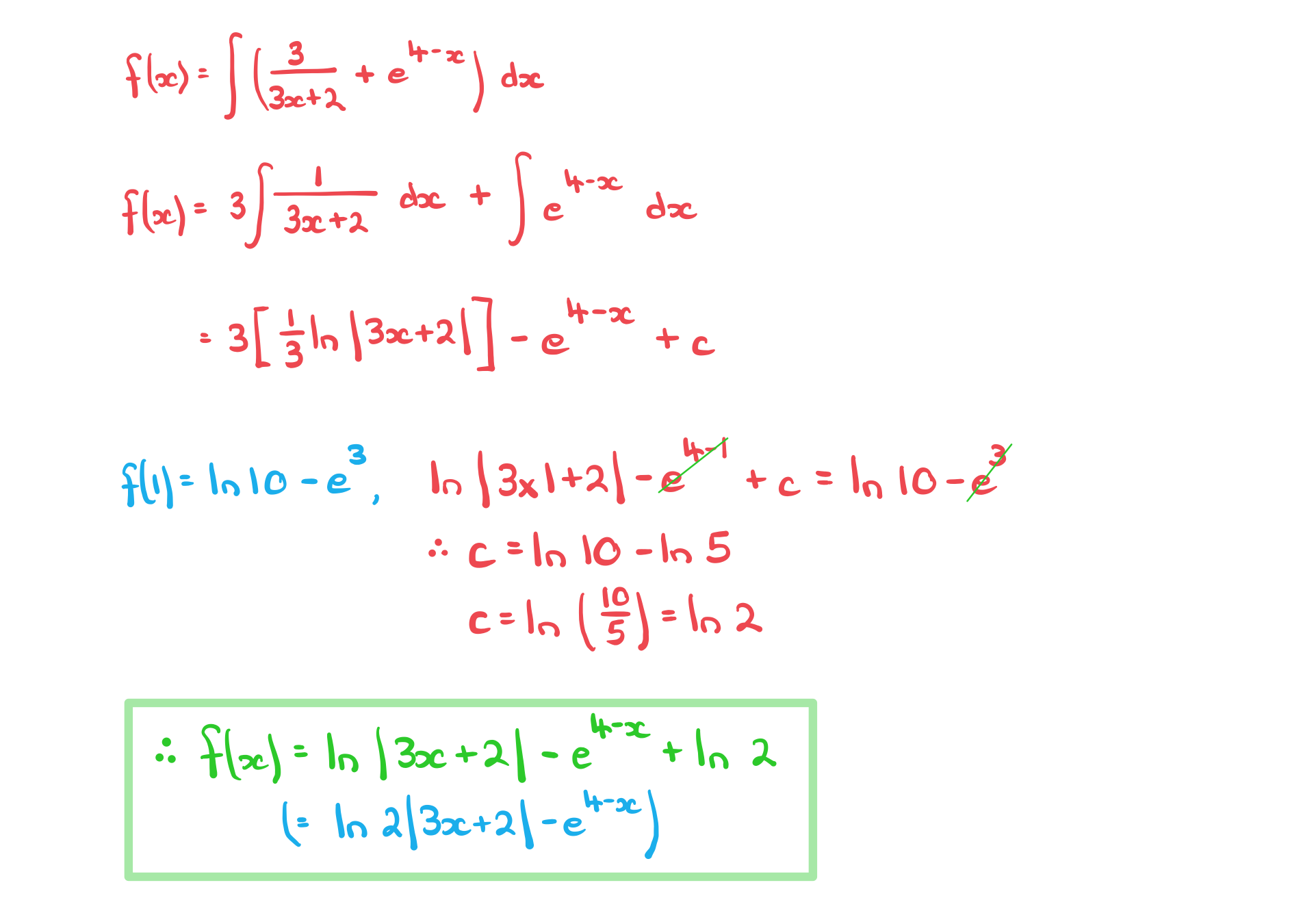Integrating Trig Functions
How do I integrate sin and cos?
- The antiderivatives for sine and cosine are
where is the constant of integration
-
- These are given in the formula booklet
- For the linear function
, where
and
are constants,
- For calculus with trigonometric functions angles must be measured in radians
- Ensure you know how to change the angle mode on your GDC
Worked Example
a)
Find, in the form%3C%2Fmo%3E%3Cmo%3E%2B%3C%2Fmo%3E%3Cmi%3Ec%3C%2Fmi%3E%3C%2Fmath%3E--%3E%3Cdefs%3E%3Cstyle%20type%3D%22text%2Fcss%22%3E%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'math117e62166fc8586dfa4d1bc0e17'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMi7iBBMAAADMAAAATmNtYXDEvmKUAAABHAAAADRjdnQgDVUNBwAAAVAAAAA6Z2x5ZoPi2VsAAAGMAAAAoWhlYWQQC2qxAAACMAAAADZoaGVhCGsXSAAAAmgAAAAkaG10eE2rRkcAAAKMAAAACGxvY2EAHTwYAAAClAAAAAxtYXhwBT0FPgAAAqAAAAAgbmFtZaBxlY4AAALAAAABn3Bvc3QB9wD6AAAEYAAAACBwcmVwa1uragAABIAAAAAUAAADSwGQAAUAAAQABAAAAAAABAAEAAAAAAAAAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAg1UADev96AAAD6ACWAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACAAAAAEAAQAAQAAACv%2F%2FwAAACv%2F%2F%2F%2FWAAEAAAAAAAABVAMsAIABAABWACoCWAIeAQ4BLAIsAFoBgAKAAKAA1ACAAAAAAAAAACsAVQCAAKsA1QEAASsABwAAAAIAVQAAAwADqwADAAcAADMRIRElIREhVQKr%2FasCAP4AA6v8VVUDAAABAIAAVQLVAqsACwBJARiyDAEBFBMQsQAD9rEBBPWwCjyxAwX1sAg8sQUE9bAGPLENA%2BYAsQAAExCxAQbksQEBExCwBTyxAwTlsQsF9bAHPLEJBOUxMBMhETMRIRUhESMRIYABAFUBAP8AVf8AAasBAP8AVv8AAQAAAAAAAQAAAAEAANV4zkFfDzz1AAMEAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FWOhNz%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Y6E3MAAP8gBIADqwAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAAD6P9qAAAXcAAA%2F7YEgAABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAgNSAFUDVgCAAAAAAAAAACgAAAChAAEAAAACAF4ABQAAAAAAAgCABAAAAAAABAAA3gAAAAAAAAAVAQIAAAAAAAAAAQASAAAAAAAAAAAAAgAOABIAAAAAAAAAAwAwACAAAAAAAAAABAASAFAAAAAAAAAABQAWAGIAAAAAAAAABgAJAHgAAAAAAAAACAAcAIEAAQAAAAAAAQASAAAAAQAAAAAAAgAOABIAAQAAAAAAAwAwACAAAQAAAAAABAASAFAAAQAAAAAABQAWAGIAAQAAAAAABgAJAHgAAQAAAAAACAAcAIEAAwABBAkAAQASAAAAAwABBAkAAgAOABIAAwABBAkAAwAwACAAAwABBAkABAASAFAAAwABBAkABQAWAGIAAwABBAkABgAJAHgAAwABBAkACAAcAIEATQBhAHQAaAAgAEYAbwBuAHQAUgBlAGcAdQBsAGEAcgBNAGEAdABoAHMAIABGAG8AcgAgAE0AbwByAGUAIABNAGEAdABoACAARgBvAG4AdABNAGEAdABoACAARgBvAG4AdABWAGUAcgBzAGkAbwBuACAAMQAuADBNYXRoX0ZvbnQATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlAAADAAAAAAAAAfQA%2BgAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAuQcRAACNhRgAsgAAABUUE7EAAT8%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'round_brackets18549f92a457f2409'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMjwHLFQAAADMAAAATmNtYXDf7xCrAAABHAAAADxjdnQgBAkDLgAAAVgAAAASZ2x5ZmAOz2cAAAFsAAABJGhlYWQOKih8AAACkAAAADZoaGVhCvgVwgAAAsgAAAAkaG10eCA6AAIAAALsAAAADGxvY2EAAARLAAAC%2BAAAABBtYXhwBIgEWQAAAwgAAAAgbmFtZXHR30MAAAMoAAACOXBvc3QDogHPAAAFZAAAACBwcmVwupWEAAAABYQAAAAHAAAGcgGQAAUAAAgACAAAAAAACAAIAAAAAAAAAQIAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAo8AMGe%2F57AAAHPgGyAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACgAAAAGAAQAAQACACgAKf%2F%2FAAAAKAAp%2F%2F%2F%2F2f%2FZAAEAAAAAAAAAAAFUAFYBAAAsAKgDgAAyAAcAAAACAAAAKgDVA1UAAwAHAAA1MxEjEyMRM9XVq4CAKgMr%2FQAC1QABAAD%2B0AIgBtAACQBNGAGwChCwA9SwAxCwAtSwChCwBdSwBRCwANSwAxCwBzywAhCwCDwAsAoQsAPUsAMQsAfUsAoQsAXUsAoQsADUsAMQsAI8sAcQsAg8MTAREAEzABEQASMAAZCQ%2FnABkJD%2BcALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAA%2FtACIAbQAAkATRgBsAoQsAPUsAMQsALUsAoQsAXUsAUQsADUsAMQsAc8sAIQsAg8ALAKELAD1LADELAH1LAKELAF1LAKELAA1LADELACPLAHELAIPDEwARABIwAREAEzAAIg%2FnCQAZD%2BcJABkALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAAAAEAAPW2NYFfDzz1AAMIAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FVre7u%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Wt7u4AAP7QA7cG0AAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAAHPv5OAAAXcAAA%2F%2F4DtwABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwDVAAACIAAAAiAAAAAAAAAAAAAkAAAAowAAASQAAQAAAAMACgACAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAABNAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABAD4AAAAAAAAAAAACAA4APgAAAAAAAAADAFwATAAAAAAAAAAEAD4AqAAAAAAAAAAFABYA5gAAAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAAAAAAAAAAIABwBGwABAAAAAAABAD4AAAABAAAAAAACAA4APgABAAAAAAADAFwATAABAAAAAAAEAD4AqAABAAAAAAAFABYA5gABAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAABAAAAAAAIABwBGwADAAEECQABAD4AAAADAAEECQACAA4APgADAAEECQADAFwATAADAAEECQAEAD4AqAADAAEECQAFABYA5gADAAEECQAGAB8A%2FAADAAEECQAIABwBGwBSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAAUgBvAHUAbgBkACAAYgByAGEAYwBrAGUAdABzACAAdwBpAHQAaAAgAGEAcwBjAGUAbgB0ACAAMQA4ADUANABSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAyAC4AMFJvdW5kX2JyYWNrZXRzX3dpdGhfYXNjZW50XzE4NTQATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlAAAAAAMAAAAAAAADnwHPAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5B%2F8AAY2FAA%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%229.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3EF%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2217.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E(%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2224.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2232.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E)%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math117e62166fc8586dfa4d1bc0e17%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2244.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%2B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2257.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ec%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) , an expression for each integral
, an expression for each integral
i)
ii)
iii)
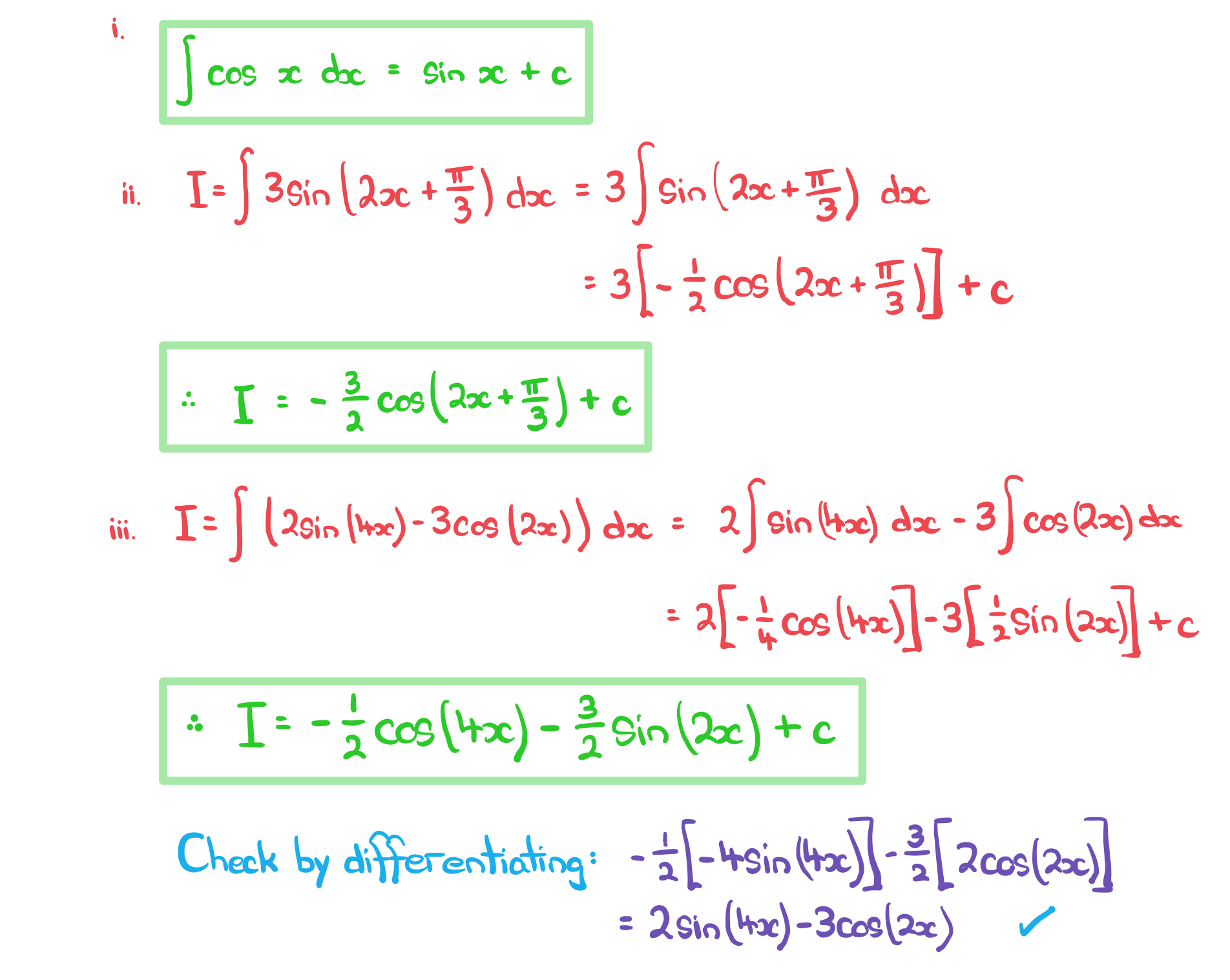
b)
The graph of%3C%2Fmo%3E%3Cmo%3E%2B%3C%2Fmo%3E%3Cmi%3Ec%3C%2Fmi%3E%3C%2Fmath%3E--%3E%3Cdefs%3E%3Cstyle%20type%3D%22text%2Fcss%22%3E%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'math1564b4c0e54101ac57a0cb68c16'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMi7iBBMAAADMAAAATmNtYXDEvmKUAAABHAAAADxjdnQgDVUNBwAAAVgAAAA6Z2x5ZoPi2VsAAAGUAAABK2hlYWQQC2qxAAACwAAAADZoaGVhCGsXSAAAAvgAAAAkaG10eE2rRkcAAAMcAAAADGxvY2EAHTwYAAADKAAAABBtYXhwBT0FPgAAAzgAAAAgbmFtZaBxlY4AAANYAAABn3Bvc3QB9wD6AAAE%2BAAAACBwcmVwa1uragAABRgAAAAUAAADSwGQAAUAAAQABAAAAAAABAAEAAAAAAAAAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAg1UADev96AAAD6ACWAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACgAAAAGAAQAAQACACsAPf%2F%2FAAAAKwA9%2F%2F%2F%2F1v%2FFAAEAAAAAAAAAAAFUAywAgAEAAFYAKgJYAh4BDgEsAiwAWgGAAoAAoADUAIAAAAAAAAAAKwBVAIAAqwDVAQABKwAHAAAAAgBVAAADAAOrAAMABwAAMxEhESUhESFVAqv9qwIA%2FgADq%2FxVVQMAAAEAgABVAtUCqwALAEkBGLIMAQEUExCxAAP2sQEE9bAKPLEDBfWwCDyxBQT1sAY8sQ0D5gCxAAATELEBBuSxAQETELAFPLEDBOWxCwX1sAc8sQkE5TEwEyERMxEhFSERIxEhgAEAVQEA%2FwBV%2FwABqwEA%2FwBW%2FwABAAACAIAA6wLVAhUAAwAHAGUYAbAIELAG1LAGELAF1LAIELAB1LABELAA1LAGELAHPLAFELAEPLABELACPLAAELADPACwCBCwBtSwBhCwB9SwBxCwAdSwARCwAtSwBhCwBTywBxCwBDywARCwADywAhCwAzwxMBMhNSEdASE1gAJV%2FasCVQHAVdVVVQAAAQAAAAEAANV4zkFfDzz1AAMEAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FWOhNz%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Y6E3MAAP8gBIADqwAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAAD6P9qAAAXcAAA%2F7YEgAABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwNSAFUDVgCAA1YAgAAAAAAAAAAoAAAAoQAAASsAAQAAAAMAXgAFAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAADeAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABABIAAAAAAAAAAAACAA4AEgAAAAAAAAADADAAIAAAAAAAAAAEABIAUAAAAAAAAAAFABYAYgAAAAAAAAAGAAkAeAAAAAAAAAAIABwAgQABAAAAAAABABIAAAABAAAAAAACAA4AEgABAAAAAAADADAAIAABAAAAAAAEABIAUAABAAAAAAAFABYAYgABAAAAAAAGAAkAeAABAAAAAAAIABwAgQADAAEECQABABIAAAADAAEECQACAA4AEgADAAEECQADADAAIAADAAEECQAEABIAUAADAAEECQAFABYAYgADAAEECQAGAAkAeAADAAEECQAIABwAgQBNAGEAdABoACAARgBvAG4AdABSAGUAZwB1AGwAYQByAE0AYQB0AGgAcwAgAEYAbwByACAATQBvAHIAZQAgAE0AYQB0AGgAIABGAG8AbgB0AE0AYQB0AGgAIABGAG8AbgB0AFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAxAC4AME1hdGhfRm9udABNAGEAdABoAHMAIABGAG8AcgAgAE0AbwByAGUAAAMAAAAAAAAB9AD6AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5BxEAAI2FGACyAAAAFRQTsQABPw%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'round_brackets18549f92a457f2409'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMjwHLFQAAADMAAAATmNtYXDf7xCrAAABHAAAADxjdnQgBAkDLgAAAVgAAAASZ2x5ZmAOz2cAAAFsAAABJGhlYWQOKih8AAACkAAAADZoaGVhCvgVwgAAAsgAAAAkaG10eCA6AAIAAALsAAAADGxvY2EAAARLAAAC%2BAAAABBtYXhwBIgEWQAAAwgAAAAgbmFtZXHR30MAAAMoAAACOXBvc3QDogHPAAAFZAAAACBwcmVwupWEAAAABYQAAAAHAAAGcgGQAAUAAAgACAAAAAAACAAIAAAAAAAAAQIAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAo8AMGe%2F57AAAHPgGyAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACgAAAAGAAQAAQACACgAKf%2F%2FAAAAKAAp%2F%2F%2F%2F2f%2FZAAEAAAAAAAAAAAFUAFYBAAAsAKgDgAAyAAcAAAACAAAAKgDVA1UAAwAHAAA1MxEjEyMRM9XVq4CAKgMr%2FQAC1QABAAD%2B0AIgBtAACQBNGAGwChCwA9SwAxCwAtSwChCwBdSwBRCwANSwAxCwBzywAhCwCDwAsAoQsAPUsAMQsAfUsAoQsAXUsAoQsADUsAMQsAI8sAcQsAg8MTAREAEzABEQASMAAZCQ%2FnABkJD%2BcALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAA%2FtACIAbQAAkATRgBsAoQsAPUsAMQsALUsAoQsAXUsAUQsADUsAMQsAc8sAIQsAg8ALAKELAD1LADELAH1LAKELAF1LAKELAA1LADELACPLAHELAIPDEwARABIwAREAEzAAIg%2FnCQAZD%2BcJABkALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAAAAEAAPW2NYFfDzz1AAMIAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FVre7u%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Wt7u4AAP7QA7cG0AAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAAHPv5OAAAXcAAA%2F%2F4DtwABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwDVAAACIAAAAiAAAAAAAAAAAAAkAAAAowAAASQAAQAAAAMACgACAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAABNAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABAD4AAAAAAAAAAAACAA4APgAAAAAAAAADAFwATAAAAAAAAAAEAD4AqAAAAAAAAAAFABYA5gAAAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAAAAAAAAAAIABwBGwABAAAAAAABAD4AAAABAAAAAAACAA4APgABAAAAAAADAFwATAABAAAAAAAEAD4AqAABAAAAAAAFABYA5gABAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAABAAAAAAAIABwBGwADAAEECQABAD4AAAADAAEECQACAA4APgADAAEECQADAFwATAADAAEECQAEAD4AqAADAAEECQAFABYA5gADAAEECQAGAB8A%2FAADAAEECQAIABwBGwBSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAAUgBvAHUAbgBkACAAYgByAGEAYwBrAGUAdABzACAAdwBpAHQAaAAgAGEAcwBjAGUAbgB0ACAAMQA4ADUANABSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAyAC4AMFJvdW5kX2JyYWNrZXRzX3dpdGhfYXNjZW50XzE4NTQATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlAAAAAAMAAAAAAAADnwHPAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5B%2F8AAY2FAA%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%228.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ey%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1564b4c0e54101ac57a0cb68c16%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2222.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%3D%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2236.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3EF%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2244.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E(%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2251.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2259.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E)%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1564b4c0e54101ac57a0cb68c16%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2271.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%2B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2284.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ec%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) for question (a) part (ii) passes through the point with coordinates
for question (a) part (ii) passes through the point with coordinates%3C%2Fmo%3E%3C%2Fmath%3E--%3E%3Cdefs%3E%3Cstyle%20type%3D%22text%2Fcss%22%3E%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'math118bf256d77607844edd9b26e32'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMi7iBBMAAADMAAAATmNtYXDEvmKUAAABHAAAADxjdnQgDVUNBwAAAVgAAAA6Z2x5ZoPi2VsAAAGUAAAA4WhlYWQQC2qxAAACeAAAADZoaGVhCGsXSAAAArAAAAAkaG10eE2rRkcAAALUAAAADGxvY2EAHTwYAAAC4AAAABBtYXhwBT0FPgAAAvAAAAAgbmFtZaBxlY4AAAMQAAABn3Bvc3QB9wD6AAAEsAAAACBwcmVwa1uragAABNAAAAAUAAADSwGQAAUAAAQABAAAAAAABAAEAAAAAAAAAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAg1UADev96AAAD6ACWAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACgAAAAGAAQAAQACACwDwP%2F%2FAAAALAPA%2F%2F%2F%2F1fxCAAEAAAAAAAAAAAFUAywAgAEAAFYAKgJYAh4BDgEsAiwAWgGAAoAAoADUAIAAAAAAAAAAKwBVAIAAqwDVAQABKwAHAAAAAgBVAAADAAOrAAMABwAAMxEhESUhESFVAqv9qwIA%2FgADq%2FxVVQMAAAEAVf9kANUAgAAKAAAzNTMVFAYHJz4BN1WALy8bHh4BgHo9URQpDjQxAAEAVQAAAsACQAAZAEEYAbAaELAN1LANELAH1LAHELAE1LAEELAY1ACwGhCwC9SwGhCwAtSwGhCwD9SwDxCwFNSwDxCwBjywDxCwFzwwMSUGIyI1AyMRFAYrATY1NCciFSM0MyEVIxMUAsAVQIABqikBVSoBVUBqAgGBAVVV1QEW%2FuqVQECVgJYrgFX%2B6sAAAAAAAQAAAAEAANV4zkFfDzz1AAMEAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FWOhNz%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Y6E3MAAP8gBIADqwAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAAD6P9qAAAXcAAA%2F7YEgAABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwNSAFUBMwBVAxYAVQAAAAAAAAAoAAAAUgAAAOEAAQAAAAMAXgAFAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAADeAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABABIAAAAAAAAAAAACAA4AEgAAAAAAAAADADAAIAAAAAAAAAAEABIAUAAAAAAAAAAFABYAYgAAAAAAAAAGAAkAeAAAAAAAAAAIABwAgQABAAAAAAABABIAAAABAAAAAAACAA4AEgABAAAAAAADADAAIAABAAAAAAAEABIAUAABAAAAAAAFABYAYgABAAAAAAAGAAkAeAABAAAAAAAIABwAgQADAAEECQABABIAAAADAAEECQACAA4AEgADAAEECQADADAAIAADAAEECQAEABIAUAADAAEECQAFABYAYgADAAEECQAGAAkAeAADAAEECQAIABwAgQBNAGEAdABoACAARgBvAG4AdABSAGUAZwB1AGwAYQByAE0AYQB0AGgAcwAgAEYAbwByACAATQBvAHIAZQAgAE0AYQB0AGgAIABGAG8AbgB0AE0AYQB0AGgAIABGAG8AbgB0AFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAxAC4AME1hdGhfRm9udABNAGEAdABoAHMAIABGAG8AcgAgAE0AbwByAGUAAAMAAAAAAAAB9AD6AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5BxEAAI2FGACyAAAAFRQTsQABPw%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'brack_sm2882ad605b1e27be87c7468'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMi7PH4UAAADMAAAATmNtYXA3kjw6AAABHAAAADxjdnQgAQYDiAAAAVgAAAASZ2x5ZkyYQ7YAAAFsAAAAkWhlYWQLyR8fAAACAAAAADZoaGVhAq0XCAAAAjgAAAAkaG10eDEjA%2FUAAAJcAAAADGxvY2EAAEKZAAACaAAAABBtYXhwBJsEcQAAAngAAAAgbmFtZW7QvZAAAAKYAAAB5XBvc3QArQBVAAAEgAAAACBwcmVwu5WEAAAABKAAAAAHAAACDAGQAAUAAAQABAAAAAAABAAEAAAAAAAAAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAg9AMD%2FP%2F8AAABVAABAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACgAAAAGAAQAAQACI5wjn%2F%2F%2FAAAjnCOf%2F%2F%2FcZdxjAAEAAAAAAAAAAAFUAFQBAAArAIwAgACoAAcAAAACAAAAAADVAQEAAwAHAAAxMxEjFyM1M9XVq4CAAQHWqwABAAAAAABVAVgAAwAfGAGwAy%2BwADyxAgL1sAE8ALEDAD%2BwAjx8sQAG9bABPBEzESNVVQFY%2FqgAAQDXAAABLAFUAAMAIBgBsAUvsAE8sAI8sQAC9bADPACwAy%2BwAjyxAAH1sAE8EzMRI9dVVQFU%2FqwAAAAAAQAAAAEAAIsesexfDzz1AAMEAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FVre5k%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Wt7mT%2FgP%2F%2FAdYBWAAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAABVP%2F%2FAAAXcP%2BA%2F4AB1gABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwDVAAABLAAAASwA1wAAAAAAAAAhAAAAWAAAAJEAAQAAAAMACgACAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAABlAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABACYAAAAAAAAAAAACAA4AJgAAAAAAAAADAEQANAAAAAAAAAAEACYAeAAAAAAAAAAFABYAngAAAAAAAAAGABMAtAAAAAAAAAAIABwAxwABAAAAAAABACYAAAABAAAAAAACAA4AJgABAAAAAAADAEQANAABAAAAAAAEACYAeAABAAAAAAAFABYAngABAAAAAAAGABMAtAABAAAAAAAIABwAxwADAAEECQABACYAAAADAAEECQACAA4AJgADAAEECQADAEQANAADAAEECQAEACYAeAADAAEECQAFABYAngADAAEECQAGABMAtAADAAEECQAIABwAxwBCAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIABzAG0AYQBsAGwAIABzAGkAegBlAFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAAQgByAGEAYwBrAGUAdABzACAAcwBtAGEAbABsACAAcwBpAHoAZQBCAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIABzAG0AYQBsAGwAIABzAGkAegBlAFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAyAC4AMEJyYWNrZXRzX3NtYWxsX3NpemUATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlAAAAAAMAAAAAAAAAqgBVAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5B%2F8AAo2FAA%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'bracketse552f5417ff4680c6b50499'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMi7RIisAAADMAAAATmNtYXBi7uzYAAABHAAAAExjdnQgBAkDLgAAAWgAAAASZ2x5Zo64f%2BkAAAF8AAABSWhlYWQLniGcAAACyAAAADZoaGVhBK4XLAAAAwAAAAAkaG10eCWq%2F90AAAMkAAAAFGxvY2EAABknAAADOAAAABhtYXhwBJIESAAAA1AAAAAgbmFtZRAA8I4AAANwAAAB3nBvc3QBwwDgAAAFUAAAACBwcmVwupWEAAAABXAAAAAHAAACggGQAAUAAAQABAAAAAAABAAEAAAAAAAAAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAg9AMEAAAAAAADgAAAAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEADgAAAAKAAgAAgACI5sjnSOeI6D%2F%2FwAAI5sjnSOeI6D%2F%2F9xm3GXcZdxkAAEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABVABWAQAALACoA4AAMgAHAAAAAgAAACoA1QNVAAMABwAANTMRIxMjETPV1auAgCoDK%2F0AAtUAAQAAAAABgAOAAAUAJBgBsAAvsAPFsQEC%2FbADELEEBP0AsQAAP7ABPLEEBj%2BwAzwwMTEzEAEjAFUBKyv%2BqwH8AYT%2BqgABAAAAAAGAA4AABQAmGAGwAC6wA8WxBQL9sAMQsQIE%2FQB8sQAGPxiwBTyxAwb2sAI8MDEREgEzABMBAVQr%2FtMCA4D91v6qAYQB%2FAAB%2F6wAAAEsA4AABQAnGAGwAC%2BwBzywA8WxAQL9sAMQsQQE%2FQCxAAA%2FsAE8sQQGP7ADPDAxISMSATMAASxVAf7UKwFVAfwBhP6rAAH%2FrAAAASwDgAAFACkYAbABL7AHPLAExbEAAv2wBBCxAwT9AHyxAQY%2FsAA8GLEEAD%2BwAzwwMRMzEAEjANdV%2FqsrASsDgP3V%2FqsBhgAAAAABAAAAAQAAeuTcpl8PPPUAAwQA%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Wt7o7%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F1a3ujv%2BsAAABgAOAAAAACgACAAEAAAAAAAEAAAOAAAAAABdw%2F6z%2FrAGAAAEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAFANUAAAEsAAABLAAAASz%2FrAEs%2F6wAAAAAAAAAJAAAAGgAAACzAAAA%2FQAAAUkAAQAAAAUACAACAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAAA%2BAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABACQAAAAAAAAAAAACAA4AJAAAAAAAAAADAEIAMgAAAAAAAAAEACQAdAAAAAAAAAAFABYAmAAAAAAAAAAGABIArgAAAAAAAAAIABwAwAABAAAAAAABACQAAAABAAAAAAACAA4AJAABAAAAAAADAEIAMgABAAAAAAAEACQAdAABAAAAAAAFABYAmAABAAAAAAAGABIArgABAAAAAAAIABwAwAADAAEECQABACQAAAADAAEECQACAA4AJAADAAEECQADAEIAMgADAAEECQAEACQAdAADAAEECQAFABYAmAADAAEECQAGABIArgADAAEECQAIABwAwABCAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIABmAHUAbABsACAAcwBpAHoAZQBSAGUAZwB1AGwAYQByAE0AYQB0AGgAcwAgAEYAbwByACAATQBvAHIAZQAgAEIAcgBhAGMAawBlAHQAcwAgAGYAdQBsAGwAIABzAGkAegBlAEIAcgBhAGMAawBlAHQAcwAgAGYAdQBsAGwAIABzAGkAegBlAFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAyAC4AMEJyYWNrZXRzX2Z1bGxfc2l6ZQBNAGEAdABoAHMAIABGAG8AcgAgAE0AbwByAGUAAAADAAAAAAAAAcAA4AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAuQf%2FAAGNhQA%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22bracketse552f5417ff4680c6b50499%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%225.5%22%20y%3D%2217%22%3E%26%23x239B%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm2882ad605b1e27be87c7468%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%225.5%22%20y%3D%2223%22%3E%26%23x239C%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm2882ad605b1e27be87c7468%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%225.5%22%20y%3D%2229%22%3E%26%23x239C%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22bracketse552f5417ff4680c6b50499%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%225.5%22%20y%3D%2245%22%3E%26%23x239D%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Cline%20stroke%3D%22%23000000%22%20stroke-linecap%3D%22square%22%20stroke-width%3D%221%22%20x1%3D%2213.5%22%20x2%3D%2228.5%22%20y1%3D%2223.5%22%20y2%3D%2223.5%22%2F%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math118bf256d77607844edd9b26e32%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2221.5%22%20y%3D%2219%22%3E%26%23x3C0%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2221.5%22%20y%3D%2241%22%3E3%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math118bf256d77607844edd9b26e32%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2233.5%22%20y%3D%2230%22%3E%2C%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Cline%20stroke%3D%22%23000000%22%20stroke-linecap%3D%22square%22%20stroke-width%3D%221%22%20x1%3D%2242.5%22%20x2%3D%2254.5%22%20y1%3D%2223.5%22%20y2%3D%2223.5%22%2F%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2248.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E5%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2248.5%22%20y%3D%2241%22%3E2%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22bracketse552f5417ff4680c6b50499%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2258.5%22%20y%3D%2217%22%3E%26%23x239E%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm2882ad605b1e27be87c7468%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2258.5%22%20y%3D%2223%22%3E%26%23x239F%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm2882ad605b1e27be87c7468%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2258.5%22%20y%3D%2229%22%3E%26%23x239F%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22bracketse552f5417ff4680c6b50499%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2258.5%22%20y%3D%2245%22%3E%26%23x23A0%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) .
