 This topic covers the production of antibodies and the cascade of reactions in blood clotting. The functions of blood cells in the immune system as well as specific immunity and antibodies. Methods of transmission of HIV is also included.
This topic covers the production of antibodies and the cascade of reactions in blood clotting. The functions of blood cells in the immune system as well as specific immunity and antibodies. Methods of transmission of HIV is also included.Learn and test your biological vocabulary for 6.3 Defence against disease using these flashcards.
These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - good revision for all students.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
Summary list for 6.3 Defence against disease
- The primary defence against pathogens are the skin and mucous membranes.
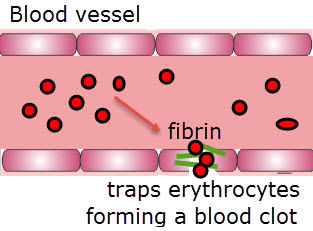
- Blood clotting seals cuts in the skin (skin diagrams are not required).
- Platelets release clotting factors.
- Fibrinogen is converted to fibrin by thrombin.
- Pathogens are ingested by phagocyte cells which gives non-specific immunity.
- Specific immunity is given by production of antibodies by lymphocytes in response to particular (antigens on) pathogens.
- Antibiotics block prokaryotic cell processes but not processes in eukaryotic cells.
- Viruses lack a metabolism and cannot be treated with antibiotics. Some strains of bacteria have evolved antibiotic resistance and even multiple resistance.
- The effects of HIV on the immune system should be limited to a reduction in the number of active lymphocytes and a loss of the ability to produce antibodies, leading to the development of AIDS.
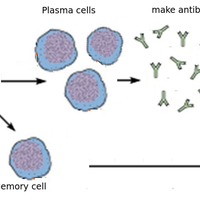
- Subgroups of phagocyte and lymphocyte are not required but students should be aware that some lymphocytes act as memory cells and can quickly reproduce to form a clone of plasma cells if a pathogen carrying a specific antigen is re-encountered.
Skills
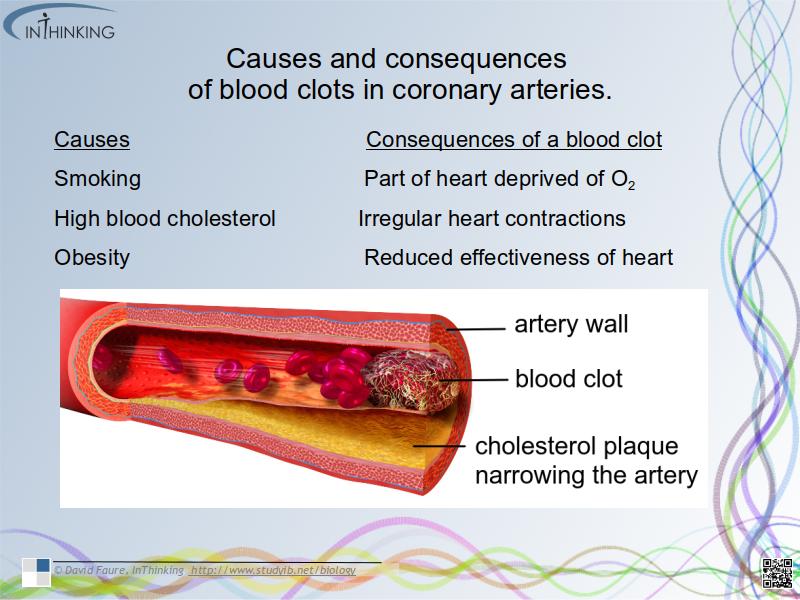
- Outline causes and consequences of blood clot formation in coronary arteries.
- Describe Florey and Chain’s experiments to test penicillin on bacterial infections in mice.
- Describe the effects of HIV on the immune system and methods of transmission.
