- Summary list for Kidney and osmoregulation 11.3
- Mindmaps
- Model answer
- Model answer
- Model answer
- Model answer
- Model answer
- Multiple choice questions
- 11.3 Kidney and osmoregulation 1/1
Learn and test your biological vocabulary using these 11.3 Kidney and osmoregulation flash cards
These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - great revision.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
Summary list for Kidney and osmoregulation 11.3
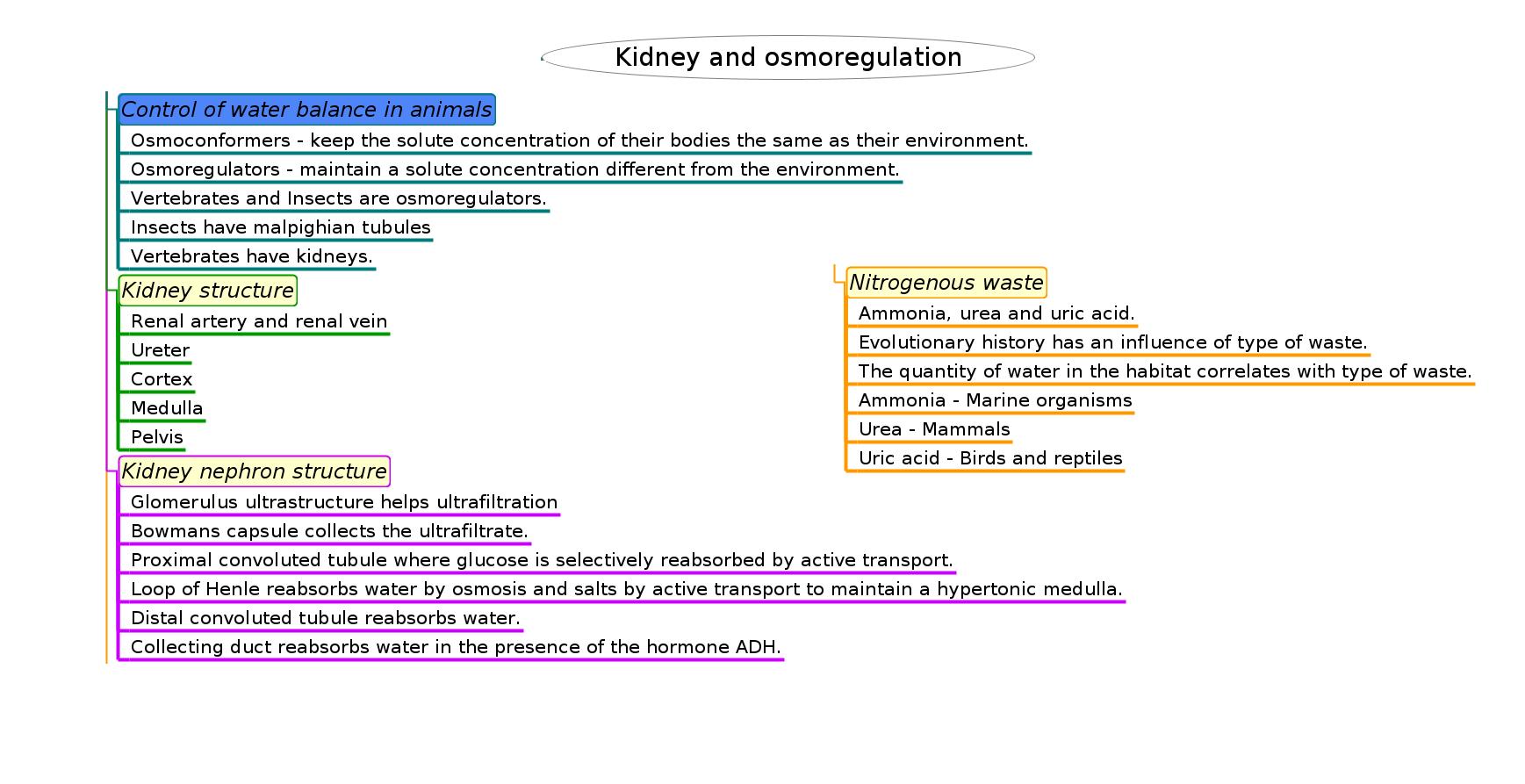
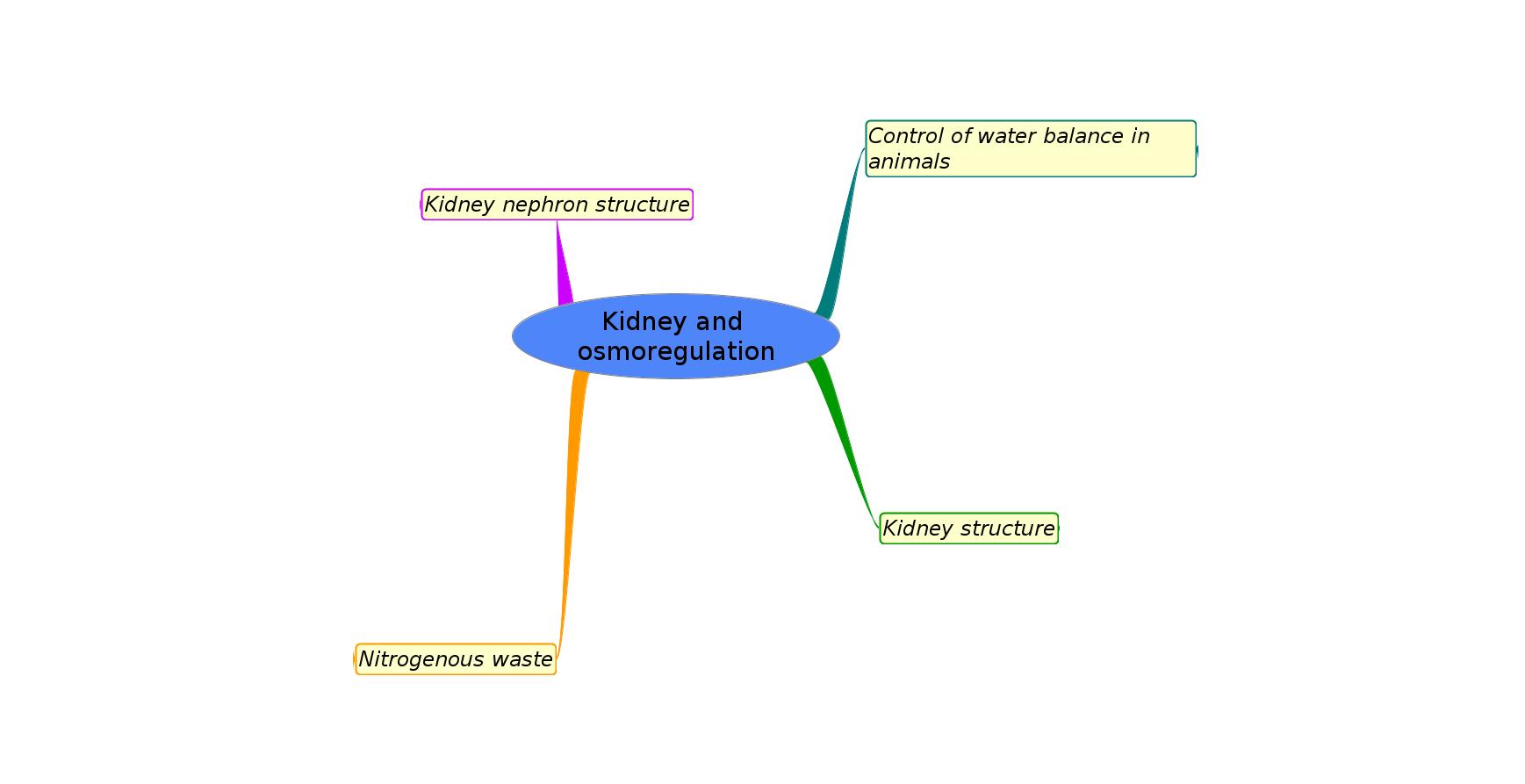
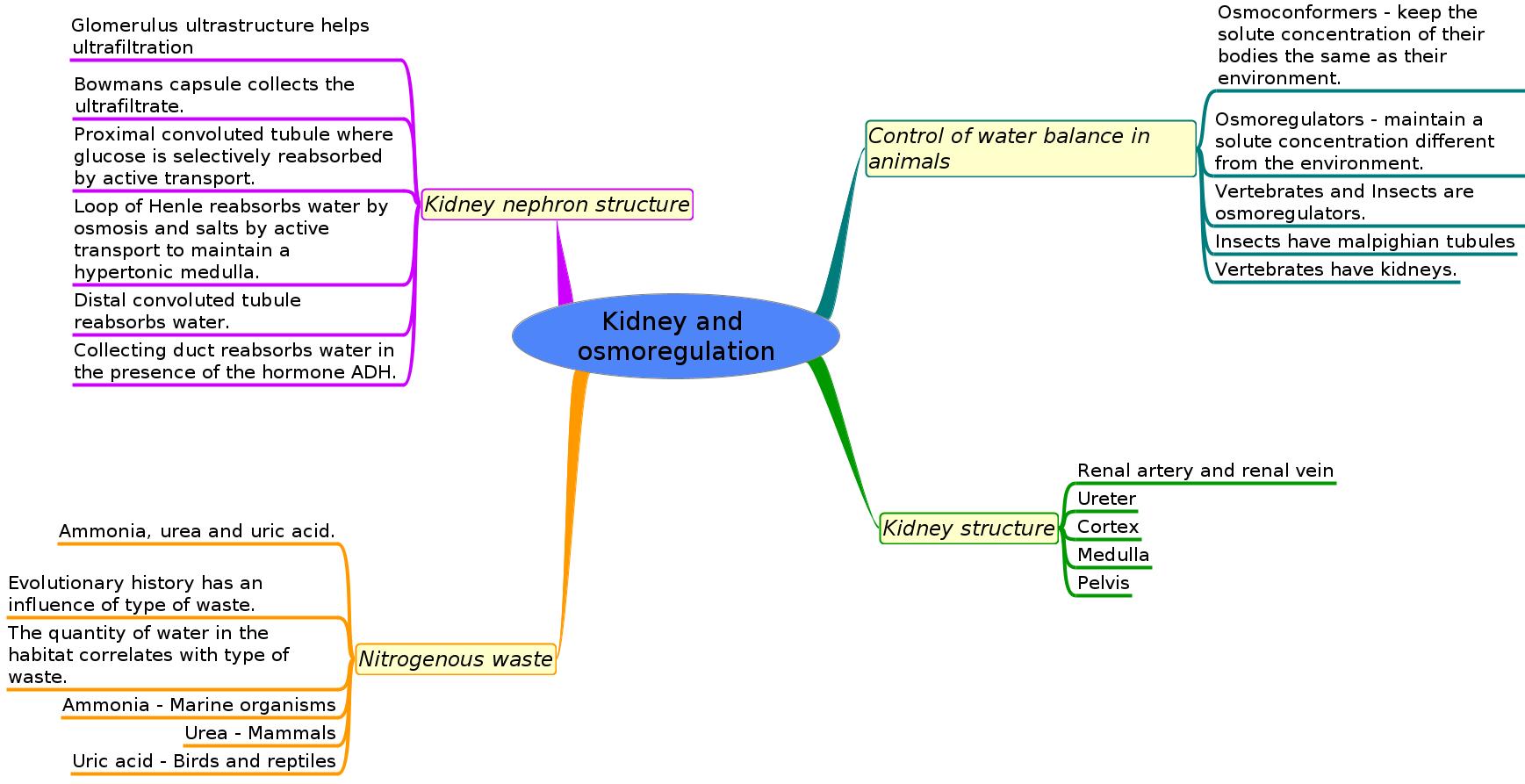
Control of water balances in different animals
- Some animals are osmoconformers - their cells have solute concentration equal to their environment (eg. marine invertebrates)
- Vertebrates and insects are osmoregulators. (so are some single cells, eg.Amoeba)
- Insects have malphighian tubules but vertebrates have kidneys to carry out osmoregulation and remove nitrogenous wastes.
- The type of nitrogenous waste in animals is correlated with evolutionary history and habitat.
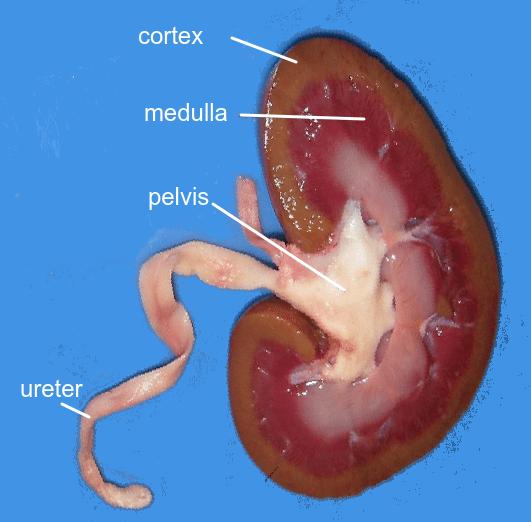
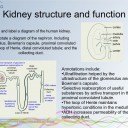
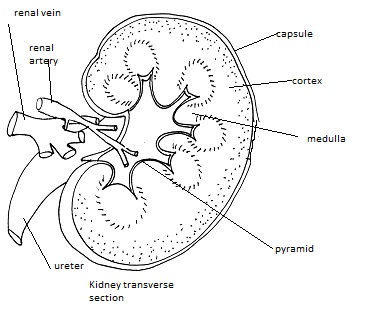
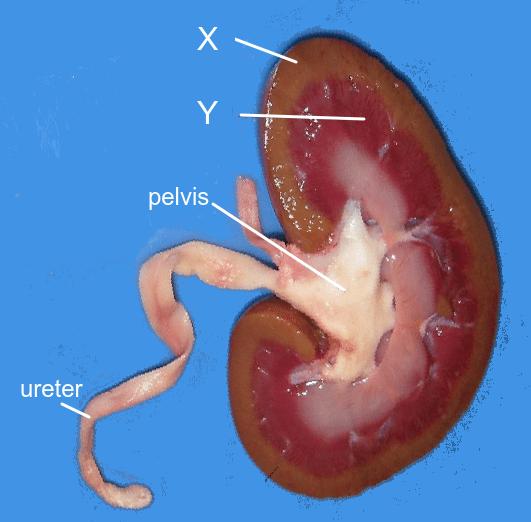
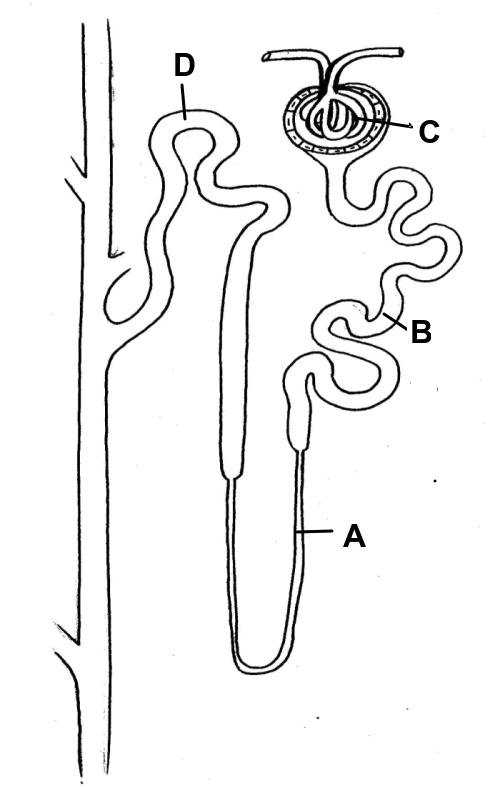
Kidney structure & function
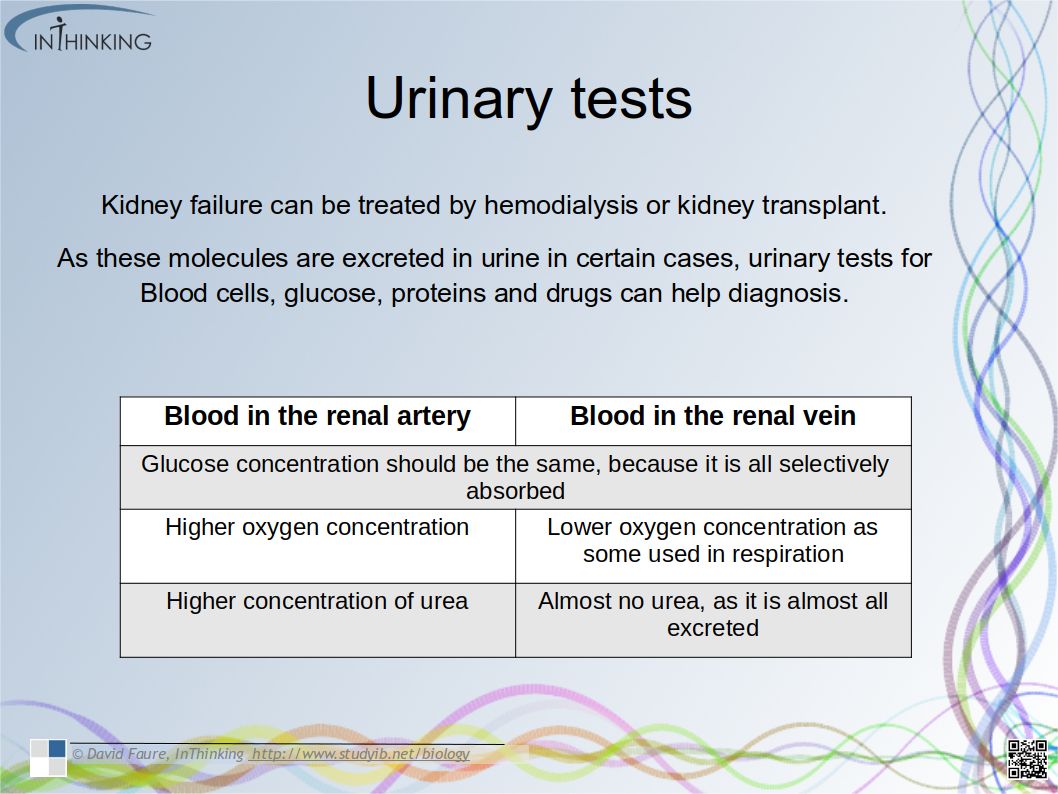
- The differences in composition of blood in the renal artery & the renal vein.
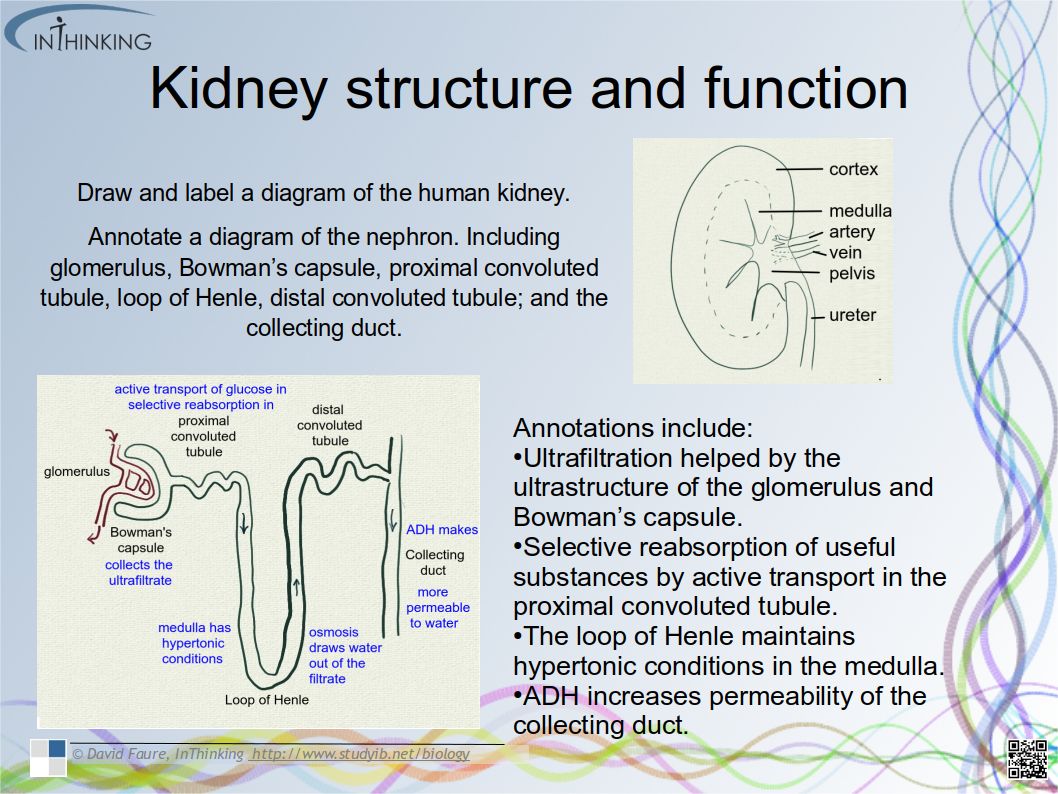
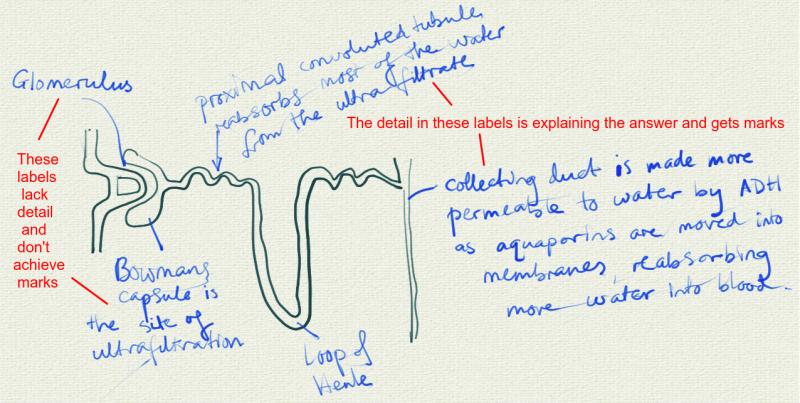
- Ultrafiltration helped by the ultrastructure of the glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule.
- Selective reabsorption of useful substances by active transport in the proximal convoluted tubule.
- The loop of Henle maintains hypertonic conditions in the medulla.
- ADH controls reabsorption of water in the collecting duct.
- The length of the loop of Henle is positively correlated with the need for water conservation in animals.
Skills & applications
- To be able to draw and label a diagram of the human kidney.
- To be able to annotate diagrams of the nephron. Including glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule, proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule; and the collecting duct
- To have considered the consequences of dehydration and over-hydration.
- To know about treatment of kidney failure by hemodialysis or kidney transplant.
- To know about urinary test for Blood cells, glucose, proteins and drugs.
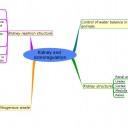
Mindmaps
These diagram summaries cover the main sections of topic 11.3 about osmoregulation and the kidney.
Study them and draw your own list or concept map from memory.
Understanding the structure of the kidney nephron is not as important as understanding it's function in osmoregulation. Many students learn the names or all the parts of a nephron but few learn the details of it's function. This question will help to practise explaining these functions.
Answer this question on a piece of paper, then check your answer against the model answer below.
Describe the formation of glomerular filtrate in the kidney and how homeostasis of water balance is achieved using selective reabsorption and ADH secretion. [8]
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
.
.
Click the + icon to see a model answer.
Multiple choice questions
This is a self marking quiz containing questions covering the topic outlined above.
Try the questions to check your understanding.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
Osmoconformers and osmoregulators.
Drag and drop the correct term into the gap to describe internal minaral and water concentrations in osmoconformers and osmoregulators.
osmoconformers concentration functions water stable increases dilute Osmoregulators homeostatic energy fall
Some aquatic animals are . They do not control their internal salt and levels but allow them to rise and depending upon the outside aquatic medium. Their body size and body fluids become more in fresh water, the opposite occuring in a marine environment. This method saves energy but can cause bodily to be less efficient.
maintain control of their body mineral and water by balancing water and mineral gain and loss. They maintain internal conditions and bodily efficiency but the process is consuming.
Explanation: Homeostatic control is energy consuming but allows the body to work at high efficiency in varied environmental conditions.
.
Everyone needs a bit of fun while they revise. Try this kidney and osmoregulation card matching game.
Can you reach the leader board.
How much of Kidney and osmoregulation 11.3 HL have you understood?










 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn