- Summary list for 11.4 Sexual reproduction
- Mindmaps
- Sexual reproduction
- Model answer
- Model answer
- Model answer
- Model answer
- Multiple choice questions
- 11.4 Sexual reproduction HL 1/1
Learn and test your biological vocabulary using these 11.4 Sexual reproduction flashcards
These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - great revision.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
Summary list for 11.4 Sexual reproduction
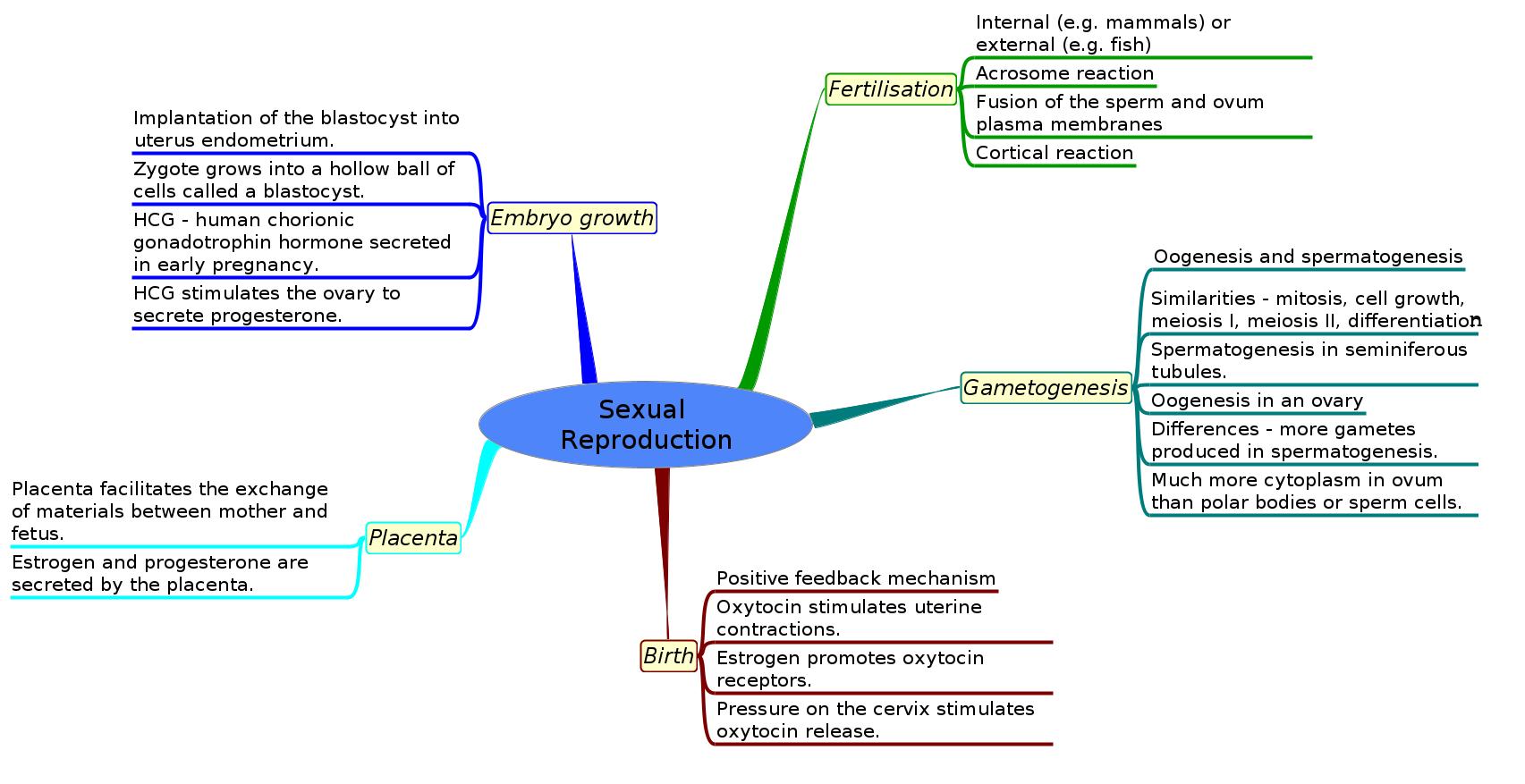
Gametogenesis
- Similarities in spermatogenesis and oogenesis include mitosis, cell growth, two divisions of meiosis and differentiation.
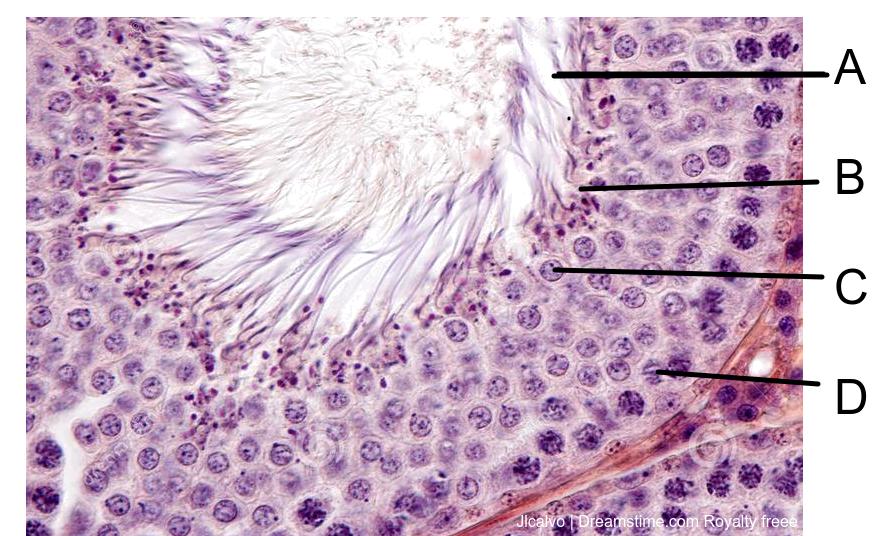
- Students need to be able to annotate diagrams of seminiferous tubule and ovary to showing these details.
- Differences between the processes in spermatogenesis and oogenesis are the different numbers of gametes produced and the different amounts of cytoplasm in these gametes.
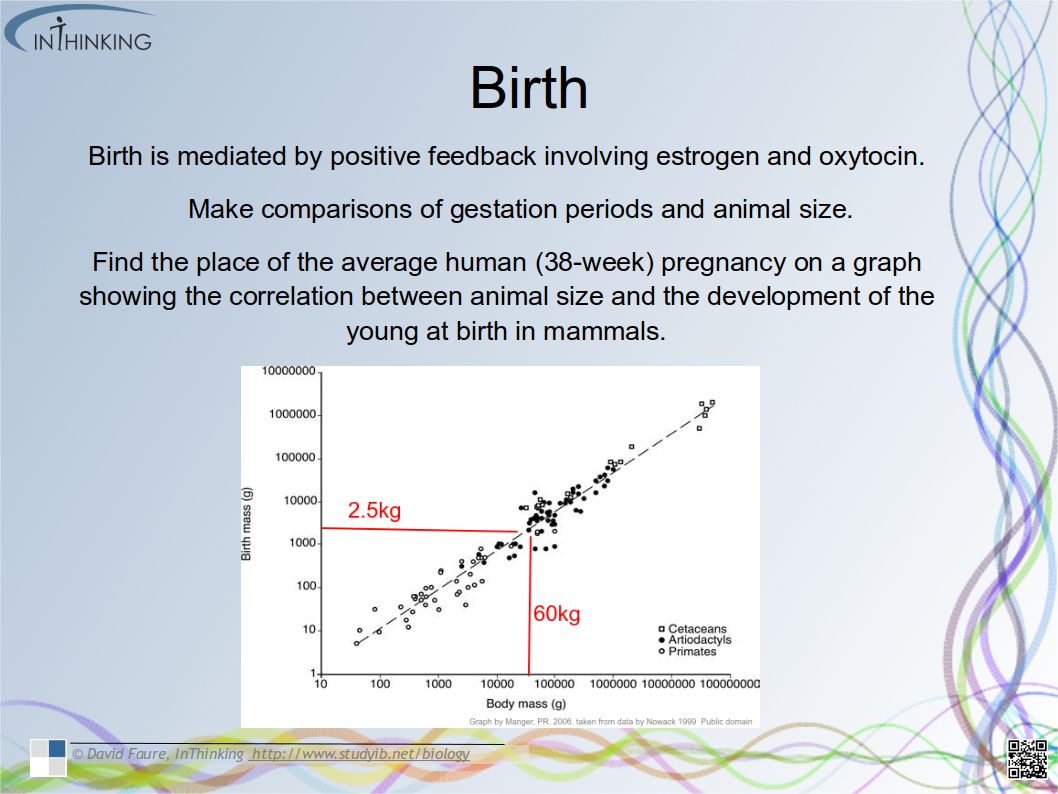
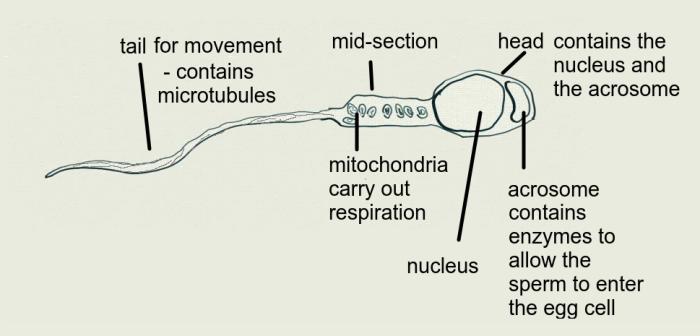
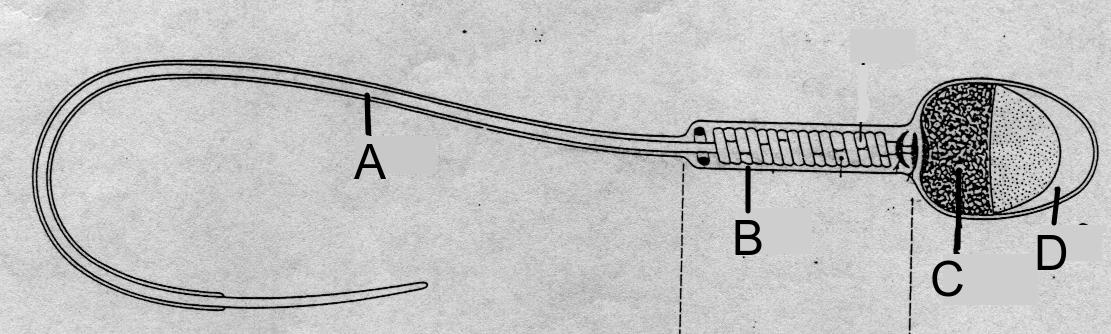
- Annotation of diagrams of mature sperm and egg to indicate functions.
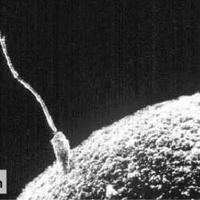
Fertilization
- Fertilization in animals can be internal or external.
- Fertilization involves the acrosome reaction, fusion of the plasma membrane of the egg and sperm and the cortical reaction (mechanisms that prevent polyspermy).
Early growth of the embryo
- Implantation of the blastocyst in the endometrium is essential for the continuation of pregnancy.
- HCG stimulates the ovary to secrete progesterone during early pregnancy.
- The placenta facilitates the exchange of materials between the mother and fetus.
- Estrogen and progesterone are secreted by the placenta once it has formed.
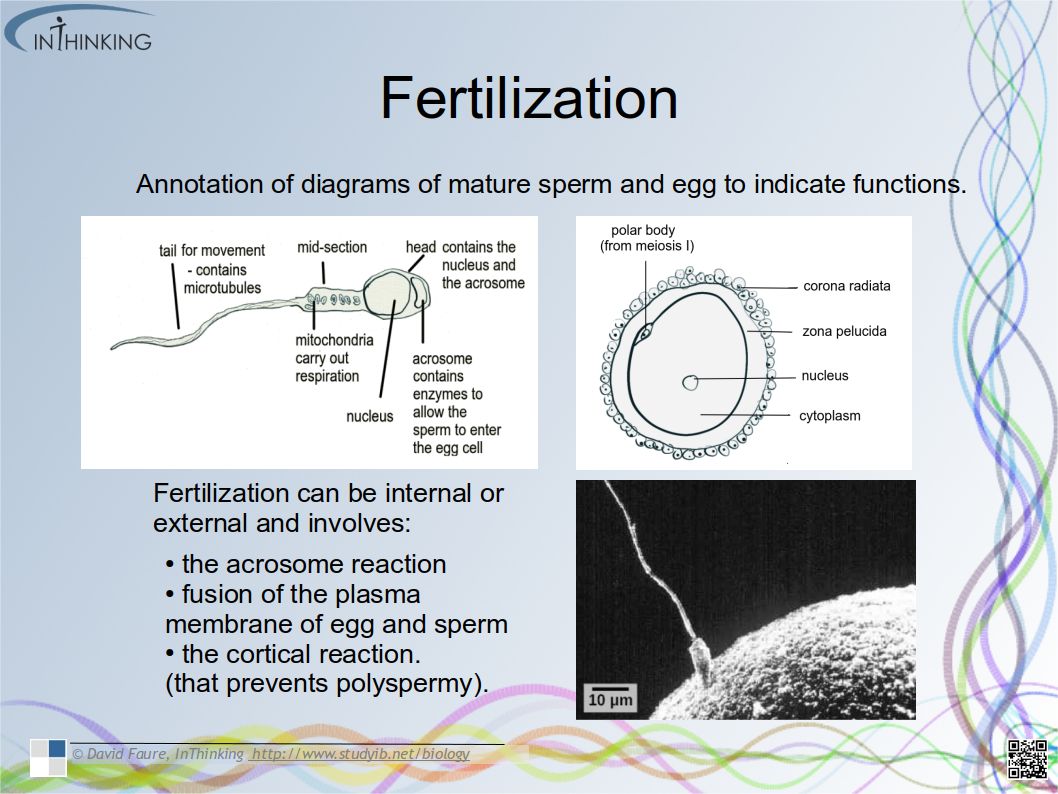
- Birth is mediated by positive feedback involving estrogen and oxytocin.
Skills & applications
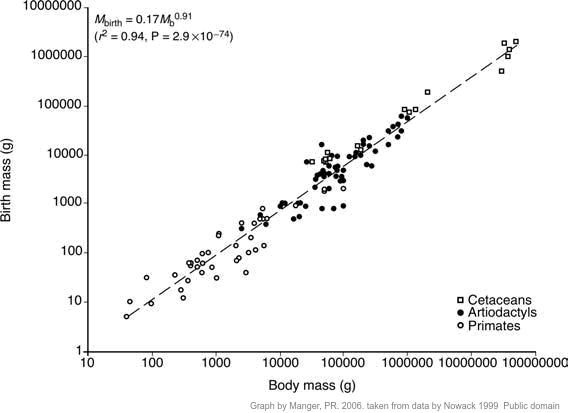
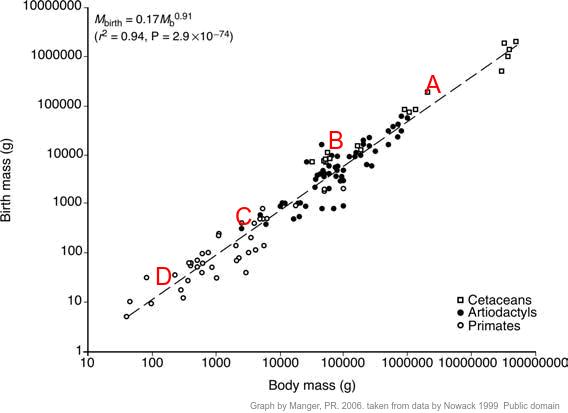
- To make comparisons of gestation periods and animal size & to find the place of the average human (38-week) pregnancy on a graph showing the correlation between animal size and the development of the young at birth in mammals.
- To annotate diagrams of stages of gametogenesis in seminiferous tubule and an ovary.
- Ability to annotate diagrams with the function of the parts of mature sperm and egg.
Mindmaps
These diagram summaries cover the main sections of topic 11.4 about sexual reproduction.
Study them and draw your own list or concept map from memory.
Sexual reproduction
Understanding the structure of mature sperm cells and the placenta are both important steps in understanding their function in this topic. Many students learn the names or all the parts of a sperm.
This question helps to practise explaining the functions of these parts.
Answer this question on a piece of paper, then check your answer against the model answer below.
Describe the structure and function of a sperm cell. [5]
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
Click the + icon to see a model answer.
Multiple choice questions
This is a self marking quiz containing questions covering the topic outlined above.
Try the questions to check your understanding.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
The process of spermatogenesis and oogenesis
Drag and drop the correct term into the gap to describe the process of gamete production in animals.
motile haploid matures diploid meiosis two organelles cytoplasm mitosis
The process of producing both male and female gametes in animals involves to produce gamete mother cells.
Gamete mother cells divide by the divisions of to produce secondary gametocytes.
The secondary gametocyte to produce a fertile haploid gamete.
The male gamete is small and whereas the female gamete is large and full of containing the and nutrients to enable the growth of the zygote after fertilisation.
Gametogenesis in the gonads has three phases, mitosis to produce a line of gamete mother cells, meiosis to produce haploid cells and maturation to produce a functional, fertile gamete.
You also need to know the details of spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
Everyone needs a bit of fun while they revise. Try this Carbon cycle card matching game.
Can you reach the leader board?
How much of Sexual reproduction 11.4 HL have you understood?



















 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn