Learn and test your biological vocabulary for 6.5 Neurones and synapses using these flashcards.
These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - good revision for all students.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
Summary list for 6.5 Neurones and synapses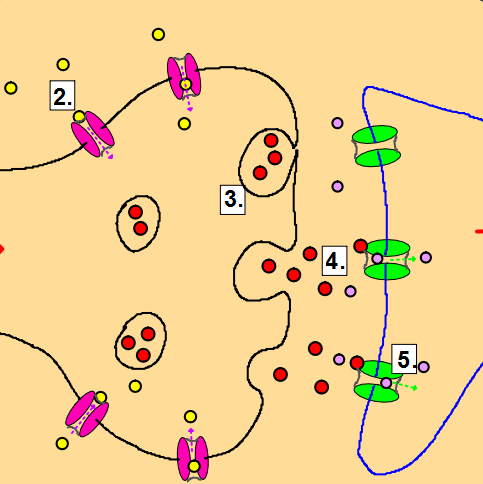
- Electrical impulses are transmitted in neurones (details of neuron types not required).
- Sodium and potassium ions are pumped across neuron membranes to generate a resting potential.
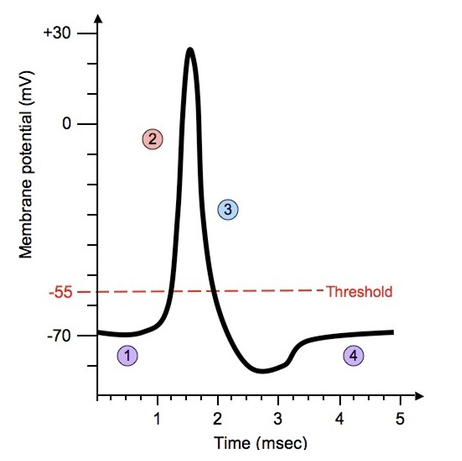
- Action potentials are depolarization and repolarization of the neuron which are propagated along the axons of neurons creating nerve impulses. (Oscilloscope traces showing resting potential & action potential).
- Local currents cause each successive part of the axon to reach the threshold potential.
- Myelin sheath cells around the axons of nerve fibres allows for saltatory conduction.
- Synapses (only chemical synapses) join neurons and also join neurons to receptor or effector cells.
- Depolarized pre-synaptic neurons release a neurotransmitter into the synapse.
- A nerve impulse is only initiated if the threshold potential is reached.
Skills
- Understand that secretion and reabsorption of acetylcholine by neurons occurs at synapses.
- Illustrate how blocking of synaptic transmission at cholinergic synapses in insects by the binding of neonicotinoid pesticides to acetylcholine receptors can work as a pesticide.
- Outline how the workings of neurotransmitters and synapses has led to the development of numerous pharmaceuticals for the treatment of mental disorders.
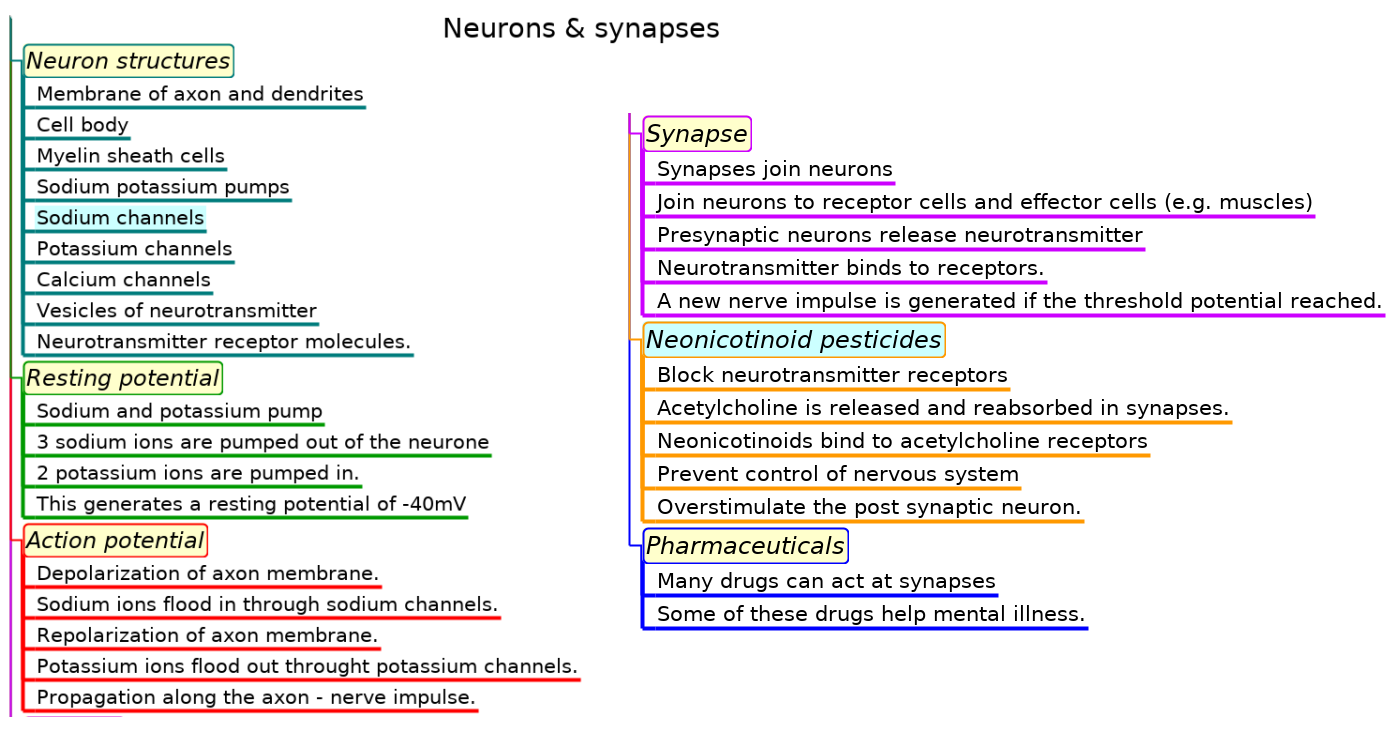
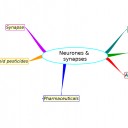
Mindmaps
This diagram summaries the main sections of topic 6.5.
