- Summary list for 9.3 Growth in plants
- Mindmaps
- Exam style question about auxin
- Model answer
- Exam style question on micropropagation.
- Model answer
- Exam style question on flowering and day length
- Model answer
- Multiple choice questions
- 9.3 Plant growth 1/1
These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - great revision.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
Summary list for 9.3 Growth in plants
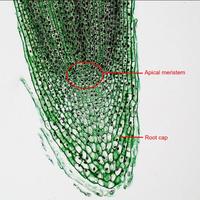
Meristems and growth
- Plant meristems are undifferentiated cells which allow indeterminate growth (ie: plants continue to grow when adult.)
- Mitosis and cell division in the shoot apex provide cells needed for the stem to get longer and for the development of leaves.
Hormonal control of shoot growth
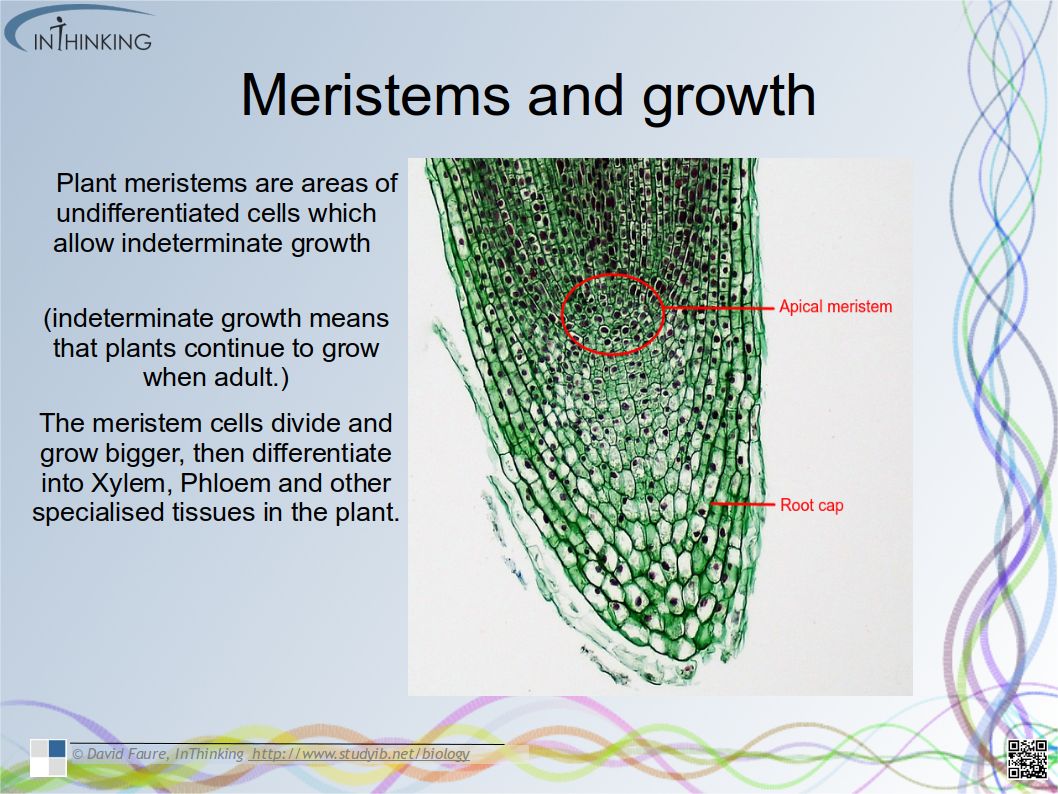
- Plant hormones (ie: auxin) control growth in the shoot apex.
- Auxin efflux pumps can create auxin concentration gradients
- Plant shoots respond to the environment by tropisms.
- Concentration gradients of auxin in plant tissue influence the rate of cell growth by changing the pattern of gene expression.
Skills
- Micropropagation of plants using tissue from the shoot apex grown on nutrient agar gels in the presence of growth hormones can be used for rapid production of new varieties, of virus-free strains of existing varieties and for propagation of orchids and other rare species.
Mindmaps
These diagram summaries cover the main sections of topic 9.3 Growth in plants.
Study them and draw your own list or concept map, from memory if you can.
Try to turn the simple mindmap into the detailed mindmap from memory.
Exam style question about auxin
Explaining the effect of auxin on plant growth is an important skill from this topic.
Answer the question below, on a piece of paper, then check your answer against the model answer below.
Describe the role of auxin in phototropism in growing shoots [5]
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
Click the + icon to see a model answer.
Multiple choice questions
This is a self marking quiz containing questions covering the topic outlined above.
Try the questions to check your understanding.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
The role of the meristem in plant growth.
Drag and drop the correct term into the gap to outline growth in flowering plants.
hormones mitosis environmental determinate indeterminate meiosis types expression totipotent flower different
Angiosperm growth is , meristematic cells divide by and produce new organs continually.
Meristems are , depending upon the growth pattern of the plant, the same meristematic cells can produce organs. For example, the stem apical meristem can produce stem, leaf or primordia (embryonic organs) and all of the cell that the organ requires.
The development of the plant is controlled by plant that alter gene in the differentiating cells by responding to conditions such as the length of the day.
Explanation: Angiosperm grwth patterns are controlled by hormones and are responses to environmental influences.
Everyone needs a bit of fun while they revise. Try this Growth in plants card matching game.
Can you reach the leader board?
How much of Growth in plants 9.3 HL have you understood?






















 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn