| Date | May 2014 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 14M.3.sl.TZ2.17 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Deduce | Question number | 17 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Food chemistry and nutritional science are two important scientific fields to which the general public relate.
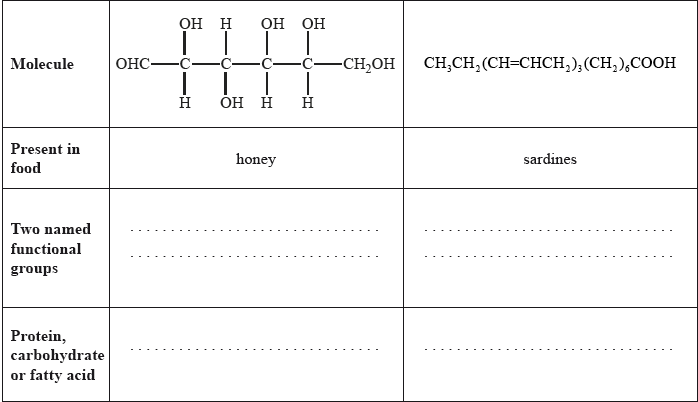
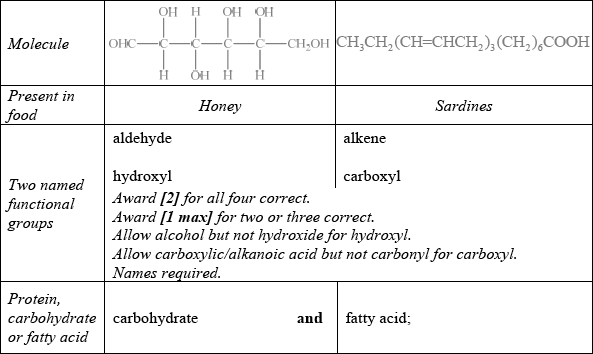
State two named functional groups present in each of the following molecules found in two different food products (honey and sardines). Identify each molecule as a protein, a carbohydrate or a fatty acid.
Butter is an example of a saturated fat and olive oil is an example of an unsaturated fat. Describe the main structural difference between these two types of fat.
Linoleic acid, whose structure is given in Table 22 of the Data Booklet, is present in peanut oil. The oil can be converted to a semi-solid using hydrogen gas. Predict the structural formula of the compound formed from the partial hydrogenation reaction of linoleic acid, and state a suitable catalyst for this reaction.
Structural formula:
Catalyst:
Partial hydrogenation can sometimes produce trans fats. Suggest why trans fats are considered unhealthy.
Olestra, with one of its structures shown below, has been used to prepare snacks such as crisps (potato chips). Deduce the type of compound that can undergo an esterification reaction involving carboxylic acid to produce olestra.
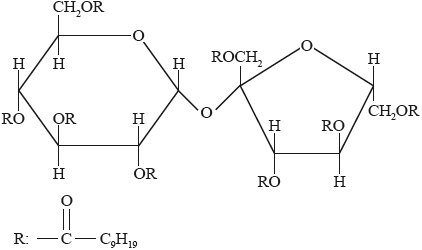
Olestra
Markscheme
Saturated fat: no carbon-carbon double bonds/no C=C/all single carbon-carbon bonds/ all C–C and Unsaturated fat: carbon-carbon double bonds/C=C/alkene groups;
Mention of carbon-carbon or alkene necessary for mark.
Structural formula:
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{)}}_4}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CH}}\)=\({\text{CH(C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{)}}_7}{\text{COOH}}\) /
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{)}}_4}{\text{CH}}\)=\({\text{CHC}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{)}}_6}{\text{COOH}}\);
Catalyst: nickel/Ni / palladium/Pd / platinum/Pt / copper/Cu / zinc/Zn;
decrease (blood) levels of HDL/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (which protects from heart disease) / increase levels of LDL/low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (increasing risk of heart disease) / less easily digested/metabolized / leads to blocked arteries;
carbohydrate / disaccharide;
Allow sucrose / sugar.
Examiners report
Well answered with most candidates gaining two marks. The most common mistake was failing to recognize OHC– as an aldehyde.
The majority of candidates distinguished between saturated and unsaturated fats correctly.
The catalyst was usually well suggested but the structural formula was only provided by the strongest candidates. Some candidates gave the saturated product not taking note of the word “partial” in the question.
Another question better answered than in previous sessions. Many candidates related trans fats to LDL cholesterol.
This was a discriminating question. Only a few candidates recognized the compound as a carbohydrate.

