- Summary list for 6.4 Gas exchange
- Mindmaps
- Exam style question about gas exchange
- Model answer
- Model answer
- Model answer
- 6.4 Gas exchange quiz 1/1
These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - good revision for all students.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
Summary list for 6.4 Gas exchange
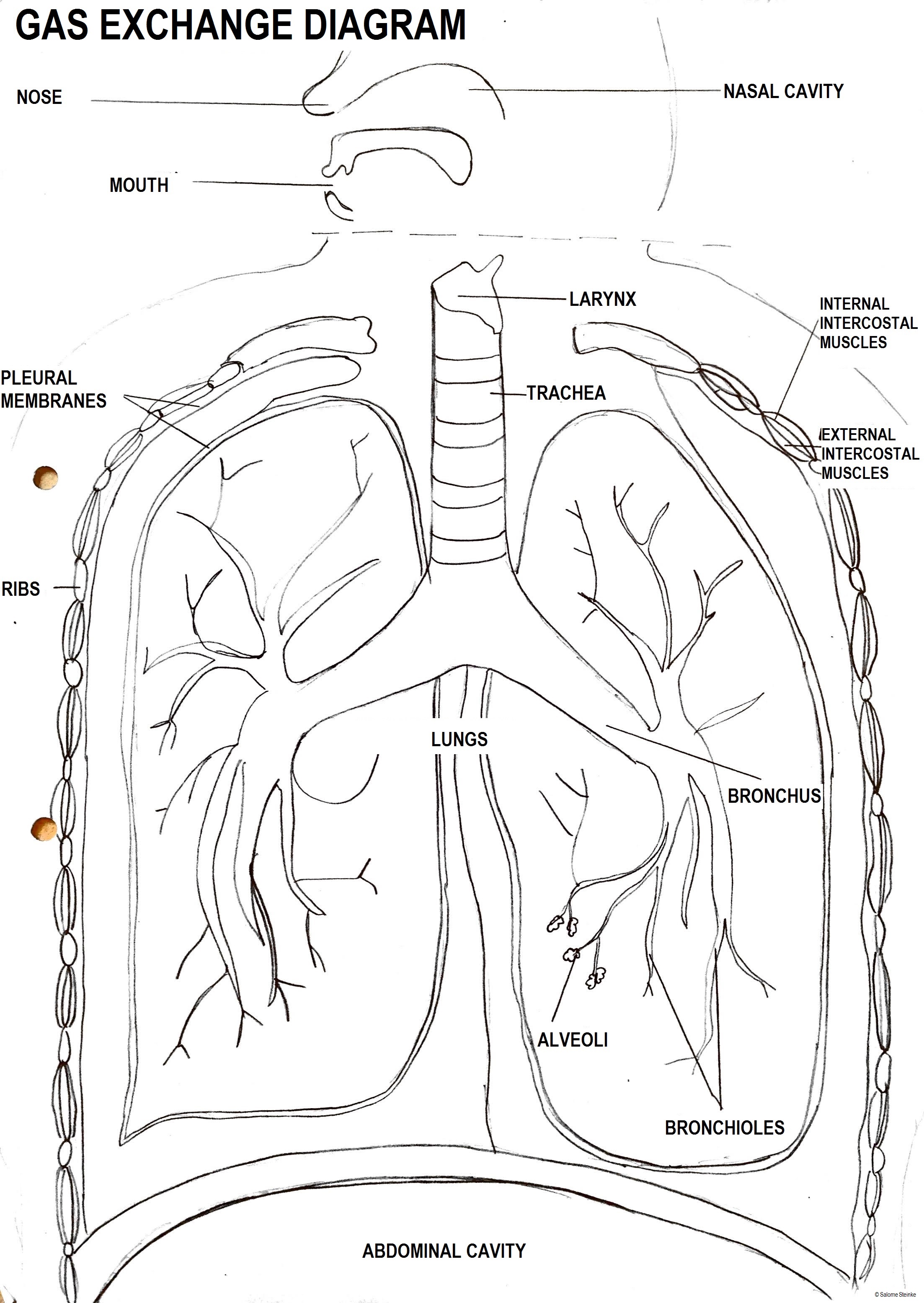
- Concentration gradients of oxygen and carbon dioxide between air in alveoli and blood flowing in adjacent capillaries are maintained by ventilation.
