| Date | November 2015 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 15N.3.SL.TZ0.21 |
| Level | Standard level | Paper | Paper 3 | Time zone | Time zone 0 |
| Command term | State | Question number | 21 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
This question is about interference of light.
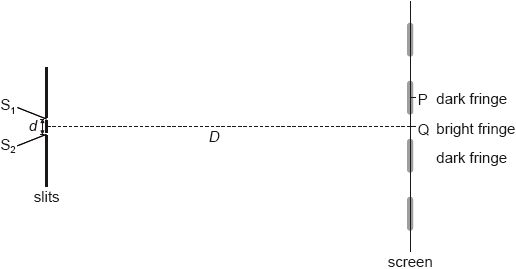
Coherent monochromatic light is incident on two narrow slits \({{\text{S}}_{\text{1}}}\) and \({{\text{S}}_{\text{2}}}\) a distance \(d\) apart. A screen is placed a distance \(D\) from the slits. An interference pattern of bright fringes and dark fringes appears on the screen. The central maximum is at Q.
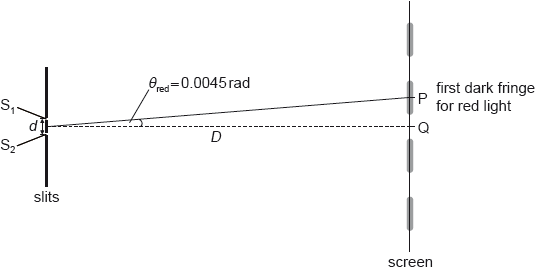
When red light of wavelength 660 nm is used the first fringe at P subtends an angle 0.0045 rad from midpoint of \({{\text{S}}_{\text{1}}}\) and \({{\text{S}}_{\text{2}}}\).
State one way to ensure that the light incident on the slits is coherent.
Light emerging from \({{\text{S}}_{\text{1}}}\) and \({{\text{S}}_{\text{2}}}\) reaches the screen. Explain why the screen appears dark at point P.
Determine the change in angle when blue light of wavelength 440 nm is used.
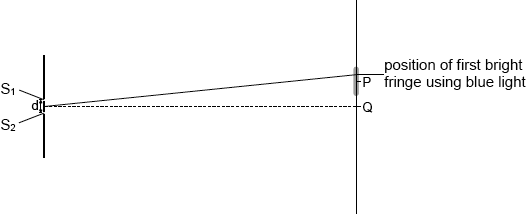
Using the diagram below, draw the approximate position of the first bright fringe using blue light. The position of the first dark fringe with red light is labelled P.
Markscheme
single slit before the double slit / use a laser light / single source;
destructive interference;
path lengths from slits differ by half a wavelength;
waves arrive antiphase / 180° out of phase / \(\pi \) out of phase;
\({\theta _{{\text{blue}}}} = \left( {\frac{{{\theta _{{\text{red}}}}{\lambda _{{\text{blue}}}}}}{{{\lambda _{{\text{red}}}}}} = \frac{{0.0045 \times 440{\text{ nm}}}}{{660{\text{ nm}}}} = } \right){\text{ }}0.0030{\text{ (rad)}}\);
\(\Delta {\theta _{{\text{blue}}}} = (0.0045 - 0.0030 = ){\text{ }}0.0015{\text{ (rad)}}\);
marking direction of shift on the diagram;
Accept any point in the upper half of the dark fringe.
Examiners report
SL candidates could generally suggest a reasonable method to make sure the light was coherent, but rarely earned full marks in explaining why P was a dark fringe.
SL candidates could generally suggest a reasonable method to make sure the light was coherent, but rarely earned full marks in explaining why P was a dark fringe.
SL candidates could generally suggest a reasonable method to make sure the light was coherent, but rarely earned full marks in explaining why P was a dark fringe.
SL candidates could generally suggest a reasonable method to make sure the light was coherent, but rarely earned full marks in explaining why P was a dark fringe.