Mindmaps
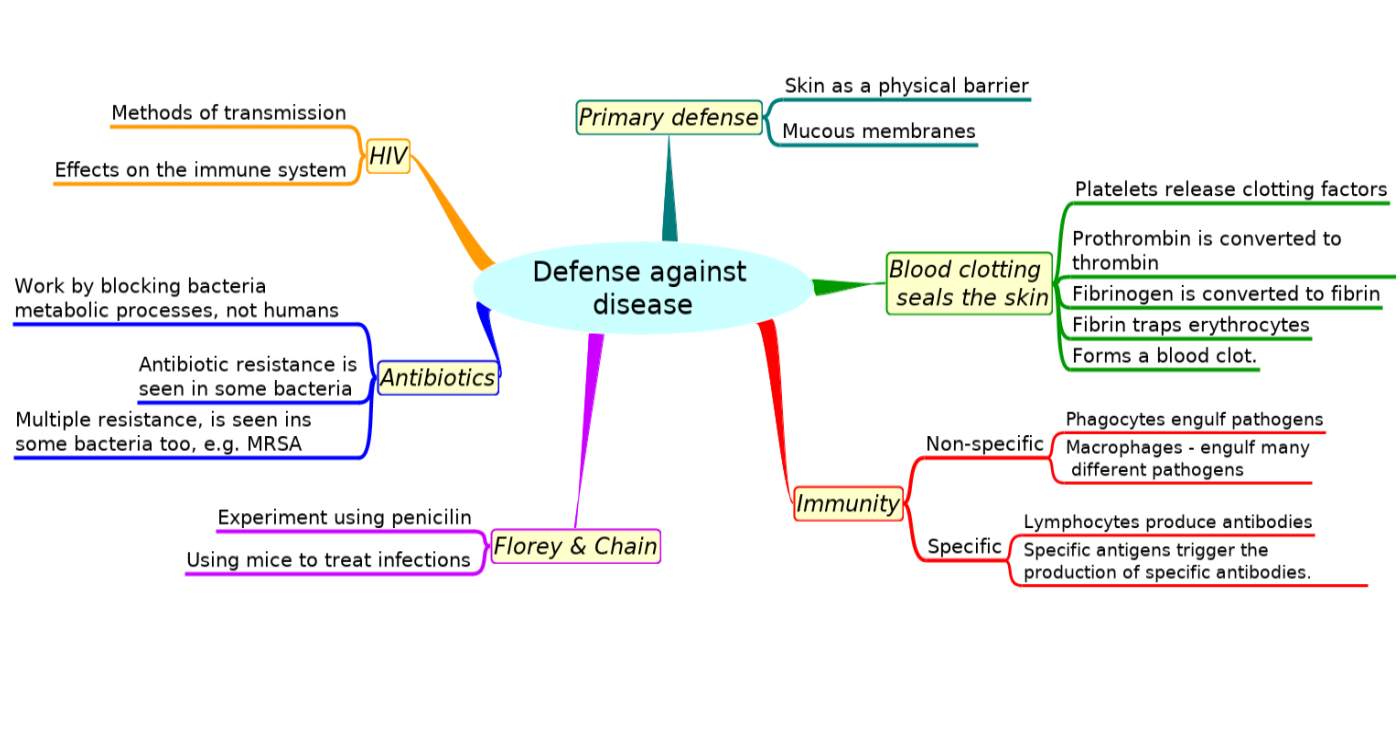
This diagram summaries the main sections of topic 6.3.
Test if you can draw something like these concept maps from memory.
Video tutorial
Watch this short video tutorial about the cascade of reactions in blood clotting. Focus on platelets, clotting factors, thrombin, fibrinogen, and fibrin as well as erythrocytes.
Note: Some details are not required, but the graphics are so good it's worth watching this two minute explanation.
Describe the role of of the following parts of the blood clotting process by completing the table.
| Blood component | Function |
|---|---|
| Platelets | Gather at the site of cell damage and release clotting factor. |
| Clotting factor | Begins the clotting cascade and triggers the formation of thrombin |
| Thrombin | (i) |
| Fibrinogen | (ii) |
| Fibrin | (iii) |
| Erythrocytes | (iv) |
Click the + to see a model answer.
Multiple choice questions
This is a self marking quiz containing questions covering the topic outlined above.
Try the questions to check your understanding.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
Florey and Chain purified and tested penicillin. It was administered to humans and proved very effective against bacterial infections. Today, drug development rwuires far more stringent controls.

Drag and drop the correct word or phrase into the gap to describe the discovery and purification of penicillin.
risk assessment mode of action antibacterial infecting penicillin injections moulds Fleming antiviral died trials on mice mice purified manufacture humans
In 1928, Alexander noticed that growing on agar plates could prevent bacterial growth.
In 1939, that Florey and Chain the substance discovered by Fleming to have properties, now known as penicillin.
They tested the penicillin on by deliberately eight mice with a blood disease and treating four of them with . The treated mice recovered, the untreated . They then repeated the investigation a number of times on and, within a few months, administered the drug to with life-threatening bacterial infections without any understanding of the of the drug. The trials were successful and penicillin began immediately.
Penicillin saved numerous lives but went to human use without sufficient testing or by today’s standards.
Penicillin is a very successful antibiotic that eventually gave rise to a whole family of antibiotics. Testing of new drugs is now a much more rigorous process. A salient fact is that, should today's regulations have been in force in 1939, penicillin would not have been available during the second world war which probably would have led to huge loss of life due to infections.
If you want to review key terminology and have some fun with your revision try this word shoot game.
It will help you remember the terms through repetition. Defence against disease arcade games.
How much of Defence against disease 6.3 have you understood?





























 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn