- Summary list for 9.1 Transport in xylem
- Mindmaps
- Exam style question about transport in xylem
- Model answer
- Exam style question about the properties of water.
- Model answer
- Model answer
- 9.1 Transport in xylem 1/1
Learn and test your biological vocabulary using these 9.1 Transport in xylem flashcards.
These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - great revision.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
Summary list for 9.1 Transport in xylem
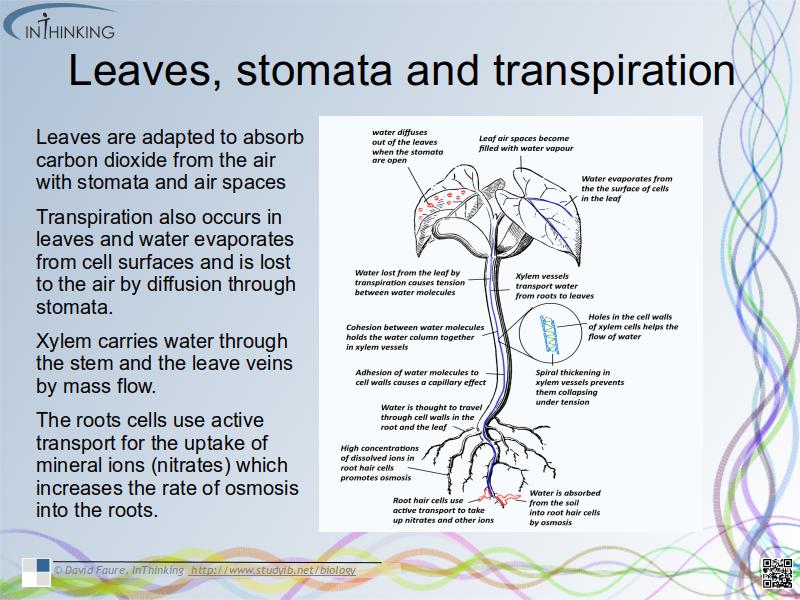
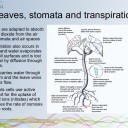
Leaf stomata & transpiration
- Leaves are adapted to absorb carbon dioxide from the air
- therefore transpiration can also occur in leaves and water is lost to the air.
Transport in xylem
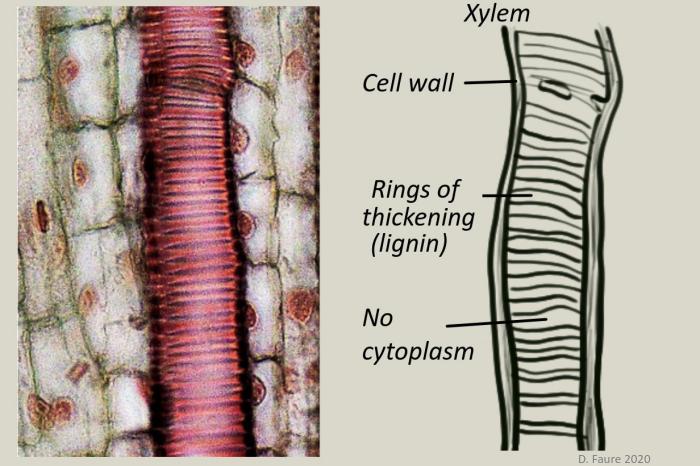
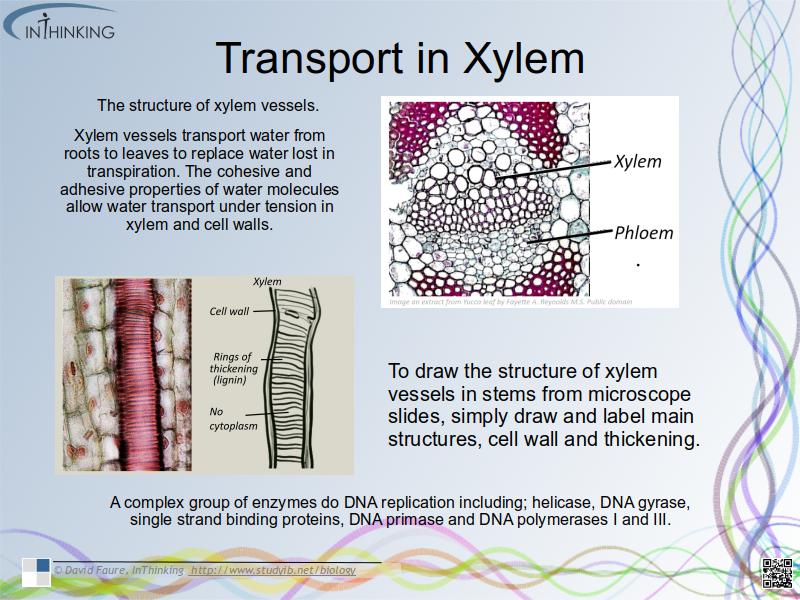
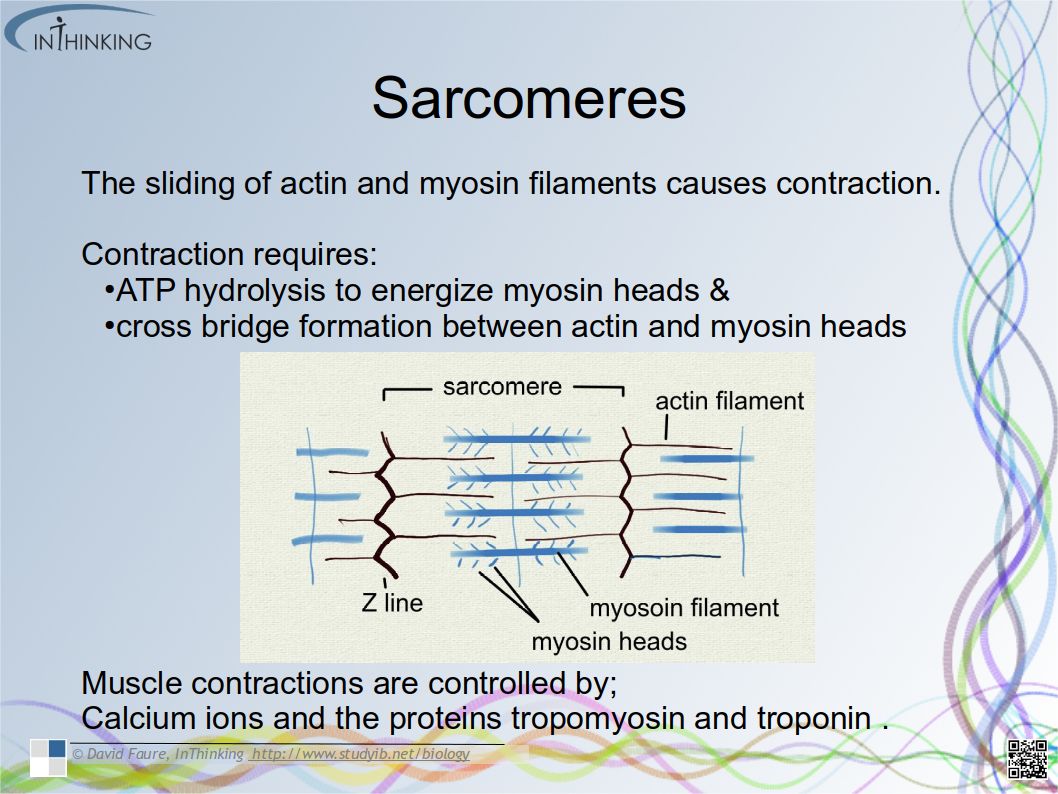
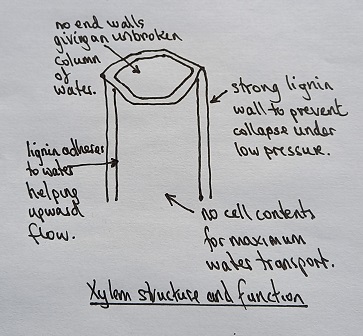
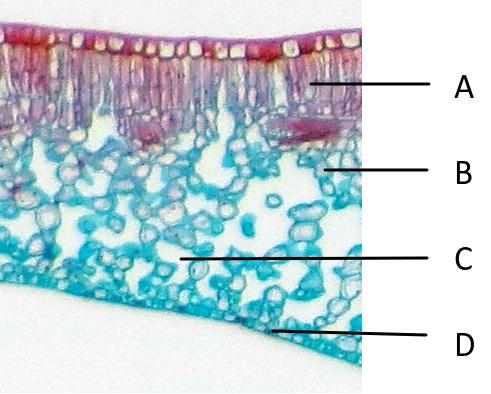
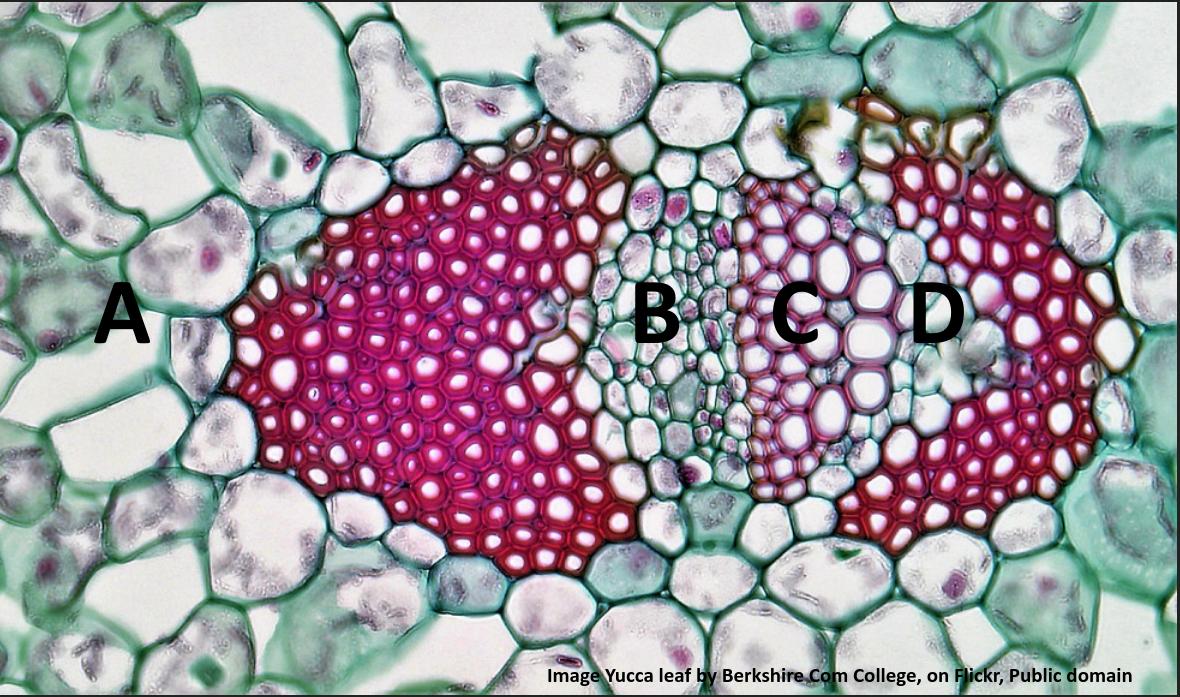
- The structure of primary xylem vessels.
- Xylem vessels transport water from roots to leaves to replace water lost in transpiration.
- The cohesive and adhesive properties of water molecules allow water transport under tension in xylem and cell walls.
- The roots cells use active transport for the uptake of mineral ions (nitrates) which causes osmosis and the absorption of water.
- Xerophytic plants in deserts have adaptations for water conservation.
Adaptations of xerophytes
- Xerophytic plants in deserts have adaptations for water conservation.