.
Find the value of .
.
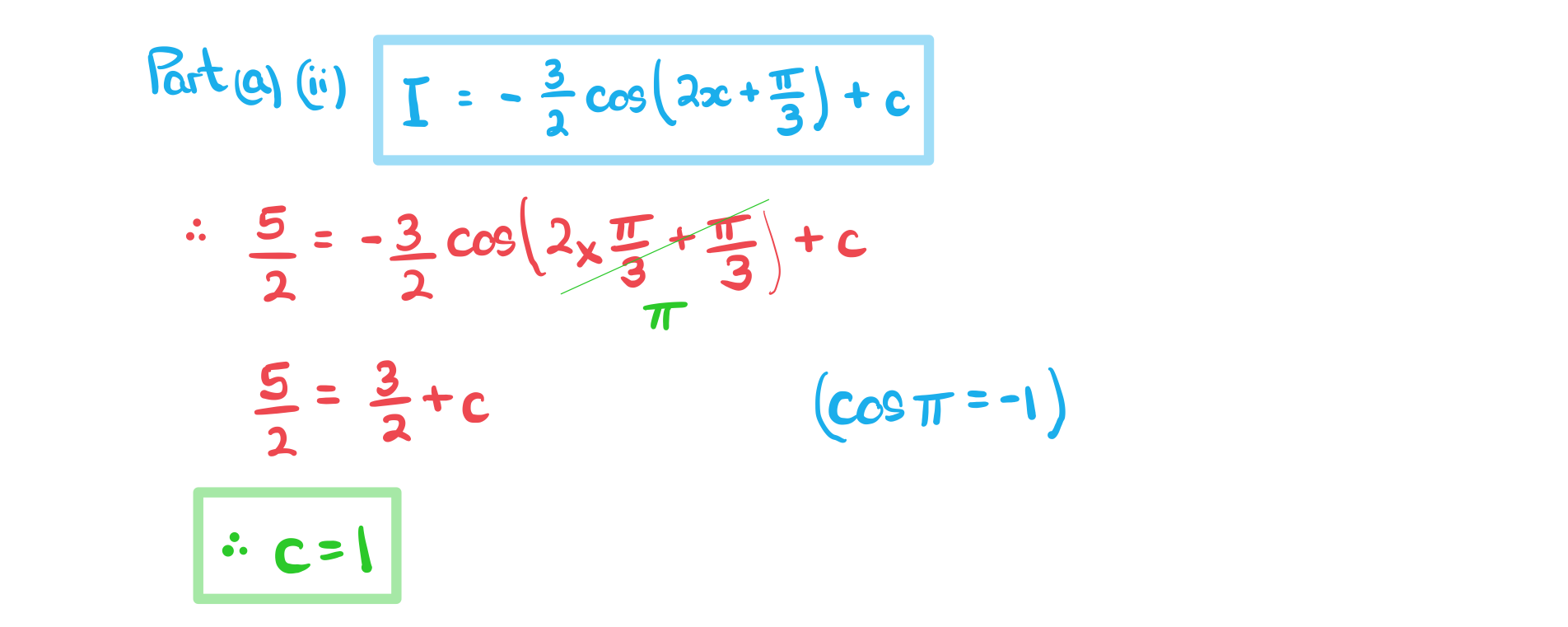
Integrating e^x & 1/x
How do I integrate exponentials and logarithms?
- The antiderivatives for
and
are
where is the constant of integration
-
- These are given in the formula booklet
- For the linear function
, where
and
are constants,
- It follows from the last result that
-
- which can be deduced using Reverse Chain Rule
- With ln, it can be useful to write the constant of integration,
, as a logarithm
- using the laws of logarithms, the answer can be written as a single term
where
is a constant
- This is similar to the special case of differentiating
when
Exam Tip
- Make sure you have a copy of the formula booklet during revision but don't try to remember everything in the formula booklet
- However, do be familiar with the layout of the formula booklet – you’ll be able to locate quickly whatever you are after, and you do not want to be searching every line of every page!
- For formulae you think you have remembered, use the booklet to double-check
Worked Example
A curve has the gradient function.
Given the exact value of is
find an expression for
.