| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 3 | Reference code | 18M.3.SL.TZ1.8 |
| Level | Standard level | Paper | Paper 3 | Time zone | Time zone 1 |
| Command term | Calculate | Question number | 8 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
A converging (convex) lens forms an image of an object on a screen.
Identify whether the image is real or virtual.
The lens is 18 cm from the screen and the image is 0.40 times smaller than the object. Calculate the power of the lens, in cm–1.
Light passing through this lens is subject to chromatic aberration. Discuss the effect that chromatic aberration has on the image formed on the screen.
A system consisting of a converging lens of focal length F1 (lens 1) and a diverging lens (lens 2) are used to obtain the image of an object as shown on the scaled diagram. The focal length of lens 1 (F1) is 30 cm.
Determine, using the ray diagram, the focal length of the diverging lens.
Markscheme
image is real «as projected on a screen»
[1 mark]
«\( - \frac{{18}}{u} = - 0.40\)»
u = 45
\(\frac{1}{{45}} + \frac{1}{{18}} = \frac{1}{f}\)
OR
f = 13 «cm»
P = \(\frac{1}{f}\) = «\(\frac{1}{{13}}\)» = 0.078 «cm–1»
Accept answer 7.7«D».
[3 marks]
refractive index depends on wavelength
light of different wavelengths have different focal points / refract differently
there will be coloured fringes around the image / image will be blurred
[3 marks]
any 2 correct rays to find image from lens 1
ray to locate F2
focal length = «–»70 «cm»
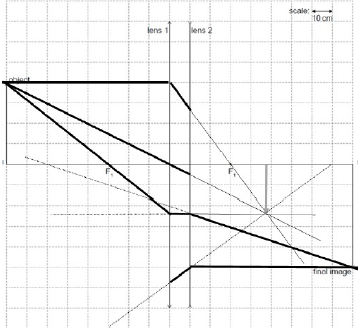
Accept values in the range: 65 cm to 75 cm.
Accept correct MP3 from accepted range also if working is incorrect or unclear, award [1].
[3 marks]