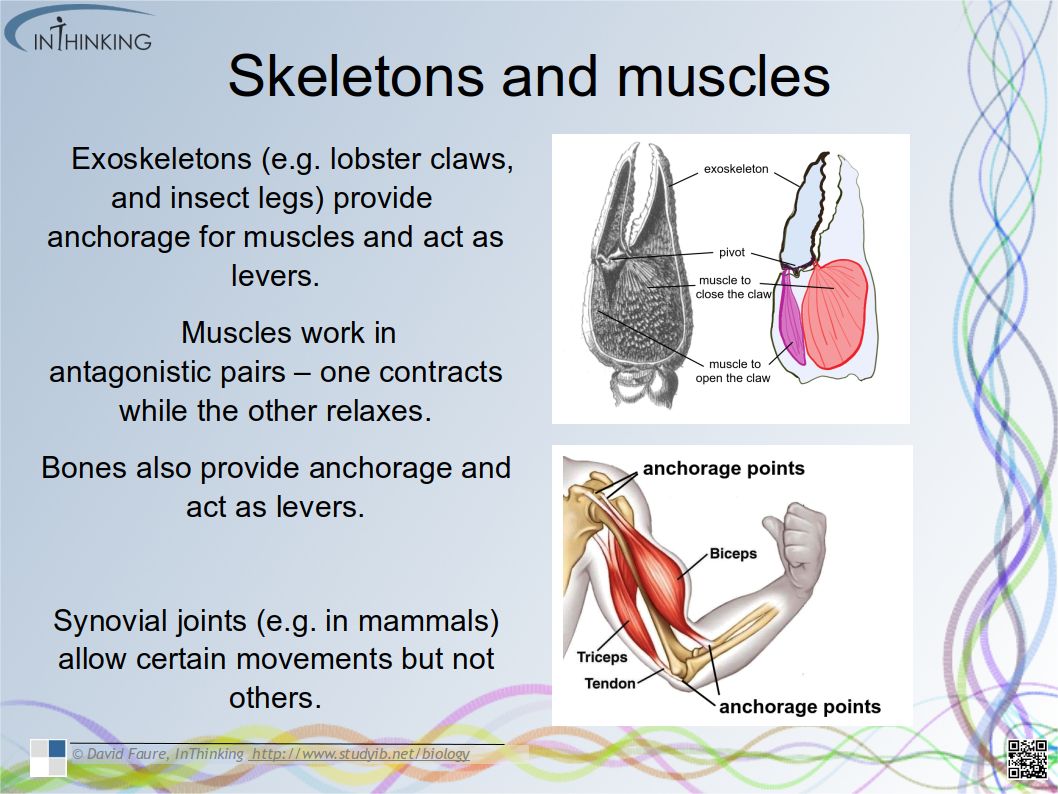
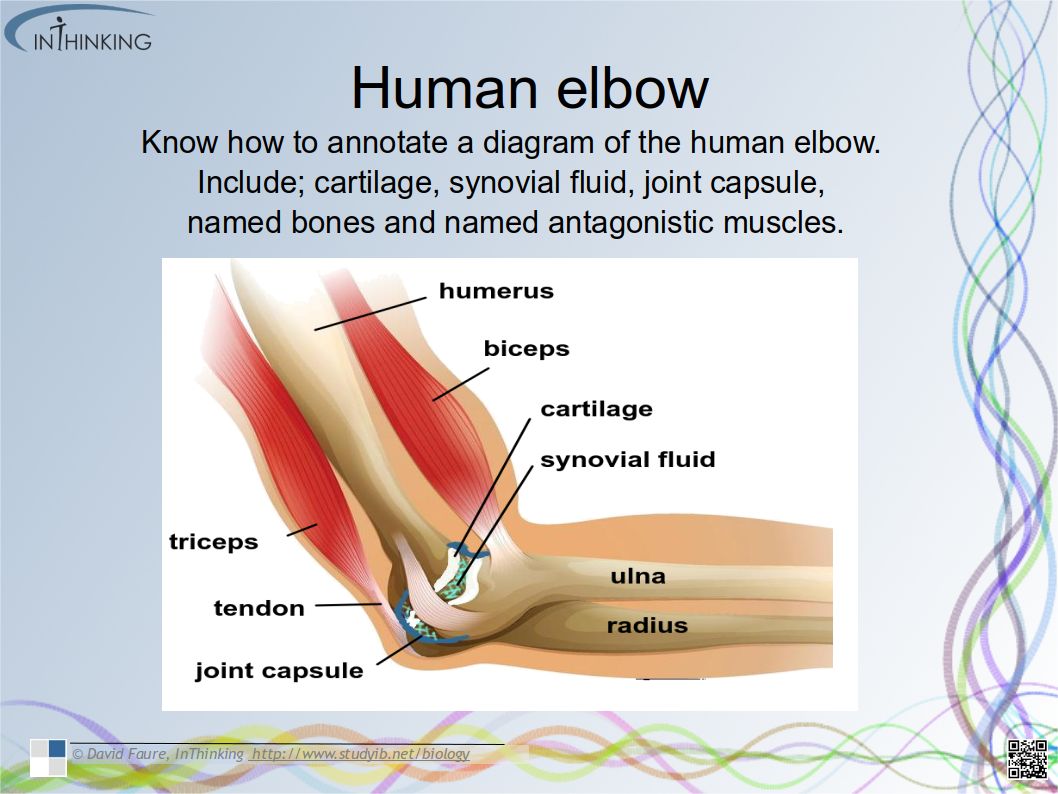
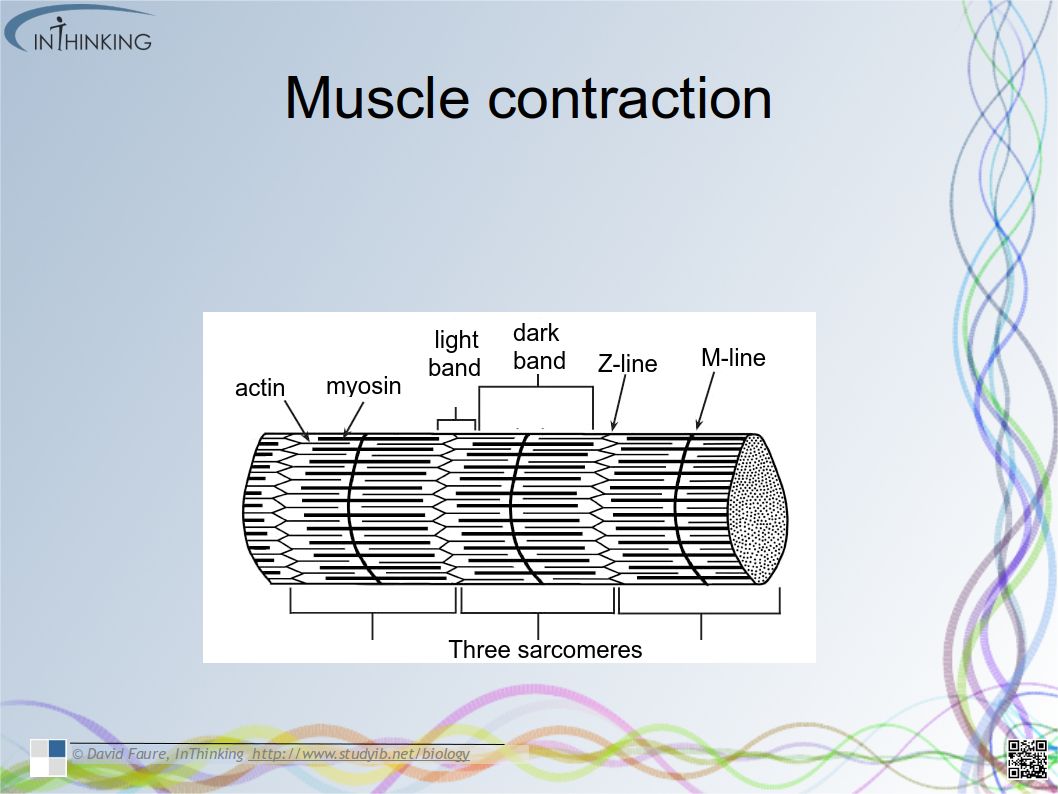
Skills
- Ability to draw the structure of primary xylem vessels in stems from microscope slides.
- Recognition of structure and function of xylem. (essential idea)
- Use potometers to measure transpiration rates
- Design an experiment to test hypotheses about the effects of abiotic factors on transpiration rates.
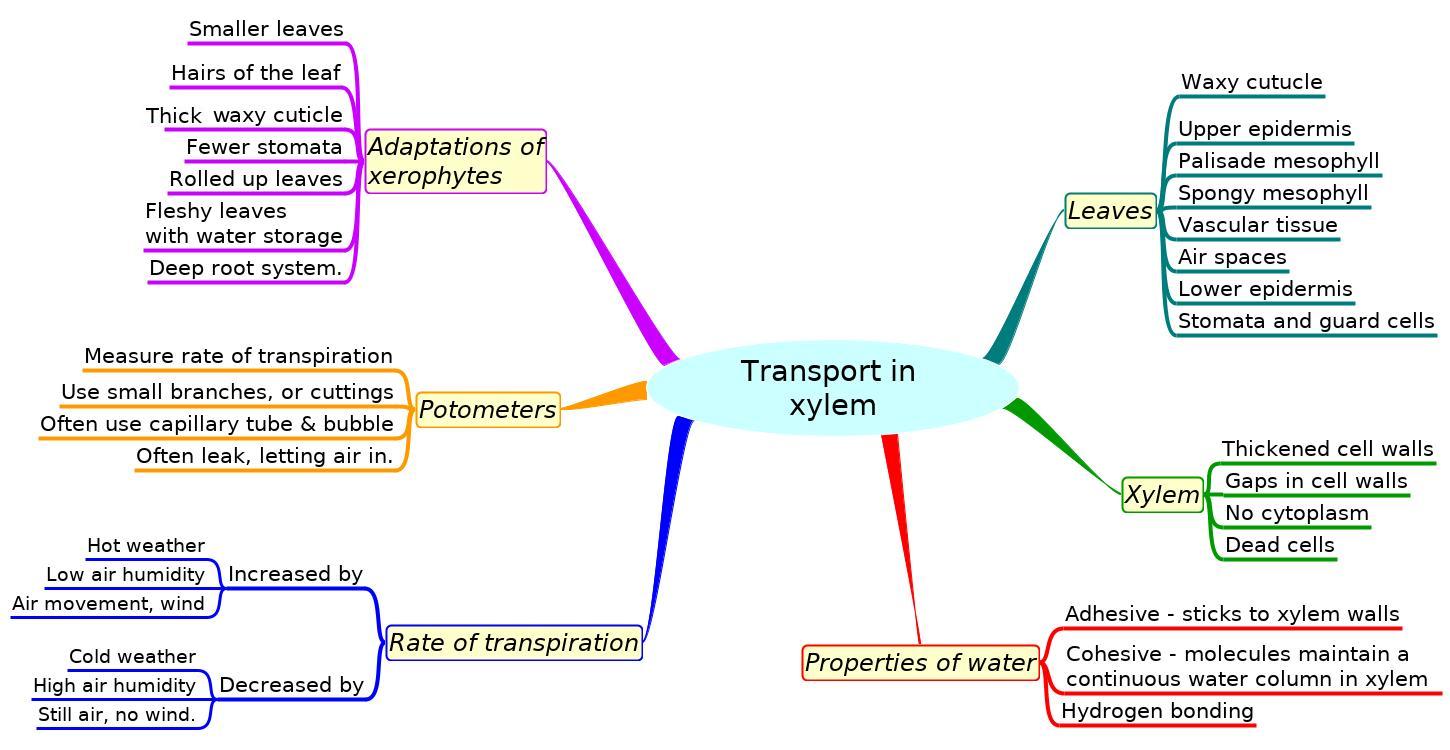
