| Date | May 2014 | Marks available | 7 | Reference code | 14M.1.hl.TZ1.11 |
| Level | HL only | Paper | 1 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Find | Question number | 11 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Consider the function \(f(x) = \frac{{\ln x}}{x},{\text{ }}x > 0\).
The sketch below shows the graph of \(y = {\text{ }}f(x)\) and its tangent at a point A.
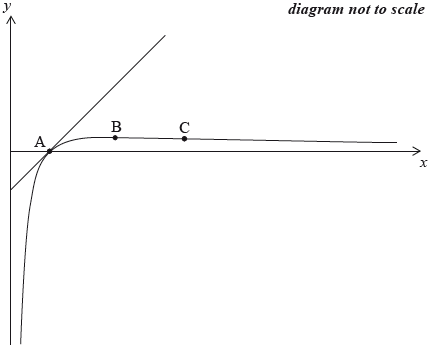
Show that \(f'(x) = \frac{{1 - \ln x}}{{{x^2}}}\).
Find the coordinates of B, at which the curve reaches its maximum value.
Find the coordinates of C, the point of inflexion on the curve.
The graph of \(y = {\text{ }}f(x)\) crosses the \(x\)-axis at the point A.
Find the equation of the tangent to the graph of \(f\) at the point A.
The graph of \(y = {\text{ }}f(x)\) crosses the \(x\)-axis at the point A.
Find the area enclosed by the curve \(y = f(x)\), the tangent at A, and the line \(x = {\text{e}}\).
Markscheme
\(f'(x) = \frac{{x \times \frac{1}{x} - \ln x}}{{{x^2}}}\) M1A1
\( = \frac{{1 - \ln x}}{{{x^2}}}\) AG
[2 marks]
\(\frac{{1 - \ln x}}{{{x^2}}} = 0\) has solution \(x = {\text{e}}\) M1A1
\(y = \frac{1}{{\text{e}}}\) A1
hence maximum at the point \(\left( {{\text{e, }}\frac{1}{{\text{e}}}} \right)\)
[3 marks]
\(f''(x) = \frac{{{x^2}\left( { - \frac{1}{x}} \right) - 2x(1 - \ln x)}}{{{x^4}}}\) M1A1
\( = \frac{{2\ln x - 3}}{{{x^3}}}\)
Note: The M1A1 should be awarded if the correct working appears in part (b).
point of inflexion where \(f''(x) = 0\) M1
so \(x = {{\text{e}}^{\frac{3}{2}}},{\text{ }}y = \frac{3}{2}{{\text{e}}^{\frac{{ - 3}}{2}}}\) A1A1
C has coordinates \(\left( {{{\text{e}}^{\frac{3}{2}}},{\text{ }}\frac{3}{2}{{\text{e}}^{\frac{{ - 3}}{2}}}} \right)\)
[5 marks]
\(f(1) = 0\) A1
\(f'(1) = 1\) (A1)
\(y = x + c\) (M1)
through (1, 0)
equation is \(y = x - 1\) A1
[4 marks]
METHOD 1
area \( = \int_1^{\text{e}} {x - 1 - \frac{{\ln x}}{x}{\text{d}}x} \) M1A1A1
Note: Award M1 for integration of difference between line and curve, A1 for correct limits, A1 for correct expressions in either order.
\(\int {\frac{{\ln x}}{x}{\text{d}}x = \frac{{{{(\ln x)}^2}}}{2}} ( + c)\) (M1)A1
\(\int {(x - 1){\text{d}}x = \frac{{{x^2}}}{2} - x( + c)} \) A1
\( = \left[ {\frac{1}{2}{x^2} - x - \frac{1}{2}{{(\ln x)}^2}} \right]_1^{\text{e}}\)
\( = \left( {\frac{1}{2}{{\text{e}}^2} - {\text{e}} - \frac{1}{2}} \right) - \left( {\frac{1}{2} - 1} \right)\)
\( = \frac{1}{2}{{\text{e}}^2} - {\text{e}}\) A1
METHOD 2
area = area of triangle \( - \int_1^e {\frac{{\ln x}}{x}{\text{d}}x} \) M1A1
Note: A1 is for correct integral with limits and is dependent on the M1.
\(\int {\frac{{\ln x}}{x}{\text{d}}x = \frac{{{{(\ln x)}^2}}}{2}( + c)} \) (M1)A1
area of triangle \( = \frac{1}{2}(e - 1)(e - 1)\) M1A1
\(\frac{1}{2}(e - 1)(e - 1) - \left( {\frac{1}{2}} \right) = \frac{1}{2}{{\text{e}}^2} - {\text{e}}\) A1
[7 marks]

