| Date | May 2017 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 17M.3.SL.TZ2.8 |
| Level | Standard level | Paper | Paper 3 | Time zone | Time zone 2 |
| Command term | Determine | Question number | 8 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
The diagram shows planar wavefronts incident on a converging lens. The focal point of the lens is marked with the letter F.
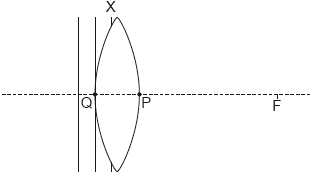
Wavefront X is incomplete. Point Q and point P lie on the surface of the lens and the principal axis.
On the diagram, sketch the part of wavefront X that is inside the lens.
On the diagram, sketch the wavefront in air that passes through point P. Label this wavefront Y.
Explain your sketch in (a)(i).
Two parallel rays are incident on a system consisting of a diverging lens of focal length 4.0 cm and a converging lens of focal length 12 cm.
The rays emerge parallel from the converging lens. Determine the distance between the two lenses.
Markscheme
line of correct curvature as shown
[1 mark]
line of approximately correct curvature as shown
Judged by eye.
Allow second wavefront Y, to have “passed” P as this is how this question is being interpreted by some.
Ignore any waves beyond Y.
[1 mark]
wave travels slower in glass than in air
OR
RI greater for glass
wavelength less in glass than air
hence wave from Q will cover a shorter distance «than in air» causing the curvature shown
OWTTE
[2 marks]
realization that the two lenses must have a common focal point
distance is 12 – 4.0 = 8.0 «cm»
Accept MP1 from a separate diagram or a sketch on the original diagram.
A valid reason from MP1 is expected.
Award [1 max] for a bald answer of 12 – 4 = 8 «cm».
[2 marks]