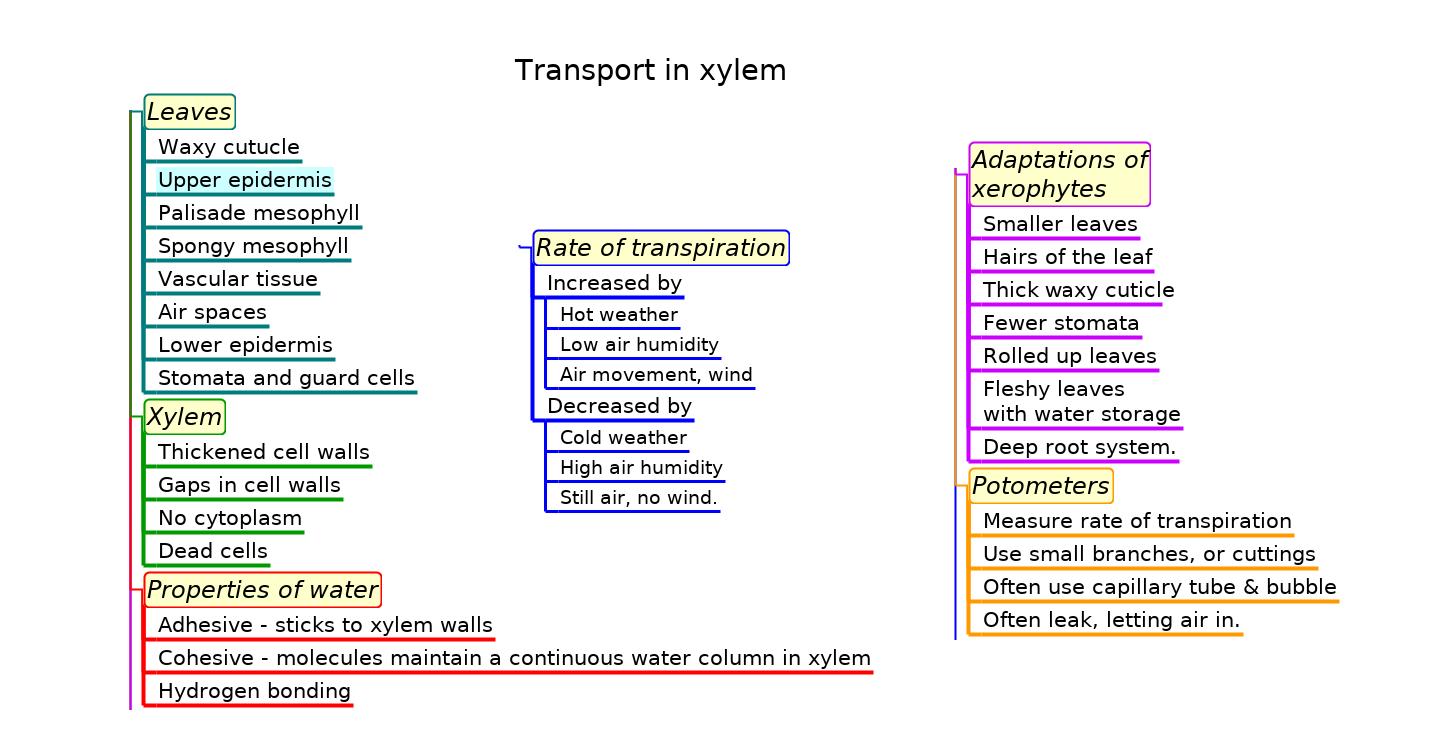
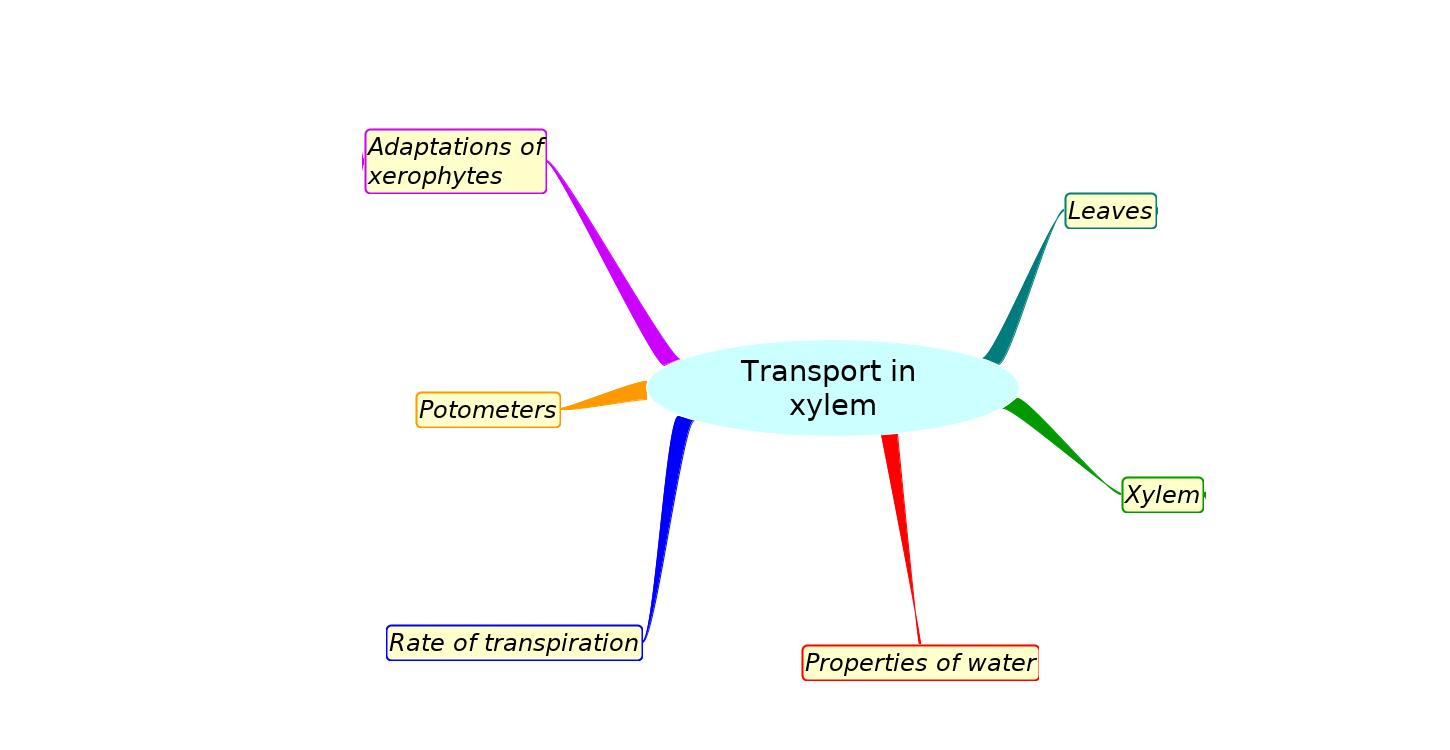
Mindmaps
These diagram summaries cover the main sections of topic 9.1 Transport in xylem.
