| Date | November 2018 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 18N.2.sl.TZ0.7 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | Determine | Question number | 7 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
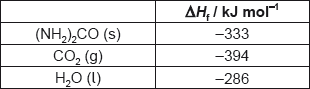
Consider the following Hess’s law cycle:
Identify the type of reaction in step 1.
Calculate the standard enthalpy change, ΔHΘ, of step 2 using section 13 of the data booklet.
Determine the standard enthalpy change, ΔHΘ, of step 1.
Suggest one reason why the calculated value of ΔHΘ using Hess’s Law in part (c) can be considered accurate and one reason why it can be considered approximate.
Markscheme
«electrophilic» addition/AE
OR
reduction ✔
Accept “hydrogenation”.
«(−286 kJ) + (−1411 kJ) =» −1697 «kJ» ✔
«−1697 kJ + 1561 kJ =» −136 «kJ»
OR
«ΔHΘ = Δ (products) − Δ (reactants) = −84 kJ − 52 kJ =» −136 «kJ» ✔
Accurate:
no approximations were made in the cycle
OR
values are specific to the compounds
OR
Hess’s law is a statement of conservation of energy
OR
method is based on a law
OR
data in table has small uncertainties ✔
Approximate:
values were experimentally determined/had uncertainties
OR
each value has been determined to only three/four significant figures
OR
different sources have «slightly» different values for enthalpy of combustion
OR
law is valid until disproved
OR
law of conservation of energy is now conservation of mass–energy
OR
small difference between two quite large terms «leads to high percentage uncertainty» ✔