| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 18M.3.sl.TZ2.3 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Discuss | Question number | 3 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) used with Mass Spectrometry (MS) or Optical Emission Spectrometry (OES) can be used to identify and quantify elements in a sample.
The following graphs represent data collected by ICP-OES on trace amounts of vanadium in oil.
Graph 1: Calibration graph and signal for 10 μg kg−1 of vanadium in oil
Graph 2: Calibration of vanadium in μg kg−1
[Source: © Agilent Technologies, Inc.1998. Reproduced with Permission, Courtesy of Agilent Technologies, Inc.]
ICP-OES/MS can be used to analyse alloys and composites. Distinguish between alloys and composites.
ICP-MS is a reference mode for analysis. The following correlation graphs between ICP-OES and ICP-MS were produced for yttrium and nickel.
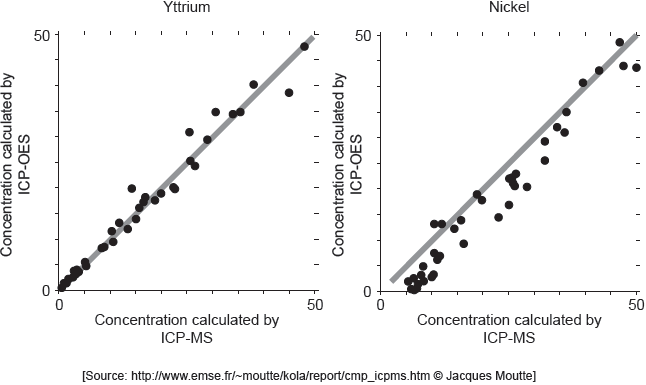
Each y-axis shows concentrations calculated by ICP-OES; each x-axis shows concentrations for the same sample as found by ICP-MS.
The line in each graph is y = x.
Discuss the effectiveness of ICP-OES for yttrium and nickel.
Identify the purpose of each graph.
Calculate, to four significant figures, the concentration, in μg kg−1, of vanadium in oil giving a signal intensity of 14 950.
Vanadium(V) oxide is used as the catalyst in the conversion of sulfur dioxide to sulfur trioxide.
SO2(g) + V2O5(s) → SO3(g) + 2VO2(s)
\(\frac{1}{2}\)O2(g) + 2VO2(s) → V2O5(s)
Outline how vanadium(V) oxide acts as a catalyst.
Markscheme
Alloy:
mixture of metal with other metals/non-metals
OR
mixture of elements that retains the properties of a metal
Composite:
reinforcing phase embedded in matrix phase
Award [1 max] for implying “composites only have heterogeneous/nonhomogeneous compositions”.
[2 marks]
effective for yttrium «but less/not for nickel»
points on nickel graph do not lie on «y = x» line
OR
cannot be used for low concentrations of nickel
OR
concentration of nickel is lower than recorded value
Accept “ICP-OES is more accurate for lower yttrium concentrations than higher concentrations” for M1.
Accept [Ni] and [Y] for concentrations of nickel and yttrium.
Accept “detection limit for yttrium is lower than for nickel” for M2.
Award [1 max] for “more accurate for yttrium at lower concentrations AND nickel at higher concentrations”.
[2 marks]
Graph 1: determines wavelength of maximum absorption/maximum intensity «for vanadium»
Graph 2: determines absorption of known concentrations «at that wavelength»
OR
estimates [V]/concentration in a sample using «the signal» intensity
Do not accept just “determines maximum wavelength/λmax” for M1.
Do not accept “calibration curve” for M2.
[2 marks]
«14 950 = 392.19x + 147.62»
x = 37.74 «μg kg–1»
Answer must be given to four significant figures.
Do not accept values obtained directly from the graph.
[1 mark]
vanadium reduced in first reaction AND oxidized in second reaction
OR
V2O5 oxidizes SO2 in first reaction AND VO2 reduces O2 in second reaction
OR
vanadium returns to original oxidation state «after reaction»
provides an alternative reaction pathway/mechanism «with a lower activation energy» ✔
Do not accept “reactants adsorb onto surface AND products desorb”.
Accept “oxidation number” for “oxidation state”.
[2 marks]