Study them and draw your own list or concept map, from memory if you can.
Try to turn the simple mindmap into the detailed mindmap from memory.
Exam style question about transport in xylem
Design an experiment to test hypotheses about the effects of abiotic factors on transpiration rates is an important skill from this topic.
Answer the question below on a piece of paper, then check your answer against the model answer below.
The rate of transpiration can be measured using a simple potometer, shown in the diagram. [3]
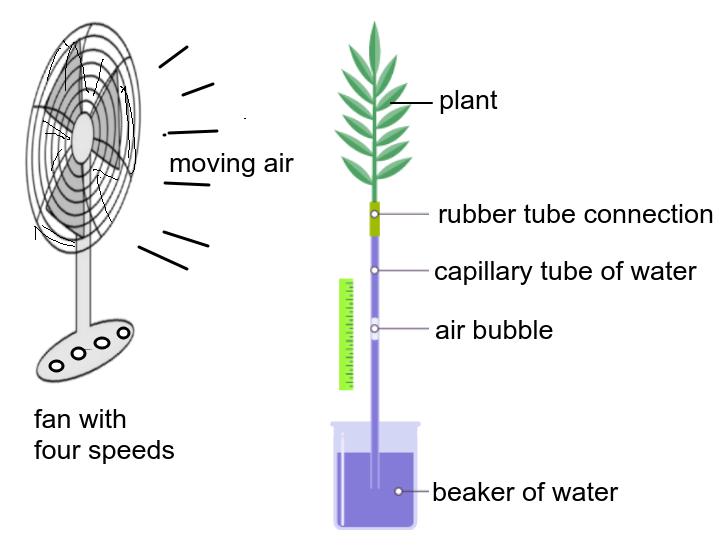
List three variables that should be controlled to ensure that only wind speed affected the movement of the bubble in the capillary tube. Explain their likely affect on the bubble movement. [3]
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
.
.
Click the + icon to see a model answer.
This is a self marking quiz containing questions covering the topic outlined above.
Try the questions to check your understanding.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
Active uptake of mineral ions in the roots causes absorption of water by osmosis.
Drag and drop the correct word or phrase into the gap to describe how plants absorb minerals from the soil.
sucrose active parasitic specific low ions hypertonic root surface osmosis fungi mutualistic concentration gradient protein ATP hypotonic
Plants absorb minerals from soil water against the by transport. This requires and several pumps in the root cell membrane, each pump being to a particular ion.
Some plants have a relationship with soil , Mycorrhiza. The fungus grows on the and actively absorbs that pass into the plant and passes from the plant tissue to the fungus.
Active absorption of minerals also creates root cell sap to soil water necessary for the inward of water from the soil into the root.
Explanation: Active transport proteins are specific to particular ions so several types are needed for the different ions required by the plant.
Halophyte (and xerophyte) adaptations to their environment is an important concept.
Drag and drop the correct term into the gap to describe halophyte adaptations to their environment.
loss removing Long osmosis saline surface area mesophytic stems gaining hydrophilic Sunken xerophytic Thickened humidity
Halophytes live in areas such as beaches, where the water is hence water gain by is lessened and the plants endure water stress.
This causes them to have habits to minimise water :
- Reduction of leaf .
- stomata to lessen water loss by maintaining high around the stomata.
- cuticle.
- Photosynthetic to compensate for reduced leaf size.
- , branching roots to reach for ground water.
They also may have structures for salt and are resistant to drought and damage..
Explanation and examiner hint: There are many similarities between halophytes and xerophytes as both have to endure water stress.
Everyone needs a bit of fun while they revise. Try this Transport in xylem terms card matching game
Can you reach the leader board?
How much of Transport in xylem 9.1 HL have you understood?














 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn