. a peak or a compression) to be made of an infinite number of small wavelet sources. Each wavelet progresses forwards, adding to give the new wave front.
The Huygens construction explains the properties of a wave by considering the wave front (e.g. a peak or a compression) to be made of an infinite number of small wavelet sources. Each wavelet progresses forwards, adding to give the new wave front. 
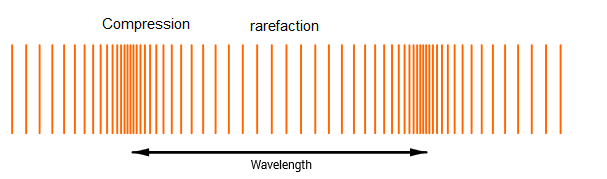
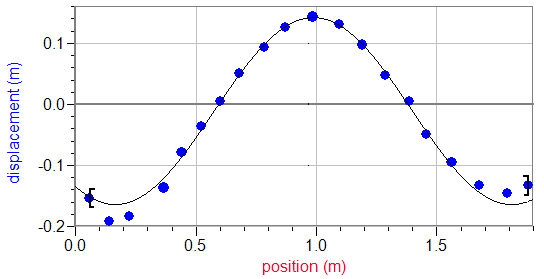
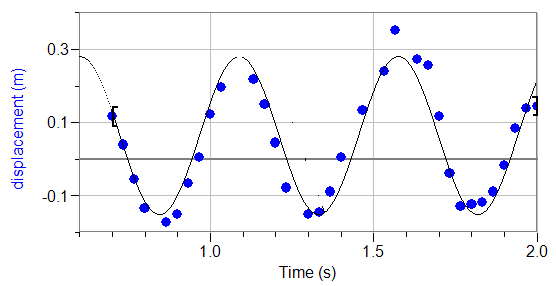
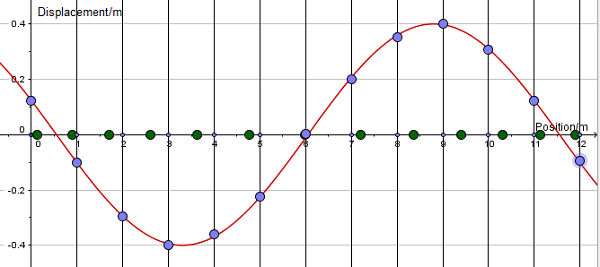
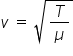
 It is possible to find an equation for how the y-displacement of a wave varies with the distance travelled (x) through the medium:
It is possible to find an equation for how the y-displacement of a wave varies with the distance travelled (x) through the medium: 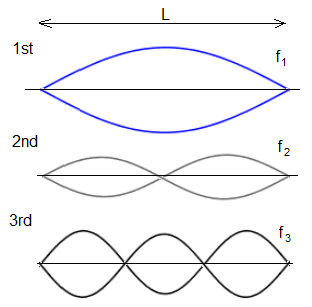




 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn