DP Chemistry Questionbank

B.9 Biological pigments (HL only)
Description
[N/A]Directly related questions
-
16N.3.hl.TZ0.16c:
A student investigated the ability of anthocyanins to act as pH indicators. He extracted juice from blackberries and used a UV-vis spectrophotometer to produce absorption spectra at different pH values. His results are shown below.
Deduce the colour of the juice at each pH, giving your reasoning. Use section 17 of the data booklet.
- 16N.3.hl.TZ0.16a: Outline why this molecule absorbs visible light.
- 16N.3.hl.TZ0.16b: With reference to its chemical structure, outline whether this pigment is found in aqueous...
-
17M.3.hl.TZ1.16b.ii:
Outline the effect of decreasing pH on the oxygen saturation of hemoglobin.
-
17M.3.hl.TZ1.16a:
Explain the shape of the curve at low oxygen partial pressure up to about 5 kPa.
-
17M.3.hl.TZ1.16b.i:
Sketch a graph on the axes above to show the effect of decreasing pH on the binding of oxygen to hemoglobin (the Bohr Effect).
-
17M.3.hl.TZ2.14a:
Explain the shape of the curve from 0 to X kPa.
-
17M.3.hl.TZ2.14b:
Explain why carbon monoxide is toxic to humans.
-
20N.3.hl.TZ0.6c(ii):
Proteins are polymers of amino acids.
Explain why the affinity for oxygen of foetal hemoglobin differs from that of adult hemoglobin.
- 20N.3.hl.TZ0.6c(i): Proteins are polymers of amino acids. Sketch and label two oxygen dissociation curves, one for...
-
17N.3.hl.TZ0.14a:
State the half-equation for the reduction of molecular oxygen to water in acidic conditions.
- 17N.3.hl.TZ0.14b: Outline the change in oxidation state of the iron ions in heme groups that occurs when molecular...
-
18M.3.hl.TZ1.10a:
Outline why anthocyanins are coloured.
-
18M.3.hl.TZ1.10b:
Explain why the blue colour of a quinoidal base changes to the red colour of a flavylium cation as pH decreases.
-
18M.3.hl.TZ2.11a:
Hemoglobin’s oxygen dissociation curve is shown at a given temperature. Sketch the curve on the graph at a higher temperature.
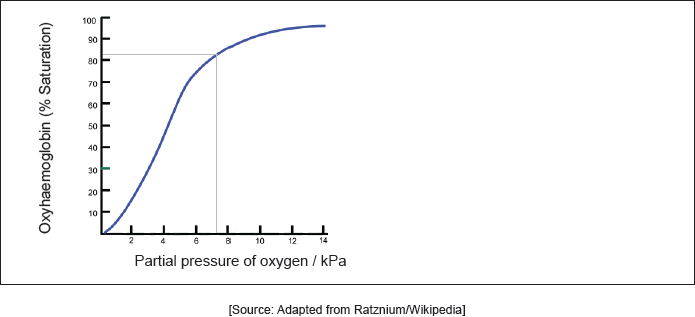
-
18M.3.hl.TZ2.11b:
Outline two differences between normal hemoglobin and foetal hemoglobin.
-
18N.3.hl.TZ0.11b:
Explain why carbon monoxide is very toxic and how it may be possible to treat carbon monoxide poisoning.
- 18N.3.hl.TZ0.11a: A graph showing saturation of oxygen against partial pressure of oxygen is shown. Explain the...
-
19M.3.hl.TZ1.11a:
The absorption spectrum of β-carotene is shown below.
Explain its colour in terms of its absorption bands. Use section 17 of the data booklet.
-
19M.3.hl.TZ1.11b:
The absorption spectrum of chlorophyll a is shown below.
Suggest how the combination of chlorophyll a and carotenoids is beneficial for photosynthesis.
-
19M.3.hl.TZ1.19b(ii):
Identify the splitting pattern of signals X and Y.
X:
Y:
-
19M.3.hl.TZ1.19b(i):
Deduce the protons responsible for signals X and Y by marking them on the structure of aspirin in (a). Use section 27 of the data booklet.
-
19M.3.hl.TZ2.13a:
Outline why the complex formed between Fe2+ and oxygen is red. Refer to the diagram above and section 17 of the data booklet.
- 19M.3.hl.TZ2.13b(ii): Sketch another line to show the effect of an increase in body temperature on the oxygen...
-
19M.3.hl.TZ2.13b(i):
Explain the shape of the curve.
- 19N.3.hl.TZ0.14a: The graph shows the change in oxygen partial pressure in blood, measured at different pH...
- 19N.3.hl.TZ0.15a: Describe the function of chlorophyll in photosynthesis.