Test if you can draw something like these concept maps from memory.
Video tutorial
To review this section why not make a stop motion video like the one below?
A quiz containing at least ten questions covering the ten skills outlined in the image above.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
The creation of an action potential across a nerve axon or dendron is a good example of active transport.
Drag and drop the correct word or phrase into the gap to describe the creation of the resting potential of a neuron.
axon or dendron. action potential +70 millivolts potential outside active potassium ions -70 millivolts impermeable concentration difference permeable sodium ions uses ATP inside
The neurone resting potential is achieved by transport.
The sodium pump in the neuron membrane energy to actively pump out in exchange for . This creates an ion across the membrane, with a higher sodium ion concentration the membrane.
The membrane is to sodium ions, maintaining this gradient until the passage of an .
This achieves a potential of on the inside of the membrane (relative to the outside).
The ion gradient is the electrical difference that allows an action potential to pass down the
Active transport pumps move ions across membranes. Te membrane must otherwise be impermeable to these ions to retain them on one side of the membrane. Electrical potential energy is used in the transmission of an impulse.
Everyone needs some fun at times while they revise.
If you can't see the content below, please click this link to Neurones and synapses arcade games.
How much of Neurones and synapses 6.5 have you understood?
















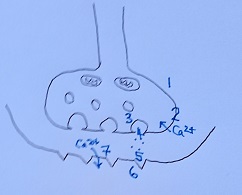
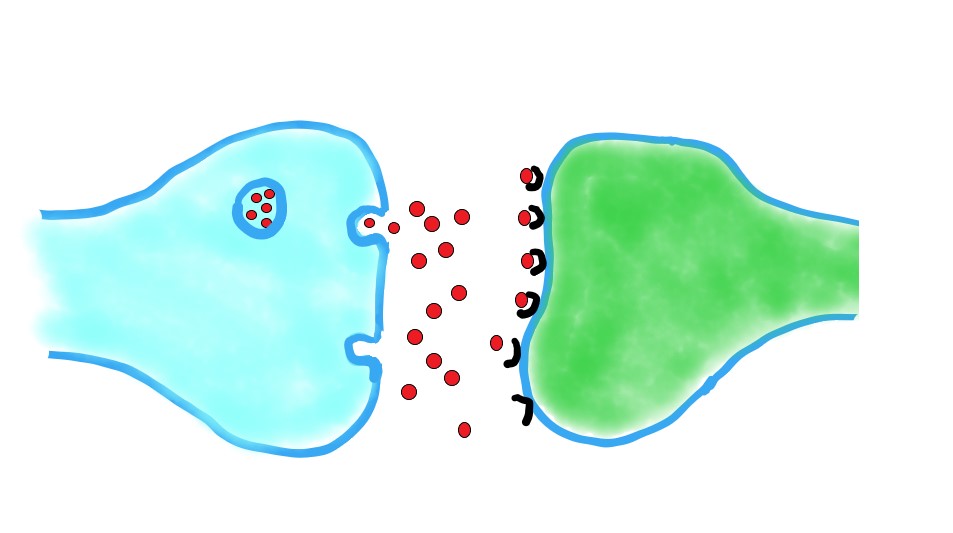 gram shows parts of two neurones at a synapse.
gram shows parts of two neurones at a synapse.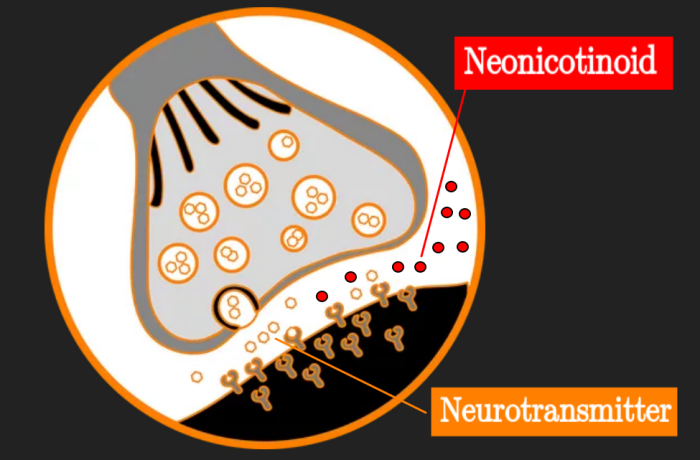 A type of pesticide called "neonicotinoid" interacts with the synapses that use the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
A type of pesticide called "neonicotinoid" interacts with the synapses that use the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.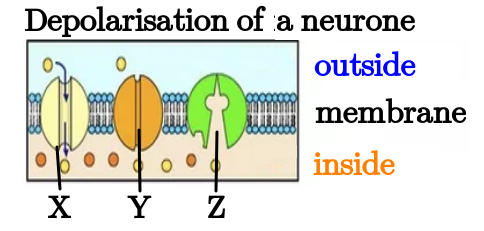
 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn