| Date | November 2014 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 14N.3.SL.TZ0.22 |
| Level | Standard level | Paper | Paper 3 | Time zone | Time zone 0 |
| Command term | Calculate | Question number | 22 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
This question is about the interference of sound waves.
Two loudspeakers, S1 and S2, each emit a musical note of frequency 2.5 kHz with identical signal amplitude. Point P lies on the line AB and is equidistant from S1 and S2. The speakers are placed 1.5 m apart from each other and 8.0 m from line AB. The speed of sound is \({\text{330 m}}\,{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\).
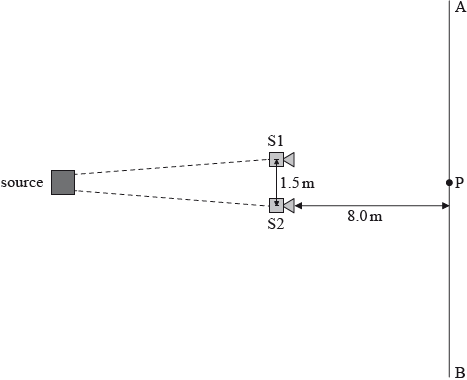
A person walking in a straight line from A to B observes that the intensity of sound alternates between high and low.
With reference to interference, explain why the intensity of sound alternates along line AB.
The sound has a maximum intensity at P. Calculate the distance along line AB to the next intensity maximum when S1 and S2 emit a musical note of frequency 2.5 kHz.
S1 and S2 are moved so that they are now 3.0 m apart. They remain at the same distance from line AB. Discuss the changes, if any, in the rate at which the intensity of sound alternates when a person is walking along line AB at half the speed.
Markscheme
the waves are coherent so interference occurs;
high intensity sound corresponds to a position where sound constructively interferes/superposes / low/zero intensity sound corresponds to a position where sound destructively interferes/cancels;
high intensity is where the path difference is an integral number of wavelengths;
low/zero intensity of sound is where the path difference is \(n + \frac{1}{2}\) wavelengths;
\(\lambda = \frac{{330}}{{2500}} = 0.132{\text{ m}}\);
\(x = \left( {\frac{{n\lambda D}}{d} = \frac{{1.0 \times 0.132 \times 8.0}}{{1.5}} = } \right){\text{ }}0.70(4){\text{ m}}\);
distance doubles so fringe width is halved;
so fringes are encountered at the same rate, no change;
Examiners report
Most described the interference in (a), without giving a cause, such as path difference.
Many answered (b) and (c) well.
Many answered (b) and (c) well.

