- Summary list for 10.2 Inheritance
- Mindmaps
- Exam style question about inheritance
- Model answer
- Model answer
- Model answer
- Test yourself - multiple choice questions
- 10.2 Inheritance HL 1/1

Learn and test your biological vocabulary using these 10.2 Inheritance flashcards.
These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - great revision.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
Summary list for 10.2 Inheritance
Linked genes
- Genes are linked when they occur on the same chromosome.
- Unlinked genes show independent segregation in meiosis.
Polygenic inheritance
- Variation between living can be discrete or continuous.
- Phenotypes controlled by many genes (polygenic) show continuous variation. They may also be influenced by environmental factors.
- Chi-squared tests are used to calculate if differences between observed and expected frequencies are statistically significant.
Student skills and applications
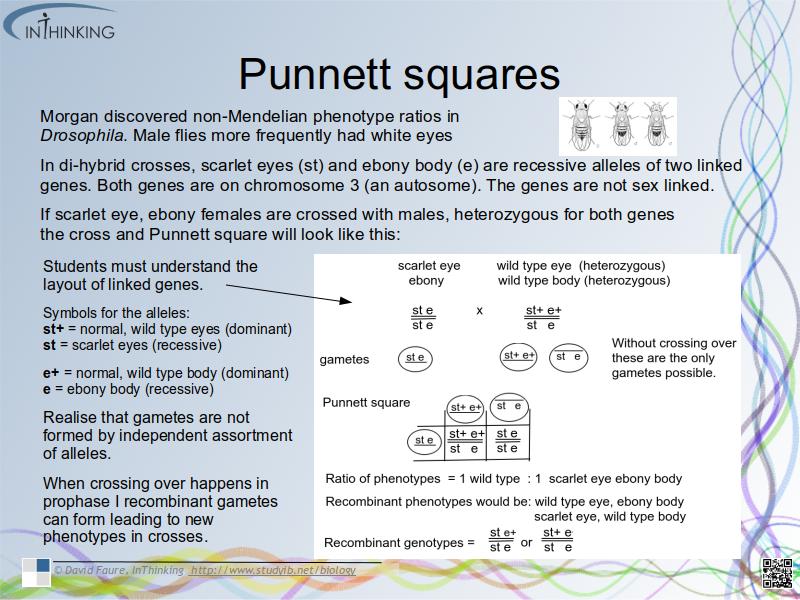
- A awareness of Morgan’s discovery of non-Mendelian ratios in Drosophila.
- The ability to complete Punnett squares for dihybrid traits and analyse them.
- Ability to calculate predicted genotypic and phenotypic ratio of offspring of dihybrid crosses involving unlinked autosomal genes.
- The skill to identify recombinants in crosses involving two linked genes and to understand when they are shown as vertical pair in crosses of linked genes.
- The skill to use of a chi-squared test on data from dihybrid cross.
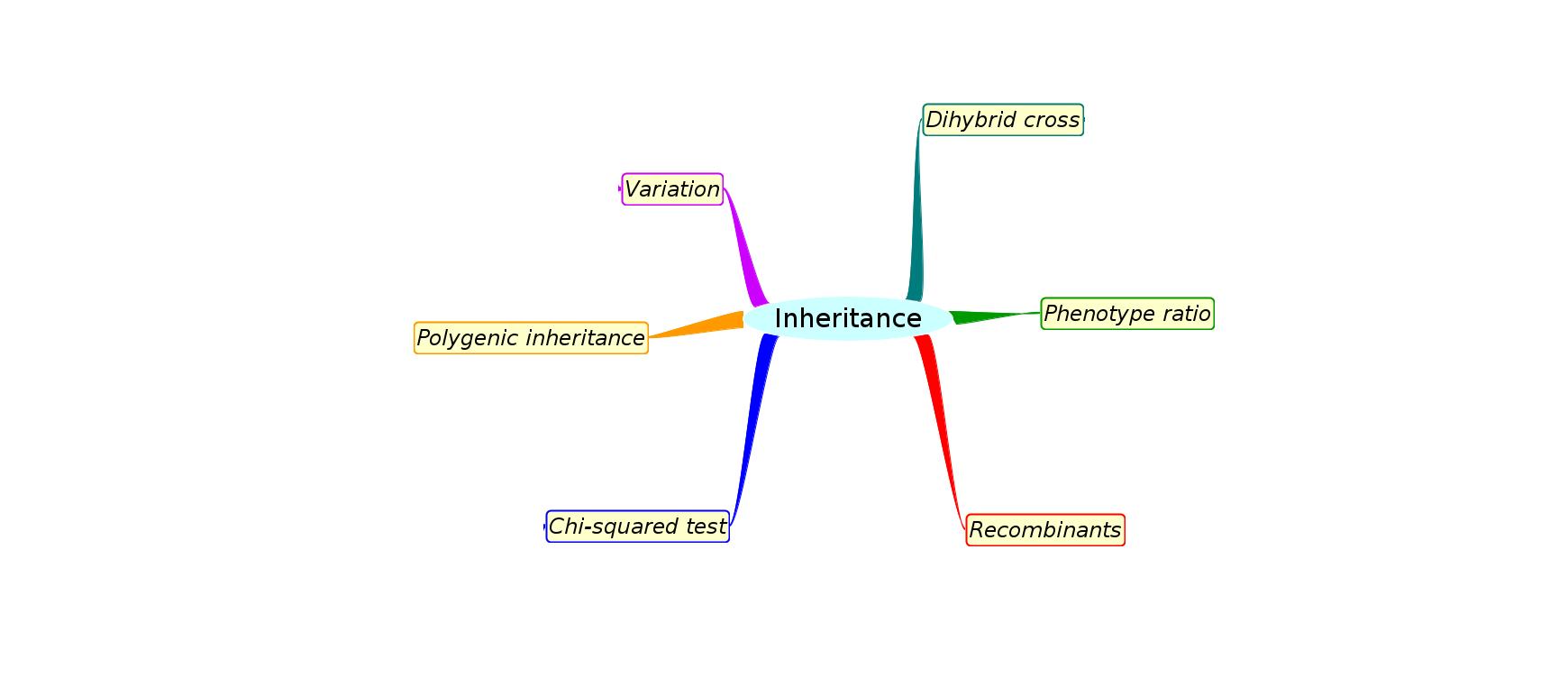
Mindmaps
This diagram summaries the main sections of topic 10.2 Inheritance HL
Test if you can draw something like these concept maps from memory.
Exam style question about inheritance
Explaining the process of Mendelian inheritance is an important skill from this topic.
Answer the question below on a piece of paper, then check your answer against the model answer.
In the mustard plant Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), there are two genes which affect plants: The tallness gene and the leaf shape gene. The allele for tall plants is T (dominant) and the allele for short plants is t. The allele for round leaves is R (dominant) and the allele for oval leaves is r.
a) Determine the phenotype of a plant with the genotype: Tt rr. [1].
.................................................................................................................
b) Plants which are tall with round leaves are crossed with plants that are short with oval leaves.
Surprisingly all the 1000 offspring were tall with round leaves.
Deduce the genotype of the offspring. [1]
.................................................................................................................
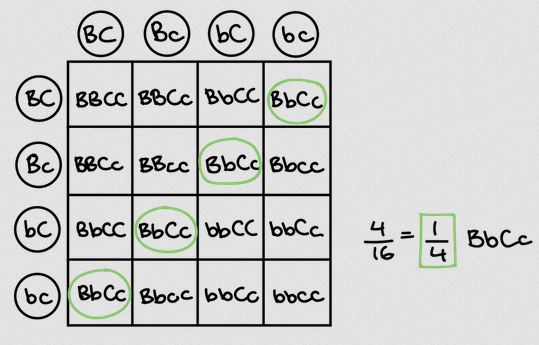
c) In another cross offspring from (b) were crossed and four different phenotypes were found in the offspring.
Suggest what the phenotype ratio of offspring would be. [2]
.................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................
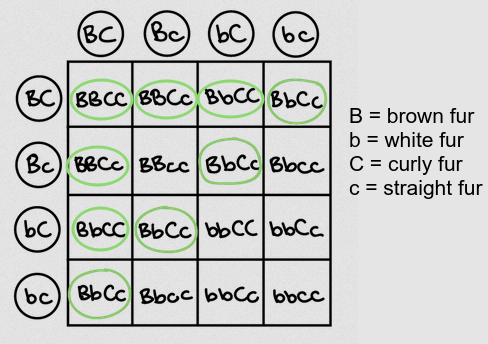
d) Identify the recombinant phenotypes in this cross. [1]
.................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................
Click the + icon to see a model answer.
Test yourself - multiple choice questions
This is a self marking quiz containing questions covering the topic outlined above.
Try the questions to check your understanding.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
You need to be able to work out parental genotypes from their offspring.
In humans, curly hair, C is dominant to straight hair, c.
The haemophilia gene is a recessive gene on the X chromosome denoted as Xh. Normal blood clotting is represented as X.
Habib’s mother, Amal and father, Omer both have curly hair and neither have haemophilia. Their son, Habib has straight hair and is a haemophiliac.
Deduce, with reasons, the genotype of Habib, Amal and Omer by dragging and dropping the correct genotype into the box beside the name.
XYhcc XhYCc XhYhcc XXhCc XhYCc XYCc XXhCC Xhc XXCc
Amal
Omer
Habib
Explanation: Habib inherited the haemophilia gene from his mother who is a carrier. Both parents are heterozygousfor curly hair.
Everyone needs a bit of fun while they revise. Try this Inheritance card matching game.
Can you reach the leader board?
How much of Inheritance 10.2 HL have you understood?



















 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn