- Summary list for 10.3 Gene pools and speciation
- Mindmaps
- Exam style question about speciation
- Model answer
- Model answer
- Model answer
- Multiple choice questions
- 10.3 Gene pools and speciation 1/1

Learn and test your biological vocabulary using these 10.3 Gene pools and speciation flashcards.
These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - great revision.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
Summary list for 10.3 Gene pools and speciation
Gene pools
- A gene pool consists of all the genes and their different alleles, present in an interbreeding population.
- Evolution requires that allele frequencies change with time in populations.
- Punctuated equilibrium implies long periods without appreciable change and short periods of rapid evolution.
Speciation
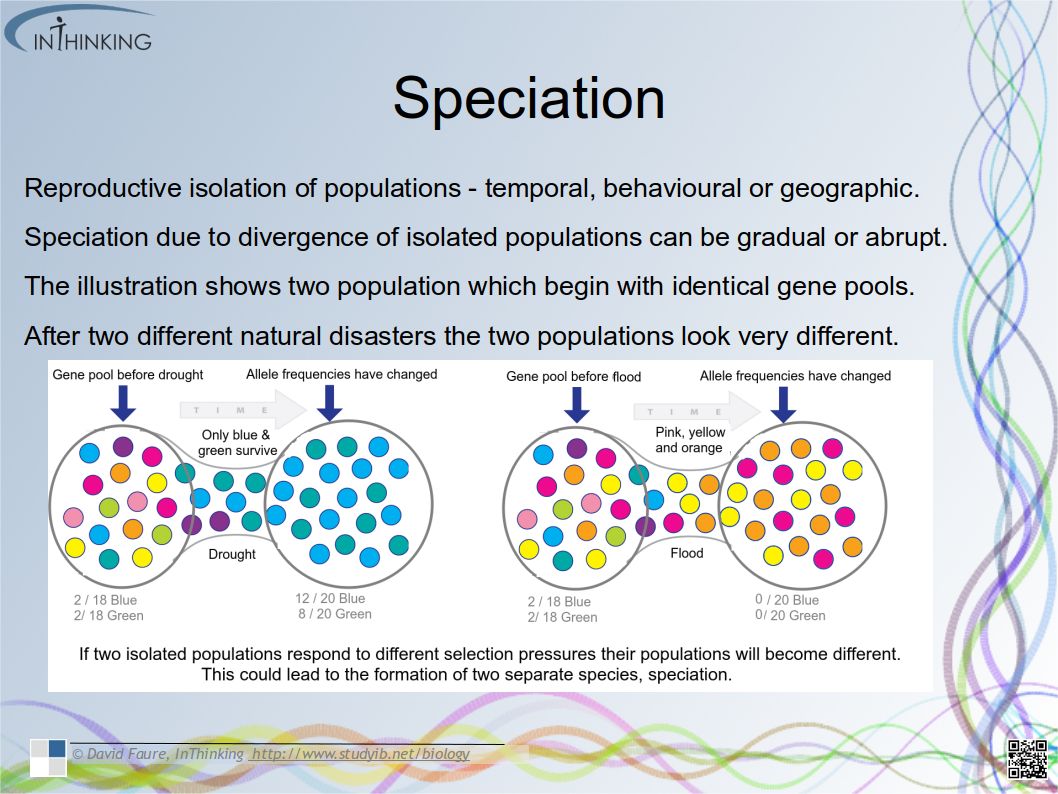
- Reproductive isolation of populations can be temporal, behavioural or geographic.
- Speciation due to divergence of isolated populations can be gradual.
- Speciation can occur abruptly.
Student skills and applications
- Application: Identifying examples of directional, stabilising and disruptive selection.