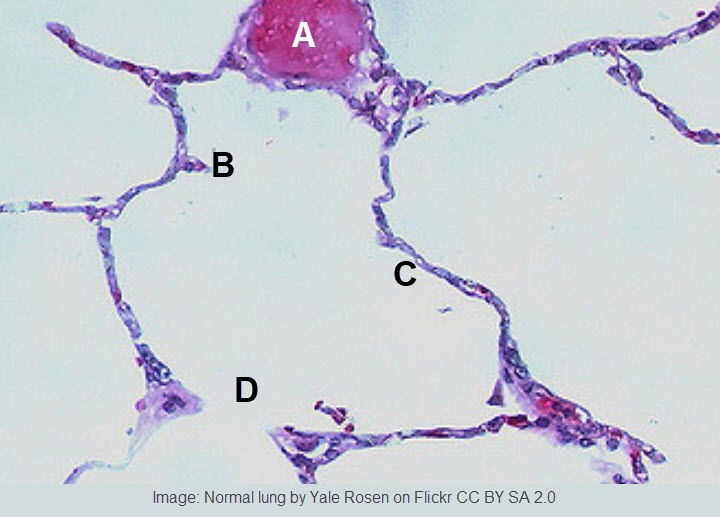
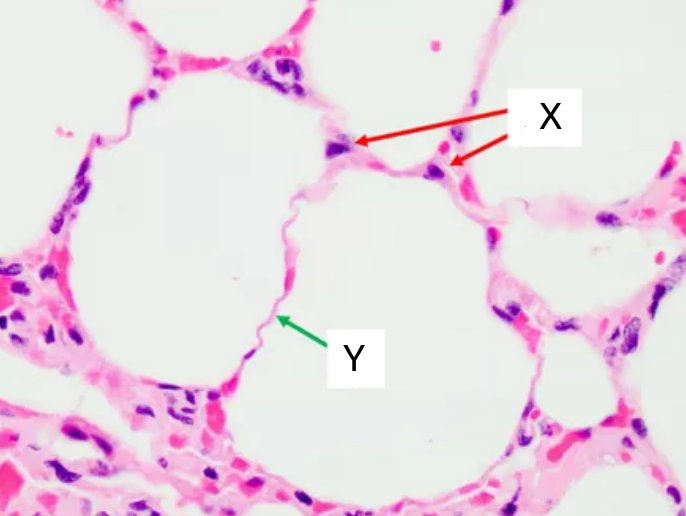
- Draw a diagram to show the structure of an alveolus and an adjacent capillary. Alveoli consist of two types of pneumocytes;
- Type I are extremely thin and are adapted to carry out gas exchange.
- Type II secrete a solution containing surfactant that creates a moist surface inside the alveoli. This reduces surface tension and prevents the sides of the alveolus sticking to each other.
- The trachea and bronchi carry air to the alveoli in bronchioles in the lungs.
- Muscle contractions cause the pressure changes inside the thorax that force air in and out of the lungs to ventilate them.
- External and internal intercostal muscles, and diaphragm and abdominal muscles are antagonistic muscles, required for inspiration and expiration because muscles only work by contracting.
Skills
- Link causes and consequences of lung cancer.& emphysema to structure of lungs.
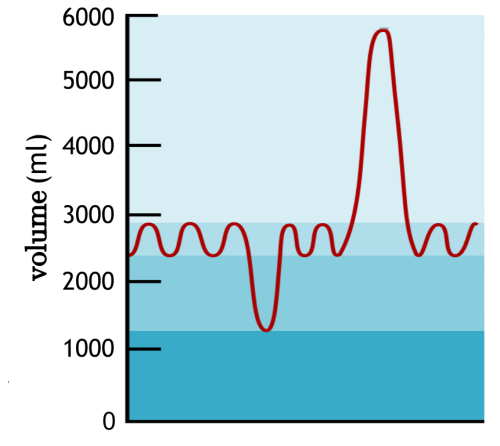
- Monitor ventilation in humans at rest and after mild and vigorous exercise (Practical 6).
- Ventilation rate and tidal volume should be measured, either be monitored by simple observation and simple apparatus or
- by data logging with a spirometer or chest belt and pressure meter. (residual vol, & vital capacity not required).
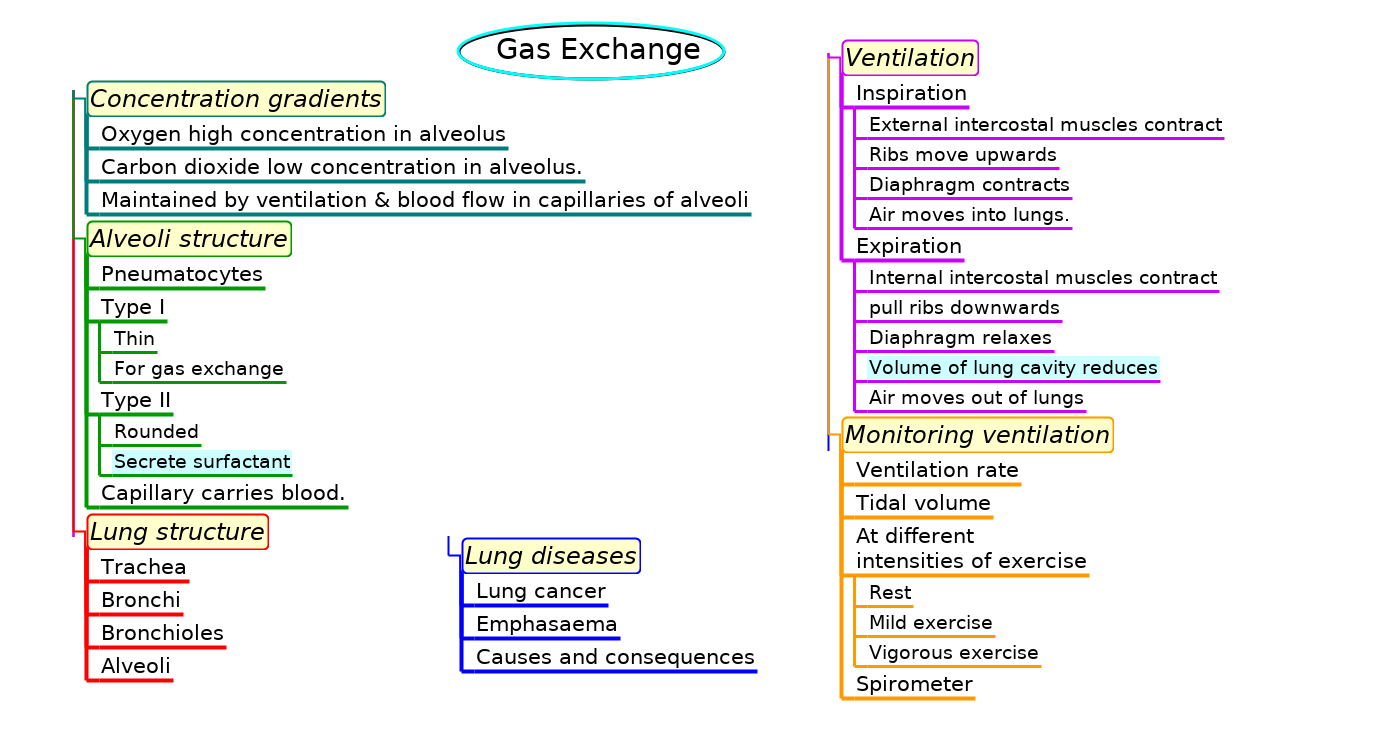
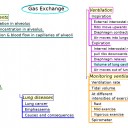
Mindmaps
This diagram summaries the main sections of topic 6.4
Test if you can draw something like these concept maps from memory.
Exam style question about gas exchange
Understanding the ventilation of the lungs is important in this topic.
Answer the question below on a piece of paper, then check your answer with the model answer.
Explain how intercostal muscles and the diaphragm help to maintain a concentration gradient of oxygen to promoter gas exchange in the alveoli. [4]
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
Click the + icon to see a model answer.
A quiz containing at least ten questions covering the ten skills outlined in the image above.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
Lung cancer is the commonest form of cancer in developed countries.

Drag and drop the correct word or phrase into the gap to outline lung cancer causes and effects.
metastase particular pollution Passive pollutants Carcinogens unregulated meiosis lung radioactive genetic mitosis tumour obesity
Cancer is a range of diseases in which a group of cells undergoes followed by growth in an manner forming a which may to other organs.
The commonest cancer in males (and rapidly increasing in females) is cancer of the and the causes are generally exposure to:
- in cigarette and other smoke.
- smoking exposure to cigarette carcinogens.
- Environmental air such as asbestos dust and from combustion.
- Exposure to or inhalation of material.
- A predisposition to lung cancer.
Unregulated mitosis and subsequent cell growth creates tumours.
D6 The ventilation rate must be controlled in order to maintain the correct concentration of respiratory gases in the blood.
flow cerebellum autonomic aorta lungs intercostal oblongata Stretch respiratory volume inhaled pH carotid medulla
The ventilation rate is controlled by the nervous system through the centre of the medulla of the brain.
Ventilation is maintained by rhythmicity and adjusted by chemoreceptors.
receptors in the thorax and inhibit inspiration and promote expiration to equalise the volumes of air and exhaled.
Chemoreceptors in the oblongata, and arteries are sensitive to blood and carbon dioxide concentration rise. They stimulate the respirarory centre which in turn sends impulses through the and phrenic nerves to increase the tidal and rate of breathing.
Rhythmicity gives coordinated intake and exhalation of air, chemoreceptors cause adjustments of exhalation rate.
If you can't see the content below, please click this link to Gas exchange card match game.
How much of Gas exchange 6.4 have you understood?












 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn