| Date | May 2011 | Marks available | 3 | Reference code | 11M.3.hl.TZ1.A4 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Explain | Question number | A4 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Phenolphthalein is colourless at pH 7 but its structure changes at pH 11 and it becomes pink. The structures of the compound at these two pH values are shown below.
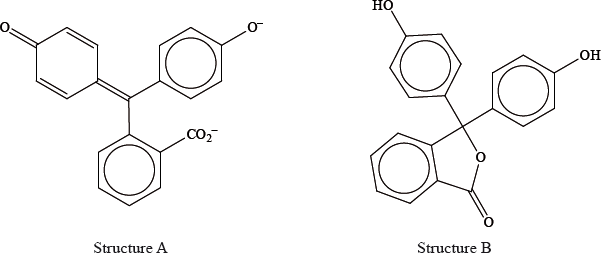
Copper(II) sulfate forms a pale blue aqueous solution. When aqueous ammonia is added to this, initially a pale blue precipitate forms; this precipitate then dissolves in excess ammonia to form a deep blue solution. Explain why these solutions are coloured and the colour with excess ammonia is a deeper blue.
Markscheme
electron transitions between (split, partially filled) d orbitals;
absorption depends on energy difference between the split d orbitals;
waters replaced by ammonias;
ammonia (ligands) increase the splitting between the d orbitals/larger energy difference;
absorption moves to shorter wavelength/higher frequency/towards blue end of spectrum;
Examiners report
Part (b) lacked proper understanding of the chemical principles and was poorly answered by most of the candidates.

