| Date | November 2015 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 15N.3.SL.TZ0.20 |
| Level | Standard level | Paper | Paper 3 | Time zone | Time zone 0 |
| Command term | Outline | Question number | 20 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
This question is about a converging (convex) lens.
Anna is unable to read small print in a newspaper. She uses a convex lens to read text more easily. Anna looks through the lens at an arrow on the page.
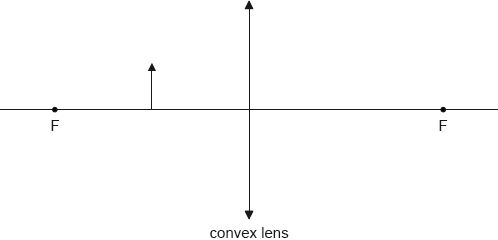
On the diagram, construct rays to locate the image of the arrow. The focal points of the lens are labelled F.
Anna places a screen at the image position. Outline why she cannot see an image on the screen.
Anna uses the same lens with an illuminated object. She finds that a clear image of the object is formed when the lens is placed a distance of 20 cm from the screen. The lens has a focal length of 5 cm. Determine the magnification of the image.
Markscheme
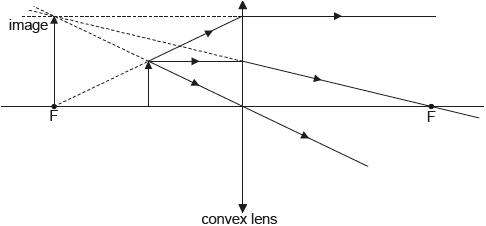
any correct ray out of the three shown above;
second ray correct;
image correctly located and labelled;
Accept rays without arrows and solid construction lines back to image.
Accept correctly constructed image even if not located in the focus.
the image is virtual;
no light rays pass through this point;
\(\frac{1}{u} = \frac{1}{f} - \frac{1}{v}\);
\(u = \frac{{20}}{3}\);
\(m = \left( { - \frac{v}{u} = - \frac{{60}}{{20}} = } \right){\text{ }}( - )3\);
Examiners report
As usual, geometrical optics is well managed by all candidates, but weaker candidates made some mistakes in calculation and in explanation of the virtual image.
As usual, geometrical optics is well managed by all candidates, but weaker candidates made some mistakes in calculation and in explanation of the virtual image.
As usual, geometrical optics is well managed by all candidates, but weaker candidates made some mistakes in calculation and in explanation of the virtual image.

