| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 18M.1.HL.TZ1.13 |
| Level | Higher level | Paper | Paper 1 | Time zone | Time zone 1 |
| Command term | Question number | 13 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
A ray of light passes from the air into a long glass plate of refractive index n at an angle θ to the edge of the plate.
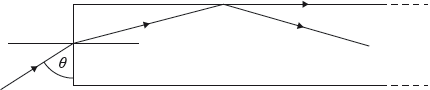
The ray is incident on the internal surface of the glass plate and the refracted ray travels along the external surface of the plate.
What change to n and what change to θ will cause the ray to travel entirely within the plate after incidence?
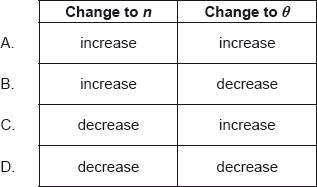
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
[N/A]
Syllabus sections
Show 68 related questions
- 18M.2.SL.TZ2.3b.ii: Draw lines on the diagram to complete wavefronts A and B in water for θ < θmax.
- 18M.2.SL.TZ2.3b.i: The speed of sound in air is 340 m s–1 and in water it is 1500 m s–1. The wavefronts make an...
- 18M.1.SL.TZ2.18: A pair of slits in a double slit experiment are illuminated with monochromatic light...
- 18M.1.SL.TZ2.16: What are the changes in the speed and in the wavelength of monochromatic light when the light...
- 18M.2.SL.TZ1.3b.ii: State two ways in which the intensity pattern on the screen changes.
- 18M.2.SL.TZ1.3b.i: Calculate the wavelength of the light in water.
- 18M.2.SL.TZ1.3a.ii: The wavelength of the beam as observed on Earth is 633.0 nm. The separation between a dark...
- 18M.1.SL.TZ1.15: The diagram shows an interference pattern produced by two sources that oscillate on the...
- 17N.2.SL.TZ0.4a.iii: Sketch, on the diagram, the subsequent path of the light ray.
- 17N.2.SL.TZ0.4a.ii: Show that no light emerges from side AB.
- 17N.2.SL.TZ0.4a.i: Calculate the speed of light inside the ice cube.
- 17N.1.SL.TZ0.15: The refractive index for light travelling from medium X to medium Y is \(\frac{4}{3}\). The...
- 17M.2.SL.TZ2.3b.i: The slits are separated by 1.5 mm and the laser light has a wavelength of 6.3 x 10–7 m. The...
- 17M.2.SL.TZ2.3a: Explain, with reference to the light passing through the slits, why a series of voltage peaks...
- 17M.2.SL.TZ1.2d: One of the slits is now covered. Describe the appearance of the pattern on the screen.
- 17M.2.SL.TZ1.2c: Explain the change to the appearance of the interference pattern when the red-light laser is...
- 17M.2.SL.TZ1.2b: Red laser light is incident on a double slit with a slit separation of 0.35 mm.A double-slit...
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.17: When a sound wave travels from a region of hot air to a region of cold air, it refracts as...
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.15: Two pulses are travelling towards each other. What is a possible pulse shape when the...
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.15: Which diagram shows the shape of the wavefront as a result of the diffraction of plane waves...
- 16N.1.SL.TZ0.16: A spring XY lies on a frictionless table with the end Y free. A horizontal pulse travels...
- 16N.1.SL.TZ0.15: A light ray is incident on an air–diamond boundary. The refractive index of diamond is...
- 16M.1.SL.TZ0.17: A light...
- 15M.1.SL.TZ2.14: A water wave entering a harbour passes suddenly from deep to shallow water. In deep water,...
- 14M.1.SL.TZ1.14: The speed of a wave in medium X is greater than the speed of the wave in medium Y. Which...
- 14M.1.SL.TZ1.15: Two loudspeakers, L1 and L2, emit identical sound waves. The waves leaving L1 and L2 are...
- 14M.1.HL.TZ1.18: Monochromatic coherent light is incident on a narrow rectangular slit. The diffracted light...
- 14M.2.HL.TZ1.4b: A source of sound is placed in front of a barrier that has an opening of width comparable to...
- 15N.1.HL.TZ0.17: Light is incident from air on the surface of a transparent medium. When V is equal to the...
- 14M.3.SL.TZ1.20a: Two radio stations, A and B, broadcast two coherent signals. The separation d between A and B...
- 14N.1.SL.TZ0.12: A high solid wall separates two gardens X and Y. Music from a loudspeaker in X can be heard...
- 15N.2.SL.TZ0.4f.i: State what is meant by the principle of superposition of waves.
- 15N.2.SL.TZ0.4f.ii: On the graph opposite, sketch the wave that results from the superposition of wave A and wave...
- 14M.3.SL.TZ1.20b: The receiver R then moves along a different line M which is at 90º to line L. Discuss the...
- 15N.3.SL.TZ0.21a: State one way to ensure that the light incident on the slits is coherent.
- 15N.3.SL.TZ0.21b: Light emerging from \({{\text{S}}_{\text{1}}}\) and \({{\text{S}}_{\text{2}}}\) reaches the...
- 15N.3.SL.TZ0.21c.i: Determine the change in angle when blue light of wavelength 440 nm is used.
- 14N.3.SL.TZ0.22a: With reference to interference, explain why the intensity of sound alternates along line AB.
- 14N.3.SL.TZ0.22b: The sound has a maximum intensity at P. Calculate the distance along line AB to the next...
- 14N.3.SL.TZ0.22c: S1 and S2 are moved so that they are now 3.0 m apart. They remain at the same distance from...
- 14M.2.SL.TZ2.5c: (i) Draw rays to show how the person at position 1 is able to hear the sound emitted by...
- 14M.2.SL.TZ2.5d: The arrangement in (c) is changed and another loudspeaker is added. Both loudspeakers emit...
- 11N.1.HL.TZ0.17: The phenomenon of diffraction is associated with A. sound waves only.B. light waves only.C....
- 13N.1.SL.TZ0.16: Two identical waves of wavelength λ leave two sources in phase. The waves meet and superpose...
- 13M.1.HL.TZ1.12: A point source of sound is placed behind a soundproof barrier as shown in the...
- 13M.2.SL.TZ1.3b: The diagram shows two point sources of sound, X and Y. Each source emits waves of wavelength...
- 12M.1.SL.TZ1.15: A ray of light travels from a vacuum into glass as shown below. In glass, light has speed...
- 13M.1.SL.TZ2.14: Light of wavelength 600 nm travels from air to glass at normal incidence. The refractive...
- 11M.3.SL.TZ2.21b: State, with reference to the wavelength, the condition that must be satisfied for a bright...
- 11M.3.SL.TZ2.21c: Air is allowed to enter gradually into one of the evacuated tubes. The brightness of the...
- 11M.3.SL.TZ2.21a: State what is meant by coherence.
- 11N.2.SL.TZ0.6d: The right-hand edge of the wave AB reaches a point where the string is securely attached to a...
- 11N.3.SL.TZ0.3a: Light from a monochromatic point source S1 is incident on a narrow, rectangular...
- 12N.2.SL.TZ0.6b: The diagram shows three wavefronts, A, B and C, of a wave at a particular instant in time...
- 13N.2.SL.TZ0.5c: The particle P in (b) is a particle in medium M1 through which a transverse wave is...
- 11M.1.HL.TZ1.12: Light travels from air into glass as shown below. The refractive index of the glass is A....
- 11M.1.SL.TZ1.15: Light travels from air into glass as shown below. What is the refractive index of...
- 13N.3.SL.TZ0.16b: The diagram shows a plan view of a harbour with a floating barrier that has two openings of...
- 13N.3.SL.TZ0.16c: The harbour in (b) is modified to have many narrower openings. The total width of the...
- 09M.1.SL.TZ1.15: What is the best estimate for the refractive index of a medium in which light travels at a...
- 10N.1.SL.TZ0.15: Monochromatic light travels from air into water. Which of the following describes the changes...
- 10N.1.HL.TZ0.16: In two separate experiments monochromatic light is incident on a single slit. The diagrams...
- 09N.1.SL.TZ0.12: A ray of light is incident on a boundary between glass and air. Which of the following is...
- 09N.1.SL.TZ0.15: An orchestra playing on boat X can be heard by tourists on boat Y, which is situated out of...
- 10N.2.HL.TZ0.B2Part2.a: Explain how these maxima and minima are formed.
- 10N.2.HL.TZ0.B2Part2.c: Describe and explain how it could be demonstrated that the microwaves are polarized.
- 10N.2.HL.TZ0.B2Part2.b: (i) wavelength of the microwaves. (ii) frequency of the microwaves.
- 10N.3.SL.TZ0.G1a: (i) monochromatic. (ii) coherent.