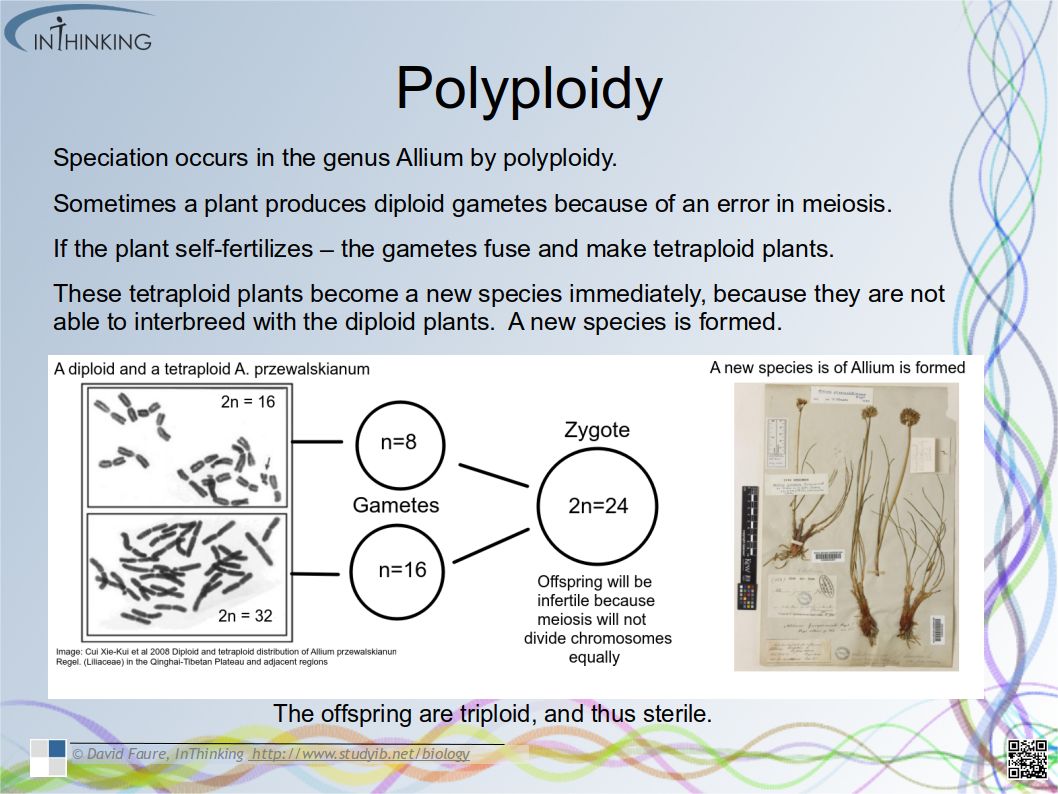
- Application: Speciation in the genus Allium by polyploidy.
- Skill: Comparison of allele frequencies of geographically isolated populations.
Mindmaps
This diagram summaries the main sections of topic 10.3 about gene pools and speciation.
Test if you can draw something like these concept maps from memory.
Exam style question about speciation
Answer the question below on a piece of paper, then check your answer against the model answer below.
Describe how geographical isolation and different selective pressures can lead to speciation [3]
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
.
.
Click the + icon to see a model answer.
Test yourself
Multiple choice questions
This is a self marking quiz containing questions covering the topic outlined above.
Try the questions to check your understanding.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
Isolation of two populations is a mechanism of speciation.
Drag and drop the correct word or phrase into the gap to outline isolation mechanisms.
Behavioural Natural mechanisms seasons Temporal interbreeding physical barrier Breeding selection pressures characteristics
Isolation prevents two groups of a species from . If each of the groups is subjected to differing , their genomes will gradually evolve in different ways due to different genes having favourable in the different environments.
Three forms of isolating are:
- Geographical isolation where a such as a river separates the two populations.
- isolation where the activity times or breeding separate the two populations.
- isolation where members of each group choose to breed only with members of that group
Isolation prevents interbreeding and can lead to speciation over time.
How much of Gene pools and speciation 10.3 HL have you understood?


















 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn