| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 18M.2.sl.TZ2.4 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Determine | Question number | 4 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Enthalpy changes depend on the number and type of bonds broken and formed.
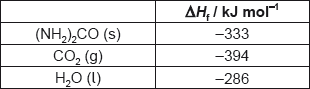
The table lists the standard enthalpies of formation, , for some of the species in the reaction above.
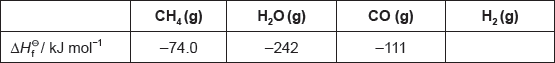
Hydrogen gas can be formed industrially by the reaction of natural gas with steam.
CH4(g) + H2O(g) → 3H2(g) + CO(g)
Determine the enthalpy change, ΔH, for the reaction, in kJ, using section 11 of the data booklet.
Bond enthalpy for C≡O: 1077 kJ mol−1
Outline why no value is listed for H2(g).
Determine the value of ΔHΘ, in kJ, for the reaction using the values in the table.
Outline why the value of enthalpy of reaction calculated from bond enthalpies is less accurate.
Markscheme
bonds broken: 4(C–H) + 2(H–O)/4(414) + 2(463)/2582 «kJ»
bonds made: 3(H–H) + C≡O/3(436) + 1077/2385 «kJ»
ΔH «= ΣBE(bonds broken) – ΣBE(bonds made) = 2582 – 2385» = «+» 197 «kJ»
Award [3] for correct final answer.
Award [2 max] for –197 «kJ».
[3 marks]
for any element = 0 «by definition»
OR
no energy required to form an element «in its stable form» from itself
[1 mark]
ΔHΘ « = (products) – (reactants) = –111 + 0 – [–74.0 + (–242)]»
= «+» 205 «kJ»
[1 mark]
«bond enthalpies» averaged values «over similar compounds»
OR
«bond enthalpies» are not specific to these compounds
[1 mark]